Abstract
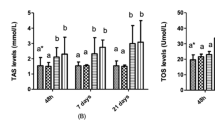
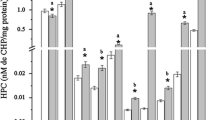
Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS, C8F17SO3; CAS No. 2795–39-3), an industrial persistent organic pollutant, has been known with significant bioaccumulation and biomagnification potential. The purpose of this study was to demonstrate the effects of PFOS on the aquatic model vertebrate common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Fish were exposed to 1 and 10 mg/L PFOS during 96 h and 21 days. There were two control groups: control (only fish) and solvent control (DMSO and fish). After exposure times, the blood samples and tissues (gill, liver, muscle, brain, and kidney) were taken from the fish. The physiological (hematocrit) and genotoxic (micronucleus) parameters were done with the blood samples. The biochemical parameters (the advanced oxidative protein products, AOPP and glutathione, GSH) were done with the muscle, gill, brain, and liver samples. While the micronucleus and nuclear abnormalities increased, the hematocrit values decreased in the 1 mg/L PFOS-exposed groups during 96 h and 21 days. The AOPP values of the muscle, gill, brain, and liver tissues significantly changed in PFOS-exposed groups at both exposure times (P < 0.05). Unlike AOPP, glutathione levels of gill did not change in both PFOS-exposed groups at 96 h (P > 0.05). Histopathological changes were seen in the gill, liver, and kidney tissues after exposure to PFOS. Therefore, even low concentrations of PFOS have genotoxic, biochemical, and histopathological effects on carp. The results help to understand the early toxicological effects of PFOS in freshwater ecosystems.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The research has no associate data.
References
3M Company. (2000). Sulfonated perfluorochemicals in the environment: Sources, dispersion, fate and effects. St. Paul MN. Available at https://fluoridealert.org/wp-content/pesticides/pfos.fr.final.docket.0005.pdf. Accessed 20 May 2022
Al-Bairuty, G., Shaw, B. J., Handy, R. D., & Henry, T. (2013). Histopathological effects of waterborne copper nanoparticles and copper sulphate on the organs of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquatic Toxicology, 126, 104–115.
Ankley, G. T., Kuehl, D. W., Kahl, M. D., Jensen, K. M., Linnum, A., Leino, R. L., & Villeneuve, D. A. (2005). Reproductive and developmental toxicity and bioconcentration of perfluorooctanesulfonate in a partial life-cycle test with the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Environment Toxicology and Chemistry, 24(9), 2316–2324. https://doi.org/10.1897/04-634R.1
Bangma, J., Eaves, L. A., Oldenburg, K., Reiner, J. L., Manuck, T., & Fry, R. C. (2020). Identifying risk factors for levels of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in the placenta in a high-risk pregnancy cohort in North Carolina. Environmental Science & Technology, 54(13), 8158–8166. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b07102
Belek, N., Erkmen, B., Sepici Dinçel, A., & Gunal, A. C. (2022). Does persistent organic pollutant PFOS (perfluorooctane sulfonate) negative impacts on the aquatic invertebrate organism, Astacus leptodactylus [Eschscholtz, 1823]. Ecotoxicology, 31, 1217–1230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-022-02579-7
Ben Amara, I., Ben Saad, H., Hamdaoui, L., et al. (2015). Maneb disturbs expression of superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase, increases reactive oxygen species production, and induces genotoxicity in liver of adult mice. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 12309–12322. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4434-6
Benli, A. C. K., Köksal, B., & Özkul, A. (2008). Sublethal ammonia exposure of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.): Effects on gill, liver and kidney histology. Chemosphere, 72(9), 1355–1358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.04.037
Benli, A. C. K., Erkmen, B., & Erkoc, F. (2016). Genotoxicity of sub-lethal di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP) in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Archives of Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology, 67(1), 25–30.
Billah, M. B., Paul, S., Sultana, S., Hasan, M. J., & Salam, M. A. (2016). Effects of perfluorooctane sulfonate on the hematology and histopathology of juvenile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Jahangirnagar University Journal of Biological Sciences, 4(2), 37–45. https://doi.org/10.3329/jujbs.v4i2.27794
Boudreau, T. M., Sibley, P. K., Mabury, S. A., Muir, D. G. C., & Solomon, K. R. (2003). Laboratory evaluation of the toxicity of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) on Selenastrum capricornutum, Chlorella vulgaris, Lemna gibba, Daphnia magna, and Daphnia pulicaria. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 44, 0307–0313.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1976.9999
Çavaş, T., & Ergene-Gözükara, S. (2005). Micronucleus test in fish cells: A bioassay for in situ monitoring of genotoxic pollution in the marine environment. Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, 46(1), 64–70.
