Abstract
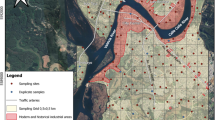
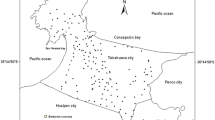
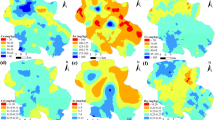
A total of 30 topsoil, subsoil samples, and 11 new and used cupels were collected around a Pb fusion fire-assay laboratory in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso, and their physico-chemical parameters and major and potentially toxic (PTE) element concentrations were determined. The results showed that the soil samples in the immediate vicinity of the used-cupel disposal site were highly polluted with Pb (up to 8900 mg/kg). Cluster analysis identified the used-cupels as the primary source of Pb, As, Cr, Cu, Ni, and Ca contamination of topsoils. Furthermore, principal component analysis revealed that abundance and mobility of Cr, Cu, Ni, and Pb were likely controlled by clay and Fe- and Al-oxyhydroxides, whereas that of As and Mn appeared to be a function of pH and oxido-reduction reactions. With pollution loading indices higher than unity, the status of all the sampling sites ranged from very high to moderate polluted. Similarly, the used-cupel disposal site had a very high average ecological risk index compared to the two relatively distant sites. Lead, As, and Cr proved to have non-carcinogenic effects on children in all sites, whereas these elements only showed non-carcinogenic effects on adults in the used-cupel disposal site. Direct ingestion was the major pathway of PTE exposure. The carcinogenic risk index for all sites and all elements exceeded the threshold. Moreover, the average total carcinogenic risk indices for Cr, Ni, As, and Pb in all sites were high enough to pose lifetime cancer risks to the exposed population with the used-cupel disposal site having the highest average value. Urgent remediation is necessary to prevent the spread of pollution to larger areas.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abdu, N., Agbenin, J. O., & Buerkert, A. (2011). Geochemical assessment, distribution, and dynamics of trace elements in urban agricultural soils under long-term wastewater irrigation in Kano, northern Nigeria. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 174(3), 447–458.
Abrahim, G. M., & Parker, R. J. (2008). Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki Estuary, Auckland. New Zealand. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 136(1–3), 227–238.
Adamo, P., Agrelli, D., & Zampella, M. (2018). Chemical speciation to assess bioavailability, bioaccessibility and geochemical forms of potentially toxic metals (PTMs) in polluted soils.Chapter 9. In B. De Vivo, H. E. Belkin, & A. Lima (Eds.), Environmental geochemistry, site characterization, data analysis and case histories (2nd ed., pp. 153–194). Elsevier
Ahmad, I., Khan, B., Asad, N., Mian, I. A., & Jamil, M. (2019). Traffic-related lead pollution in roadside soils and plants in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan: Implications for human health. International Journal of Environmental Science & Technology, 16, 8015–8022.
Ajmone-Marsan, F., Biasioli, M., Kralj, T., Grčman, H., Davidson, C. M., Hursthouse, A. S., Madrid, L., & Rodrigues, S. (2008). Metals in particle-size fractions of the soils of five European cities. Environmental Pollution, 152, 73–81.
Alijagić, J., & Šajn, R. (2011). Distribution of chemical elements in an old metallurgical area, Zenica (Bosnia and Herzegovina). Geoderma, 162, 71–85.
Alloway, B. J. (1995). Heavy metals in soils. Blackie Academic and Professional.
Argyraki, A., & Kelepertzis, E. (2014). Urban soil geochemistry in Athens, Greece: The importance of local geology in controlling the distribution of potentially harmful trace elements. Science of the Total Environment, 482–483, 366–377.
Antoniadis, V., Shaheen, S. M., Boersch, J., Frohne, T., Du Laing, G., & Rinklebe, J. (2017). Bioavailability and risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in garden edible vegetables and soils around a highly contaminated former mining area in Germany. Journal of Environmental Management, 186, 192–200.
