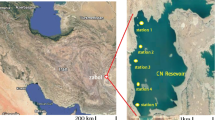
Abstract
The quality of water has a great impact on the life of aquatic species. The frequency of algal proliferation has increased all over the world due to changes in the water quality factors of the water systems. This study determined the correlation between Uroglena americana (U. americana) and water quality factors. U. americana mainly proliferated in late April at the surface level of the source water when the water temperature was in the range of 15.8–17.9 °C. Water temperature was negatively correlated with U. americana throughout the sampling period. In spring, the dissolved nitrogen (DN), dissolved organic carbon (DOC), fluorescence substance (peaks 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5), and electrical conductivity (EC) were positively correlated with the U. americana whereas the pH, dissolved oxygen (DO), oxidative reduction potential (ORP), turbidity, color, and dissolved phosphorus (DP) were negatively correlated. The total bacteria (16S rDNA) of source water showed a strong positive correlation (r = 0.66 at p = 0.05) with U. americana. The proliferation of U. americana also could be influenced by the associated microalgae species of source water. The Peridinium and Asterionella species were negatively correlated with U. americana, whereas the Euglena, Chlamydomonas, and Nitzchia species were positively correlated; among them, Euglena sp showed a significant positive correlation (r = 0.90, at p = 0.01) with U. americana. The obtained results of this study could be applied to the source water quality management and the optimization of the operating conditions of drinking water treatment plants to ensure the quality of drinking water.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
We confirm that the findings supporting data of this study exist within the manuscript and/or its supplementary information data sheet.
References
APHA/AWWA/WEF. (2017). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (23rd ed.). American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation.
Bordet, F., Fontanarrosa, M. S., & Farrell, I. O. (2017). Influence of light and mixing regime on bloom-forming phytoplankton in a subtropical reservoir. River Research and Application, 33, 1315–1326. https://doi.org/10.1002/rra.3189
Cai, O., Xiong, Y., Yang, H., Liu, J., Wang, H. (2020). Phosphorus transformation under the influence of aluminum, organic carbon, and dissolved oxygen at the water-sediment interface: a simulative study. Frontiers Environmental Science and Engineering, 14(50). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-020-1227-z
Cui, G., Li, F., Li, S., Bhat, S. A., Ishiguro, Y., Wei, Y., Yamada, T., Fu, X., & Huang, K. (2018). Changes of quinolone resistance genes and their relations with microbial profiles during vermicomposting of municipal excess sludge. Science of the Total Environment, 644, 494–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.015
Currie, D. J., & Kalff, J. (1984). A comparison of the abilities of fresh water algae and bacteria to acquire and retain phosphorus. Limnology and Oceanography, 29, 298–310. https://aslopubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.4319/lo.1984.29.2.0298.
Ellegaard, M., & Ribeiro, S. (2018). The long term persistence of phytoplankton resting stages in aquatic seed banks. Biological Review., 93, 166–183. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12338
Fuentes, J. L., Garbayo, I., Cuaresma, M., Montero, Z., Gonzalez-del-Valle, M., & Vilchez, C. (2016). Impact of microalgae-bacteria interactions on the production of algal biomass and associated compounds. Marine Drugs, 14, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14050100
García-González, M., Moreno, J., Manzano, C., Florencio, F. J., & Guerrero, M. G. (2005). Production of Dunaliella salina biomass rich in 9-cis β-carotene and lutein in a closed tubular photobioreactor. Journal of Biotechnology, 115(1), 81–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2004.07.010
Green, W. R., & Hufhines, B. (2017). A rare Uroglena bloom in Beaver Lake, Arkansas, spring 2015. Lake and Reservoir Management, 33, 8–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/10402381.2016.1238427
Guo, Q., Chen, X., Yang, K., Yu, J., Liang, F., Wang, C., Yang, B., Chen, T., Li, Z., Li, X., & Ding, C. (2023). Identification and evaluation of fishy odorants produced by four algae separated from drinking water source during low temperature period: Insight into odor characteristics and odor contribution of fishy odor-producing algae. Chemosphere, 324, 138328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.138328
Holen, D. A., & Boraas, M. E. (1995). Mixotrophy in chrysophytes. In C. D. Sandgren, J. P. Smol, & J. Kristiansen (Eds.), Chrysophyte algae. Ecology, phylogeny and development (pp. 119–140). Cambridge University Press.