Cavaş, T., & Könen, S. (2008). In vivo genotoxicity testing of the amnesic shellfish poison (domoic acid) in piscine erythrocytes using the micronucleus test and the comet assay. Aquatic Toxicology, 90(2), 154–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2008.08.011
Ellman, G. L. (1959). Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 82, 70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6
Erkmen, B., Günal, A. C., Polat, H., Erdoğan, K., Civelek, H., & Erkoç, F. (2022). Sublethal effects of acrylamide on thyroid hormones, complete blood count and micronucleus frequency of vertebrate model organism (Cyprinus carpio). Turkish Journal of Biochemistry, 47(6), 811–818.
Fagbayigbo, B. O., Opeolu, B. O., & Fatoki, O. S. (2020). Adsorption of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) from water using leaf biomass (Vitis vinifera) in a fixed-bed column study. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 18, 221–233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-020-00456-1
Fair, P. A., Peden-Adams, M. M., Mollenhauer, M. A., Bossart, G. D., Keil, D. E., & White, N. D. (2021). Effects of an environmentally relevant PCB-mixture on immune function, clinical chemistry, and thyroid hormone levels in adult female B6C3F1 mice. Journal of Toxicology Environmental Health Part A, 84(7), 279–297.
Fang, C., Huang, Q., Ye, T., Chen, Y., Liu, L., Kang, M., Lin, Y., Shen, H., & Dong, S. (2013). Embryonic exposure to PFOS induces immunosuppression in the fish larvae of marine medaka. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 92, 104–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.03.005
Giesy, J. P., & Kannan, K. (2001). Global distribution of perfluorooctane sulfonate in wildlife. Environmental Science & Technology, 35(7), 339–1342. https://doi.org/10.1021/es001834k
Gopal, R., Narmada, S., Vijayakumar, R., & Jaleel, C. A. (2009). Chelating efficacy of CaNa2 EDTA on nickel-induced toxicity in Cirrhinus mrigala (Ham.) through its effects on glutathione peroxidase, reduced glutathione and lipid peroxidation. Comptes Rendus Biology, 332(8), 685–696.
Gül, A., Benli, Ç. K., Ayhan, A., Memmi, B. K., Selvi, M., Sepici-Dinçel, A., Çakiroğullari, G., & Erkoç, F. (2012). Sublethal propoxur toxicity tojuvenile common carp (Cyprinus carpio L., 1758): Biochemical, hematological, histopathological, and genotoxicity effects. Environment Chemistry and Toxicology, 31(9), 2085–2092.
Günal, A. Ç., Erkmen, B., Paçal, E., Arslan, P., Yıldırım, Z., & Erkoç, F. (2020). Sub-lethal effects of imidacloprid on Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Water Air & Soil Pollution, 231, 4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4366-8
Hagenaars, A., Knapen, D., Meyer, I. J., Van der Ven, K., Hoff, P., & De Coen, W. (2008). Toxicity evaluation of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) in the liver of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquatic Toxicology, 88(3), 155–163.
Han, J., & Fang, Z. (2010). Estrogenic effects, reproductive impairment and developmental toxicity in ovoviparous swordtail fish (Xiphophorus helleri) exposed to perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS). Aquatic Toxicology, 99(2), 281–290.
Hermenean, A., Damache, G., Albu, P., Ardelean, A., Ardelean, G., Ardelean, D. P., Horge, M., Nagy, T., Braun, M., Zsuga, M., et al. (2015). Histopathological alterations and oxidative stress in liver and kidney of Leuciscus cephalus following exposure to heavy metals in the Tur River, North Western Romania. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 119, 198–205.
Hoff, P. T., Van Campenhout, K., Van de Vijver, K., Covaci, A., Bervoets, L., Moens, L., Huyskens, G., Goemans, G., Belpaire, C., Blust, R., & De Coen, W. (2005). Perfluorooctane sulfonic acid and organohalogen pollutants in liver of three freshwater fish species in Flanders (Belgium): Relationships with biochemical and organismal effects. Environmental Pollution, 137(2), 324–333.