Appenroth, K. J. (2010). Definition of “heavy metals” and their role in biological systems. In I. Sherameti & A. Varma (Eds.), Soil heavy metals (pp. 19–29). Springer.
Asner, G.P., Llactayo, W., Tupayachi, R. & Luna, E.R. (2013). Elevated rates of gold mining in the Amazon revealed through high-resolution monitoring. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110, 18454–18459
Baker, L. R., White, P. M., Gary, M., & Pierzynski, G. M. (2011). Changes in microbial properties after manure, lime, and bentonite application to a heavy metal-contaminated mine waste. Applied Soil Ecology, 48, 1–10.
Balaram, V. (2008). Recent advances in the determination of PGE in exploration studies – a review. Journal of Geological Society of India, 72, 661–677.
Banwart, S. A., Benasconi, S. M., Blum, W. H., de Souza, D. M., Chabaux, F., Duffy, C., Kercheva, M., Kràm, P., Lair, G. J., Ludin, L., Menon, M., Nikolaidis, N. P., Novak, M., Panagos, P., Ragnarsdottir, K. V., Robinson, D. A., de Rousseva, S., Ruiter, P., van Gaans, P., … Zhang, B. (2017). Soil functions in Earth’s critical zone: Key results and conclusion. Advances in Agronomy, 142, 1–27.
Barbieri, M., Nigro, A., & Sappa, G. (2015). Soil contamination evaluation by enrichment factor (EF) and geoaccumulation index (Igeo). Sense Sciences., 2(3), 94–97.
Béziat, D., Dubois, M., Debat, P., Nikiéma, S., Salvi, S., & Tollon, F. (2008). Gold metallogeny in the Birimian craton of Burkina Faso (West Africa). Journal of African Earth Sciences, 50(2–4), 215–233.
Bhuiyan, M. A., Parvez, L., Islam, M. A., Dampare, S. B., & Suzuki, S. (2010). Heavy metal pollution of coal mine-affected agricultural soils in the northern part of Bangladesh. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 173, 384–392.
Bravo, S., Amorós, J. A., Pérez-De-Los-Reyes, C., García Navarro, F. J., Moreno, M. M., Sánchez Ormeño, M., & Higueras, P. (2017). Influence of the soil pH in the uptake and bioaccumulation of heavy metal (Fe, Zn, Cu, Pb and Mn) and other elements (Ca, K, Al Sr and Ba) in vine leaves, Castilla-La Mancha (Spain). Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 174, 79–83.
Bugbee, E. E. (1981). A textbook of fire assaying (3rd ed.). Colorado School of Mines Press.
CalEPA. (2005). Human-exposure-based screening numbers developed to aid estimation of cleanup costs for contaminated soil. Integrated Risk Assessment Section, Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment, California Environmental Protection Agency.
Caporale, A. G., Adamo, P., Capozzi, F., Langella, G., Terribile, F., & Vinginani, S. (2018). Monitoring metal pollution in soils using portable-XRF and conventional laboratory based techniques: Evaluation of the performance and limitation according to metal properties and sources. Science of the Total Environment, 643, 516–526.
Carreras, H. A., Wannaz, E. D., & Pignata, M. L. (2009). Assessment of human health risk related to metals by the use of biomonitors in the province of Cordoba, Argentina. Environmental Pollution, 157, 117–122.
Castaing, C., Billa, M., Milesi, J. P., Thieblemont, D., Le Metour, J., Egal, E., Donzeau, M., Buerrot, C., Cocherie, A., Chevremont, P., Tegyey, M., Itard, Y., Zida, B., Ouedraogo, I., Kote, S., Kabore, B. E., Ouedraogo, C., Ki, J. C. & Zunino, C. (2003). Notice explicative de la Carte géologique et minière du Burkina Faso à 1/1 000 000. Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso.