Huang, X., Huang, B., Chen, J., & Liu, X. (2016). Cellular responses of the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum donghaiense Lu to phosphate limitation and chronological ageing. Journal of Plankton Research, 38(1), 83–93. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbv112
Huang, K., Xia, H., Cui, G., & Li, F. (2017). Effects of earthworms on nitrification and ammonia oxidizers in vermicomposting systems for recycling of fruit and vegetable wastes. Science of the Total Environment, 578, 337–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.172
Hudori, H., Rosadi, M. Y., Yamada, T., Bhat, S. A., & Li, F. (2021). Effect of the recycling process on drinking water treatment: evaluation based on fluorescence EEM analysis using the peak-picking technique and self-organizing map. Water, 13, 3456. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233456
Ishida, Y., Kimura, B., Kadota, H., & Nakahara, H. (1982). Analysis of major nutrient effecting Uroglena americana bloom in the Northern Lake Biwa, by use of algal bioassay. Bulletin of the Japanese Society of Scientific Fisheries, 48, 1281–1287.
Juneja, A., Ceballos, R. M., & Murthy, G. S. (2013). Effects of environmental factors and nutrient availability on the biochemical composition of algae for biofuels production: A review. Energies, 6, 4607–4638. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6094607
Kimura, B. (1989). Studies on chemical and biological factors influencing the growth of Uroglena americana, a red tide Chrysophyceae in lake Biwa. The Journal of Shiminoseki University of Fisheries, 38, 23–70. https://www.fish-u.ac.jp/kenkyu/sangakukou/kenkyuhoukoku/38/38-1-5.pdf.
Kimura, B., & Ishida, Y. (1986a). Effect of naturally collected bacteria on growth of Uroglena americana, a freshwater red tide Chrysophyceae. Bulletin of the Japanese Society of Scientific Fisheries, 52(4), 691–696. https://doi.org/10.2331/suisan.52.691
Kimura, B., & Ishida, Y. (1986b). Possible phagotrophic feeding of bacteria in a freshwater red tide Chrysophyceae, Uroglena americana. Bulletin of the Japanese Society of Scientific Fisheries, 52(4), 697–701. https://doi.org/10.2331/suisan.52.697
Kimura, B., & Ishida, Y. (1989). Phospholipid as a growth factor of Uroglena americana. A red tide Chrysophyceae in lake Biwa. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi, 55, 799–804. https://doi.org/10.2331/suisan.55.799
Kishida, N., Sagehashi, M., Takanashi, H., Fujimoto, N., & Akiba, M. (2015). Nationwide survey of organism-related off-flavor problems in Japanese drinking water treatment plants (2010–2012). Journal of Water Supply: Research and Technology-Aqua, 64(7), 832–838. https://doi.org/10.2166/aqua.2014.171
Konopka, A., & Brock, T. D. (1978). Effect of temperature on blue-green algae (cyanobacteria) in lake Mendota. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 36(4), 572–576. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.36.4.572-576.1978
Leach, T. H., Beisner, B. E., Carey, C. C., Pernica, P., Rose, K. C., Huot, Y., Brentrup, J. A., Domaizon, I., Grossart, H., Ibelings, B. W., Jacquet, S., Kelly, P. T., Rusak, J. A., Stockwell, J. D., Straile, D., & Verburg, P. (2018). Patterns and drivers of deep chlorophyll maxima structure in 100 lakes: The relative importance of light and thermal stratification. Limnology and Oceanography., 63, 628–646. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.10656
Lee, J., Rai, P. K., Jeon, Y. J., Kim, K. H., & Kwon, E. E. (2017). The role of algae and cyanobacteria in the production and release of odorants in water. Environmental Pollution, 227, 252–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.04.058
Leon, J. G., Beamud, S. G., Temporetti, P. F., Atencio, A. G., Diaz, M. M., & Pedrozo, F. L. (2016). Stratification and residence time as factors controlling the seasonal variation and the vertical distribution of chlorophyll-a in a subtropical irrigation reservoir. International Review of Hydrobiology, 101, 36–47. https://doi.org/10.1002/iroh.201501811