Houde, M., Martin, J. W., Letcher, R. J., Solomon, K. R., & Muir, D. C. G. (2006). Biological monitoring of polyfluoroalky substances: A review. Environmental Science & Technology, 40(11), 3463–3473. https://doi.org/10.1021/es052580b
Huang, H., Huang, C., Wang, L., Ye, X., Bai, C., Simonich, M. T., Tanguay, R. L., & Dong, Q. (2010). Toxicity, uptake kinetics and behavior assessment in zebrafish embryos following exposure to perfluorooctanesulphonicacid (PFOS). Aquatic Toxicology, 98, 139–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.02.003
Huang, J., Sun, L., Mennigen, J. A., Liu, Y., Liu, S., Zhang, M., Wang, Q., & Tu, W. (2020). Developmental toxicity of the novel PFOS alternative OBS in developing zebrafish: An emphasis on cilia disruption. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 409, 124491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124491
Huset, C. A., Barlaz, M. A., Barofsky, D. F., & Field, J. A. (2011). Quantitative determination of fluorochemicals in municipal landfill leachates. Chemosphere, 82, 1380–1386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.11.072
Hussain, B., Sultana, T., Sultana, S., Masoud, M. S., Ahmed, Z., & Mahboob, S. (2018). Fish eco-genotoxicology: Comet and micronucleus assay in fish erythrocytes as in situ biomarker of freshwater pollution. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 25(2), 393–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2017.11.048
Inoue, Y., Hashizume, N., Yoshida, T., Murakami, H., Suzuki, Y., Koga, Y., Takeshige, R., Kikushima, E., Yakata, N., & Otsuka, M. (2012). Comparison of bioconcentration and biomagnification factors for poorly water-soluble chemicals using common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 63(2), 241–248.
Jantzen, C. E., Annunziato, K. M., & Cooper, K. R. (2016). Behavioral, morphometric, and gene expression effects in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryonically exposed to PFOA, PFOS, and PFNA. Aquatic Toxicology, 180, 123–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.09.011
Jones, P. D., Hu, W., De Coen, W., Newsted, J. L., & Giesy, J. P. (2003). Binding of perfluorinated fatty acids to serum proteins. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 22(11), 2639–2649. https://doi.org/10.1897/02-553
Kannan, K., Tao, L., Sinclair, E., Pastva, S. D., Jude, D. J., & Giesy, J. P. (2005). Perfluorinated compounds in aquatic organisms at various trophic levels in a Great Lakes food chain. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 48, 559–566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-004-0133-x
Kaur, S., Khera, K. S., & Kondal, J. K. (2018). Heavy metal induced histopathological alterations in liver, muscle and kidney of freshwater cyprinid, Labeo rohita (Hamilton). Journal of Entomology and Zoology Studies, 6, 2137–2144.
Khan, M. S., Javed, M., Rehman, T., Urooj, M., & Ahmad, I. (2020). Heavy metal pollution and risk assessment by the battery of toxicity tests. Science Reports, 10, 16593.
Kim, W.-K., Lee, S.-K., & Jung, J. (2010). Integrated assessment of biomarker responses in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) exposed to perfluorinated organic compounds. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 180, 395–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.04.044
Kirsch-Volders, M., Sofuni, T., Aardema, M., Albertini, S., Eastmond, D., Fenech, M., Ishidate, M., Jr., Lorge, E., Norppa, H., Surralles, J., Lorge, E., Norppa, H., Surrallés, J., von der Hude, W., & Wakata, A. (2000). Report from the in vitro micronucleus assay working group. Environmental Molecular and Mutagenetics, 35, 167–172.
Kissa, E. (2001). Fluorinated surfactants and repellants (2nd ed., pp. 1–21). Marcel Decker.
Kumar, N., Thorat, S. T., Gite, A., & Patole, P. B. (2022). Selenium nanoparticles and omega-3 fatty acid enhanced thermal tolerance in fish against arsenic and high temperature. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C Toxicology and Pharmacolology, 261, 109447.