Cerceau, C. I., Carvalho, C. F., Rabelo, A. C. S., dos Santos, C. G., Dias, S. M., & Vieira Varejão, G. E. V. (2016). Recovering lead from cupel waste generated in gold analysis by Pb-Fire assay. Journal of Environmental Management, 183, 771–776.
Cornelis, G., Johnson, C. A., Gerven, T. V., & Vandecasteele, C. (2008). Leaching mechanisms of oxyanionic metalloid and metal species in alkaline solid wastes: A review. Applied Geochemistry, 23, 955–976.
Corti, C. W., & Holliday, R. J. (2005). Increasing gold demand: New industrial applications. Applied Earth Science, 114, 115–121.
Corti, C. W., Holliday, R. J., & Thompson, D. T. (2005). Commercial aspects of gold catalysis. Applied Catalysis A: General, 291, 253–261.
Covelli, S., & Fantolan, G. (1997). Application of normalization procedure in determining regional geochemical baseline. Environmental Geology, 30, 34–45.
Dao, L., Morrison, L., & Zhang, C. (2010). Spatial variation of urban soil geochemistry in a roadside sports ground in Galway, Ireland. Science of Total Environment, 408, 1076–1084.
DEA. (2010). Framework for the management of contaminated land (p. 74p). Republic of South Africa.
de Miguel, E., Iribarren, I., Chacón, E., Ordoñez, A., & Charlesworth, S. (2007). Risk-based evaluation of the exposure of children to trace elements in playgrounds in Madrid (Spain). Chemosphere, 66, 505–513.
Di Bonito, M., Breward, N., Crout, N., Smith, B., Young, S. D., & Zhang, H. (2018). Chapter 10 – extraction and characterization of pore water in contaminated soils A2 - vivo, Benedetto De. In: Belkin, H.E., Lima, A.B.T.-E.G. (Second E. (Eds.). Elsevier, pp. 195–235
Ding, Z., & Hu, X. (2014). Ecological and human health risks from metal (loid)s in peri-urban soil in Nanjing, China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 36, 399–408.
Dorne, J. L. C. M., Fernàndez-Cruz, M. L., Bertelsen, U., Renshaw, D. W., Peltonen, K., Anadon, A., Feil, A., Sanders, P., Wester, P., & Fink-Gremmels, J. (2011). Risk assessment of Coccidostatics during feed cross-contaminations: Animal and human health aspects. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 270(3), 196–203.
Du, Y., Gao, B., Zhou, H., Ju, X., Hoa, H., & Yin, S. (2013). Health risk assessment of heavy metals in road dusts in urban parks of Beijing, China. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 18, 299–309.
Ehlert, K., Mikutta, C., & Kretzschmar, R. (2014). Impact of birnessite on arsenic and iron speciation during microbial reduction of arsenic-bearing ferrihydrite. Environmental Science & Technology, 48, 11320–11329.
Ezemonye, L. I., Adebayo, P. O., Enuneku, A. A., Tongo, I., & Ogbomida, E. (2018). Potential health risk consequences of heavy metal concentrations in surface water, shrimp (Macrobrachium macrobrachion) and fish (Brycinus longipinnis) from Benin River, Nigeria. Toxicology Reports, 6, 1–9.
Fellows, M. (2010). Gauging the long-term cost of gold mine production. Alchemist, 60, 3–6.
Getaneh, W., & Alemayehu, T. (2006). Metal contamination of the environment by placer and primary gold mining in the Adola region of southern Ethiopia. Environmental Geology, 50, 339–352.
Guéniat, M. & White, N. (2015). A golden racket: the true source of Switzerland’s “Togolese” gold. Public Eye Report
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach. Water Research., 14, 975–1001.
Han, Y. M., Du, P. X., Cao, J. J., & Posmentier, E. S. (2006). Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Science of the Total Environment, 355(1–3), 176–186.
Horváth, A., Szűcs, P., & Bidló, A. (2015). Soil condition and pollution in urban soils: Evaluation of the soil quality in a Hungarian town. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 15, 1825–2183.