Lindstrom, A. B., Strynar, M. J., & Libelo, E. L. (2011). Polyfluorinated compounds: Past, present, and future. Environmental Science & Technology, 45, 7954–7961. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2011622
Liu, C., Chang, V. W., Gin, K. Y., & Nguyen, V. T. (2014). Genotoxicity of perfluorinated chemicals (PFCs) to the green mussel (Perna viridis). Science of the Total Environment, 487, 117–122.
Liu, Z., Lu, Y., Wang, P., Wang, T., Liu, S., Johnson, A. C., Sweetman, A. J., & Baninla, Y. (2017). Pollution pathways and release estimation of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in central and eastern China. Science of the Total Environment, 580, 1247–1256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.085
Mahmood, Y., Hussain, R., Ghaffar, A., Ali, F., Nawaz, S., Mehmood, K., & Khan, A. (2022). Acetochlor affects bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) by producing oxidative stress, lowering tissue proteins, and inducing genotoxicity. BioMed Research International, 9140060. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/9140060
Mallatt, J. (1985). Fish gill structural changes induced by toxicants and other irritants: A statistical review. Canadian Journal of Fish and Aquatic Science, 42, 630–648. https://doi.org/10.1139/f85-083
Martin, J. W., Whittle, D. M., Muir, D. C., & Mabury, S. A. (2004). Perfluoroalkyl contaminants in a food web from Lake Ontario. Environmental Science & Technology, 38(20), 5379–5385. https://doi.org/10.1021/es049331s
Meng, L., Song, B., Lu, Y., Lv, K., Gao, W., Wang, Y., & Jiang, G. (2021). The occurrence of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in fluoropolymer raw materials and products made in China. Research Journal of Environmental Science, 107, 77–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2021.01.027
Moody, C. A., Hebert, G. N., Strauss, S. H., & Field, J. A. (2003). Occurrence and persistence of perfluorooctanesulfonate and other perfluorinated surfactants in groundwater at a fire-raining area at Wurtsmith Air Force Base, Michigan, USA. Journal of Environment Monitoring, 5, 341–345. https://doi.org/10.1039/B212497A
Oliaei, F., Kriens, D., Weber, R., & Watson, A. (2013). PFOS and PFC releases and associated pollution from a PFC production plant in Minnesota (USA). Environment Science and Pollution Research, 20, 1977–1992. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1275-4
Parihar, M. S., Javeri, T., Hemnani, T., Dubey, A. K., & Prakash, P. (1997). Responses of superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase and reduced glutathione antioxidant defenses in gills of the freshwater catfish (Heteropneustes fossilis) to short-term elevated temperature. Journal of Thermal Biology, 22(2), 151–156.
Poulino, M. G., Souza, N. E. S., & Fernandes, M. N. (2012). Subchronic exposure to atrazine induces biochemical and histopathological changes in the gills of a neotropical freshwater fish, Prochilodus lineatus. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 80, 6–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.02.001
Rahman, M. F., Peldszus, S., & Anderson, W. B. (2014). Behaviour and fate of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in drinking water treatment: A review. Water Resource, 50, 318–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.10.045
Roberts, R. J. (2001). Fish Pathology (3rd ed., p. 492). London: Saunders.
Schultz, M. M., Barofsky, D. F., & Field, J. A. (2004). Quantitative determination of fluorotelomer sulfonates in groundwater by LC MS/MS. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 1828–1835. https://doi.org/10.1021/es035031j
Schumann, S., Negrato, E., Edoardo, P., Bonato, M., Irato, P., Marion, A., Santovito, G., & Bertotto, D. (2022). Species-specific physiological responses in freshwater fish exposed to anthropogenic perfluorochemical (PFAS) pollution. Available at https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4257912. Accessed 15 Mar 2023
Selvi, M., Cavaş, T., Benli Karasu Caglan, A., Koçak Memmi, B., Cinkılıç, N., Dinçel, A. S., Vatan, O., Yılmaz, D., Sarıkaya, R., Zorlu, T., & Erkoç, F. (2013). Sublethal toxicity of esbiothrin relationship with total antioxidant status and in vivo genotoxicity assessment in fish (Cyprinus carpio L., 1758) using the micronucleus test and comet assay. Environmental Toxicology, 28(11), 644–51. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.20760
Sepici-Dinçel, A., Benli, A. Ç. K., Selvi, M., Sarıkaya, R., Şahin, D., Özkul, I. A., & Erkoç, F. (2009). Sublethal cyfluthrin toxicity to carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) fingerlings: Biochemical, hematological, histopathological alterations. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 72(5), 1433–1439.