Hooda, P. S. (2010). Trace elements in soils. Wiley.
Hu, X. J., Wang, J. S., Liu, Y. G., Li, X., Zeng, G. M., Bao, Z. L., Zeng, X. X., Chen, A. W., & Long, F. (2011). Adsorption of chromium (VI) by ethylenediamine-modified cross-linked magnetic chitosan resin: Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 185(1), 306–314.
Hu, B., Jia, X., Hu, J., Xu, D., Xia, F., & Li, Y. (2017). Assessment of heavy metal pollution and health risks in the soil-plant-human system in the Yangtze River Delta, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(9), 1042.
Huang, F., Wang, X., Lou, L., Zhou, Z., & Wu, J. (2010). Spatial variation and source apportionment of water pollution in Qiantang River (China) using statistical techniques. Water Research, 44, 1562–1572.
Ihedioha, J. N., Ukoha, P. O., & Ekere, N. R. (2017). Ecological and human health risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in soil of a municipal solid waste dump in Uyo, Nigeria. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 39, 497–515.
Jia, Z., Li, S., & Wang, L. (2018). Assessment of soil heavy metals for eco-environment and human health in a rapidly urbanization area of the upper Yangtze Basin. Scientific Reports, 8, 3257.
Jones, G. (2005). Garden cultivation of staple crops and its implications for settlement location and continuity. World Archaeology, 37, 164–176.
Juvonen, R., & Kontas, E. (1999). Comparison of three analytical methods in the determination of gold in six finnish gold ores, including a study on sample preparation and sampling. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 65, 219–229.
Kabata-Pendias, A. (2011). Trace elements in soils and plants (4th ed., p. 520). Boca Raton FL: CRC Press.
Kaiser, H. F. (1958). The varimax criteria for analytical rotation in factor analysis. Psychometrika, 23, 187–200.
Khaledian, Y., Kiani, F., & Ebrahimi, E. (2012). The effect of land use change on soil and water quality in northern Iran. Journal of Mountain Science, 9(6), 798–816.
Klerks, P. L., & Levinton, J. S. (1989). Rapid evolution of metal resistance in a benthic oligochaete inhabiting a metal polluted site. Biological Bulletin, 176, 135–141.
Klitzke, S., & Lang, F. (2009). Mobilization of soluble and dispersible lead, arsenic, and antimony in a polluted, organic-rich soil – effects of pH increase and counterion valency. Journal of Environmental Quality, 38, 933–939.
Kumar, A., Kumar, A. M. M. S., Chaturvedi, C.-P., Shabnam, A. K., Subrahmanyam, A. A., Mondal, G. R., Gupta, D. K., Mlyan, S. K., Kumar, S. K., Khan, S. A., & Yadav, K. (2020). Lead toxicity Health hazards, influence on food Chain, and sustainable remediation approaches. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(2179), 1–33.
Lafferty, B. J., Ginder-Vogel, M., & Sparks, D. L. (2010). Arsenite oxidation by a poorly crystalline manganese-oxide 1. Stirred-Flow Experiments. Environmental Science & Technology., 44, 8460–8466.
Landrigan, P. J., Fuller, R., Acosta, N. J. R., Adeyi, O., Arnold, R., Basu, N. N., et al. (2018). The Lancet Commission on pollution and health. Lancet, 391, 462–512.
Li, Y., Ji, L., Mi, W., Xie, S., & Bi, Y. (2021). Health risks from groundwater arsenic on residents in northern China coal-rich region. Science of the Total Environment, 773, 1–9.
Liang, Y., Yi, X., Dang, Z., Wang, Q., Luo, H., & Tang, J. (2017). Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment in the vicinity of a tailing pond in Guangdong, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(1557), 1–17.
Liar, G. J., Gerzabek, M. H., & Haberhauer, G. (2007). Sorption of heavy metals on organic and inorganic soil constituents. Environmental Chemistry Letter, 5, 23–27.