Shahid, S., Sultana, T., Sultana, S., Hussain, B., Al-Ghanim, K. A., Al-Bashir, F., Riaz, M. N., & Mahboob, S. (2022). Detecting aquatic pollution using histological investigations of the gills, liver, kidney, and muscles of Oreochromis niloticus. Toxics, 10, 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100564
Shi, X., Liu, C., Wu, G., & Zhou, B. (2009). Waterborne exposure to PFOS causes disruption of the hypothalamus–pituitary–thyroid axis in zebrafish larvae. Chemosphere, 77, 1010–1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.07.074
Srikanth, K., Pereira, E., Duarte, A. C., & Ahmad, I. (2013). Glutathione and its dependent enzymes’ modulatory responses to toxic metals and metalloids in fish—A review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20(4), 2133–2149.
Strzyzewska, E., Szarek, J., & Babinska, I. (2016). Morphologic evaluation of the gills as a tool in the diagnostics of pathological conditions in fish and pollution in the aquatic environment: A review. Veterinarni Medicina, 61(3), 123–132. https://doi.org/10.17221/8763-VETMED
Touaylia, S., Khazri, A., Mezni, A., & Bejaoui, M. (2019). Effects of emerging persistent organic pollutant perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) on the Crustacean Gammarus insensibilis. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 25, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1489717
Tse, W. K. F., Li, J. W., Tse, A. C. K., Chan, T. F., Ho, J. C. H., Wu, R. S. S., Wong, C. K. C., & Lai, K. P. (2016). Fatty liver disease induced by perfluorooctane sulfonate: Novel insight from transcriptome analysis. Chemosphere, 159, 166–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.05.060
UNEP. (2006). In: Draft risk profile: Perflorooctane sulfonate (PFOS). Programme U.N.E.
UNEP (2009). The conference of the parties 4 of the Stockholm Convention (COP-4) in Geneva placed perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctane sulfonyl fluoride (PFOS and PFOSF) in Annex B. Available at http://chm.pops.int/Convention/Pressrelease/COP4Geneva9May2009/tabid/542/language/en-US/Default.aspx. Accessed 17 Mar 2023
Wilkinson, J. L., Hooda, P. S., Swinden, J., Barker, J., & Barton, S. (2018). Spatial (bio)accumulation of pharmaceuticals, illicit drugs, plasticisers, perfluorinated compounds and metabolites in river sediment, aquatic plants and benthic organisms. Environment Pollution, 234, 864–875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.11.090
Witko-Sarsat, V., Friedlander, M., Capeillère-Blandin, C., Nguyen-Khoa, T., Nguyen, A. T., Zingraff, J., Jungers, P., & Descamps-Latscha, B. (1996). Advanced oxidation protein products as a novel marker of oxidative stress in uremia. Kidney Internation, 49(5), 1304–1313. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.1996.186
Xia, J. G., Nie, L. J., Mi, X. M., Wang, W. Z., Ma, Y. J., Cao, Z. D., & Fu, S. J. (2015). Behavior, metabolism and swimming physiology in juvenile Spinibarbus sinensis exposed to PFOS under different temperatures. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 41, 1293–1304.
Xiao, F. (2000). Emerging poly-and perfluoroalkyl substances in the aquatic environment: A review of current literatüre. Water Resource, 124, 482–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.07.024
Yancheva, V. S., Stoyanova, S. G., Georgieva, E. S., & Velcheva, I. G. (2018). Mussels in ecotoxicological studies - Are they better indicators for water pollution than fish? Ecologica Balcanica, 10(1), 57–84.
Zhou, Y., Zhang, Y., Wei, S., Li, W., Li, W., Wu, Z., Jiang, S., Lu, Y., Xu, Q., & Chen, L. (2022). Reduced hypoxia tolerance and altered gill morphology at elevated temperatures may limit the survival of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) under global warming. Fishes, 7, 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050216
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Gazi University Academic Writing Application and Research Center for proofreading the article (Certificate number: 03.03.2023/0035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PA and ACG conceptualization; PA, GG, and ACG methodology; ACG supervision; PA and ACG writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Arslan, P., Gül, G. & Günal, A.Ç. How Does the Persistent Organic Pollutant Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) Affect Health of the Common Carp?. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 634 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06651-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06651-8