Likar, M., Vogel-Mikus, K., Potisek, M., Hancevic, K., Radic, T., Necemer, M., & Regvar, M. (2015). Importance of soil and vineyard management in the determination of grape vine mineral composition. Science of the Total Environment, 505, 724–731.
Luo, X. S., Yu, S., Zhu, Y. G., & Li, X. D. (2012). Trace metal contamination in urban soils of China. Science of the Total Environment, 421–422, 17–30.
Majer, A. P., Petti, M. A. V., Corbisier, T. N., Ribeiro, A. P., Theophilo, C. Y. S., de Lima Ferreira, P. A., & Figueira, R. C. L. (2014). Bioaccumulation of potentially toxic trace elements in benthic organisms of Admiralty Bay (King George Island, Antarctica). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 79(1), 321–325.
Manta, D. S., Angelone, M., Bellanca, A., Neri, R., & Sprovieri, M. (2002). Heavy metals in urban soils: A case study from the city of Palermo (Sicily), Italy. Science of the Total Environment, 300, 229–243.
Markwitz, V., Hein, K. A. A., & Miller, J. (2016). Compilation of West African minerals deposits: Spatial distribution and mineral endowment. Precambrian Research, 274(61), 81.
Marques, J. J., Schulze, D. G., Curi, N., & Mertzman, S. A. (2004). Major element geochemistry and geomorphic relationships in Brazilian Cerrado soils. Geoderma, 119, 179–195.
Marschner, P. (2012). Nutrition of higher plants (3rd ed.). Elsevier.
Massart, D. L., & Kaufman, L. (1983). The interpretation of analytical chemical data by the use of cluster analysis. Wiley.
McBride, M. (1994). Environmental chemistry of soils. Oxford University Press.
Minnikova, T. V., Denisova, T. V., Mandzhieva, S. S., Kolesnikov, S. I., Minkina, T. M., Chaplygin, V. A., Burachevskaya, M. V., Sushkova, S. N., & Bauer, T. V. (2017). Assessing the effect of heavy metals from the Novocherkassk power station emissions on the biological activity of soils in the adjacent areas. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 174, 70–78.
Mirzaei, M., Marofi, S., Solgi, E., Abbasi, M., Karimi, R., & Riyahi Bakhtyari, H. R. (2019). Ecological and health risks of soil and grape heavy metals in long-term fertilized vineyards (Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari province of Iran). Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 42(1), 27–43.
Müller, G. (1981). Die Schwermetallbelastung der sedimente des Neckars und seiner Nebenflusse: Eine Bestandsaufnahme. Chemiker Zeitung, 105, 157–164.
Muir, A., Mitchell, J., Flatman, S. R., & Sabbagha, C. (2005). A practical guide to retreatment of gold processing residues. Minerals Engineering, 18, 811–824.
Pitcairn, I. K. (2011). Background concentrations of gold in different rock types. Transactions of the Institution of Mining and Metallurgy b., 120, 31–38.
Pokorny, B., von Lübke, C., Dayamba, S. D., & Helga Dickow, H. (2019). All the gold for nothing? Impacts of mining on rural livelihoods in Northern Burkina Faso. World Development, 119, 23–39.
Pulleman, M., Creamer, R., Hamer, U., Helder, J., Pelosi, C., Peres, G., & Rutgers, M. (2012). Soil biodiversity, biological indicators and soil ecosystem services an overview of European approaches. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 4(5), 529–538.
Qing, X., Yutong, Z., & Shenggao, L. (2015). Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risk in urban soils of steel industrial city (Anshan), Liaoning, Northeast China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 120, 377–385.
Rahman, I. M. M. & Begum, Z. A. (2019). Introductory chapter: how to assess metal contamination in soils? In Z. A. Begum, I. M. M. Rahman, & H. Hasegawa (Eds.), Metals in soil—Contamination and remediation (pp. 1–9). IntechOpen.
Ryan, J. D., & Windom, H. L. (1988). A geochemical and statistical approach for assessing metal pollution in coastal sediments. In U. Seeliger, L. D. de Lacerda, S. R. Patchineelam (Eds.), Metals in coastal environments of Latin America (pp. 47–58). Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-71483-2_6
Reimann, C., & De Caritat, P. (2005). Distinguishing between natural and anthropogenic sources for elements in the environment: Regional geochemical surveys versus enrichment factors. Sciences of the Total Environment, 337, 91–107.
Reyment, R. A., & Jöreskog, K. G. (1993). Applied factor analysis in the natural sciences. Cambridge University Press.
Rinklebe, J., Antoniadis, V., Shaheen, S. M., Rosche, O., & Altermann, M. (2019). Health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in soils along the Central Elbe River, Germany. Environment International, 126, 76–88.
Robertson, M., & Peters, L. (2016). West African goldfields. Episodes, 39, 155–176.
Rosano, M., Gracía-Ruiz, E., McIontosh, K. S., Hinrichs, J., Deconninck, I., & Vanhaecke, F. (2006). Comparison of the solid sampling techniques laser ablation-ICP-MS, glow discharge-MS and spark-OES for the determination of platinum group metals in Pb buttons obtained by fire assay of platiniferous ores. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 21, 899–909.
Saidi, D. (2012). Importance and role of cation exchange capacity on the physicals properties of the Cheliff saline soils (Algeria). Procedia Engineering, 33, 435–449.
Salvarredy-Aranguren, M. M., Probst, A., Roulet, M., & Isaure, M. P. (2008). Contamination of surface waters by mining wastes in the Milluni valley (Cordillera Real, Bolivia): Mineralogical and hydrological influences. Applied Geochemistry, 23(5), 299–324.
Scullett-Dean, G., Hamilton, J. L., Repina, O., Brand, H. E. A., Burton, E. D., Saunders, M., & Santini, T. C. (2023). Uptake and incorporation of Al, Cr, V, Zn and Mo in hematite: Competition, synergies and influence on structural properties. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 445, 130630.
Shafiee, S., & Topal, E. (2010). An overview of global gold market and gold price forecasting. Resource Policy, 35, 178–189.
Shahid, M., Khalid, S., Abbas, G., Shahid, N., Nadeem, M., Sabir, M., Aslam, M. & Dumat, C. (2015). Heavy metal stress and crop productivity. In K. R. Hakeem (Ed.), Crop production and global environmental issues (pp. 1–25). Cham: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-23162-4_1
Skrbić, B. D., Đuriŝić-Mladenović, N., Tadić, D. J., & Cvejanov, J. D. (2017). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban soil of Novi Sad, Serbia: Occurrence and cancer risk assessment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24, 16148–16159.
Sinex, S. A., & Wright, D. A. (1988). Distribution of trace metals in the sediments and biota of Chesapeake Bay. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 19(9), 425–431.
Singh, J., & Kalamdhad, A. S. (2013). Chemical speciation of heavy metals in compost and compost ammended soil—a review. International Journal of Environmental Engineering Research, 2, 27–37.
Sinha, S., Gupta, A. K., Bhatt, K., Pandey, K., Rai, U. N., & Singh, K. P. (2006). Distribution of metals in the edible plants grown at Jajmau, Kanpur (India) receiving treated tannery wastewater: Relation with physico-chemical properties of soil. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 115, 1–22.
Smith, S. R. (2009). A critical review of the bioavailability and impacts of heavy metals in municipal solid waste composts compared to sewage sludge. Environment International., 35(1), 142–156.
Stefanowicz, A. M., Woch, M. W., & Kapusta, P. (2014). Inconspicuous waste heaps left by historical Zn–Pb mining are hot spots of soil contamination. Geoderma, 235–236, 1–8.
Tang, L., Tang, X. Y., Zhu, Y. G., Zheng, M. H., & Miao, Q. L. (2005). Contamination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in urban soils in Beijing, China. Environment International, 31, 822–828.
Taylor, S. R., & McLennan, S. M. (1995). The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Reviews in Geophysics., 33, 241–265.
Tchounwou, P. B., Yedjou, C. G., Patlolla, A. K., & Sutton, D. J. (2012). Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. In A. Luch (Ed.), Molecular, clinical and environmental toxicology (pp. 133–164). Springer.
Thongyuan, S., Khantamoon, T., Aendo, P., & Binot, A. (2020). Ecological and health risk assessment, carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic effects of heavy metals contamination in the soil from municipal solid waste landfill in Central, Thailand. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 27(2), 1–22.
Tomlinson, D. L., Wilson, J. G., Harris, C. R., & Jeffrey, D. W. (1980). Problems in the assessment of heavy metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen, 33, 566–575.
USEPA. (2002). Supplemental guidance for developing soil screening levels for superfund sites. USEPA.
USEPA (2005). Guidelines for Carcinogen risk assessment. In Risk Assessment Forum. Washington, DC: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
USEPA. (2017). Human health risk assessment for the smurfit-stone/frenchtown mill operable unit 1 site located in Missoula County, Montana. Washington, DC: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Vanhaecke, F., Resano, M., Koch, J., McIntosh, K., & Gunther, D. (2010). Femtosecond laser ablation-ICP-mass spectrometry analysis of a heavy metallic matrix: Determination of platinum group metals and gold in lead fire-assay buttons as a case study. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 25, 1259–1267.
Varol, M. (2011). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 195, 355–364.
Wang, J., Li, S., Cui, X., Li, H., Qian, X., & Wang, C. (2016). Bioaccessibility, sources and health risk assessment of trace metals in urban park dust in Nanjing, Southeast China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 128, 161–170.
Ward, J. H. (1963). Ward’s method. Journal of American Statistical Association, 58, 236–246.4th ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press
Wedepohl, K. H. (1995). The composition of the continental crust. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 59, 1217–1239.
Wilson, S. C., Lockwood, P. V., Ashley, P. M., et al. (2010). The chemistry and behaviour of antimony in the soil environment with comparisons to arsenic: A critical review. Environmental Pollution, 158, 1169–1181.
Wu, S., Peng, S., Zhang, X., Wu, D., Luo, W., Zhang, T., Zhou, S., Yang, G., Wan, H., & Wu, L. (2015). Levels and health risk assessments of heavy metals in urban soils in Dongguan, China. Journal Geochemical Exploration., 148, 71–78.
Yongming, H., Peixuan, D., Junji, C., & Posmentier, E. S. (2006). Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Cent, China. Science of Total Environment, 355, 176–186.
Zabsonré, A., Agbo, M., & Somé, J. (2018). Gold exploitation and socioeconomic outcomes: The case of Burkina Faso. World Development, 109, 206–221.
Zereini, F., Alt, F., Messerschmidt, J., Wiseman, C., Feldmann, I., Von Bohlen, A., Müller, J., Liebl, K., & Püttmann, W. (2005). Concentration and distribution of heavy metals in urban airborne particulate matter in Frankfurt am Main, Germany. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 2983–2989.
Zhang, R., Pian, H., Santosh, M., & Zhang, S. (2015). The history and economics of gold mining in China. Ore Geology Reviews, 65, 718–727.
Zöttl, H. W. (1987). Responses of forest decline to experimental fertilization. In T. C. Hutchinson & K. M. Meema (Eds.), Effects of atmospheric pollutants on forests, wetlands and agricultural ecosystems. NATO ASI Series (Vol. 16, pp. 255–265). Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions which had greatly improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sako, A., Coulibaly, K. & Yé, L. Environmental Geochemistry and Human Health Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Urban Soils in the Vicinity of a Pb Fire-Assay Laboratory in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 712 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06718-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06718-6