Li, F., Yuasa, A., Chiharada, H., & Matsui, Y. (2003). Storm impacts upon the composition of organic matrices in Nagara River - A study based on molecular weight and activated carbon adsorbability. Water Research, 37, 4027–4037. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00330-0
Li, Y., Cao, W., & Su, C. (2011). Nutrient sources and composition of recent algal blooms and eutrophication in the northern Jiulong River, Southeast China. Marine Pollution Bulletine, 63, 249–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.02.021
Li, X., Yu, J. W., Guo, Q. Y., Su, M., Liu, T., Yang, M., & Zhao, Y. (2016). Source water odor during winter in the Yellow River area of China: Occurrence and diagnosis. Environmental Pollution, 218, 252–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.06.069
Li, Y., Meng, J., Zhang, C., Ji, S., Kong, Q., Wang, R., & Liu, J. (2020). Bottom-up and top-down effects on phytoplankton communities in two freshwater lakes. PLoS One, 15, e0231357. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0231357
Liu, L., Yang, J., Lv, H., & Yu, Z. (2014). Synchronous dynamics and correlations between bacteria and phytoplankton in a subtropical drinking water reservoir. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 90, 126–138. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6941.12378
Lopez, C. B., Karim, A., Murasko, S., Marot, M., Smith, C. G., & Corcoran, A. A. (2019). Temperature mediates secondary dormancy in resting cysts of Pyrodinium bahamense (Dinophyceae). Journal of Phycology, 55, 924–935. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpy.12883
Moncelon, R., Goutaze, M., Pineau, P., Beneteau, E., Breret, M., Philippine, O., Robin, F. X., Dupuy, C., & Metzger, E. (2021). Coupling between sediment biogeochemistry and phytoplankton development in a temperate freshwater marsh (Charente-Maritime, France): evidence of temporal pattern. Water Research, 189, 116567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116567
Nichols, K. H., & Wujek, D. E. (2015). Chrysophyceae and phaeothamniophyceae. In J. D. Wehr, R. G. Sheath, & J. P. Kociolek (Eds.), Freshwater algae of North America (pp. 537–586). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-385876-4.00012-8
Nygaard, K., & Tobiesen, A. (1993). Bacterivory in algae: A survival strategy during nutrient limitation. Limnology and Oceanography, 38, 273–279. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1993.38.2.0273
Ou, L., Huang, X., Huang, B., Qi, Y., & Lu, S. (2015). Growth and competition for different forms of organic phosphorus by the dinoglagellate Prorocentrum donghaiense with the dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella and the diatom Skeletonema costatum s.l. Hydrobiologia, 754, 29–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-014-1994-2
Persson, P. E. (1983). Off-flavours in aquatic ecosystems – an introduction. Water Science & Technology, 15(6–7), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.1983.0125
Price, J. I., & Heberling, M. T. (2018). The effects of source water quality on drinking water treatment costs: A review and synthesis of empirical literature. Ecological Economics, 151, 195–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2018.04.014
Rao, K., Zhang, X., Yi, X. J., Li, Z. S., Huang, G. W., & Guo, X. X. (2018). Interactive effects of environmental factors on phytoplankton communities and benthic nutrient interactions in a shallow lake and adjoining rivers in China. Science of the Total Environment, 619–620, 1661–1672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.135
Renaud, S. M., Thinh, L. V., Lambridis, G., & Parry, D. L. (2002). Effect of temperature on growth, chemical composition and fatty acid composition of tropical Australian microalgae grown in batch cultures. Aquaculture, 211(1–4), 195–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(01)00875-4
Reynolds, C. S. (2006). The ecology of phytoplankton. Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511542145
Rodríguez-Vidal, F. J., García-Valverde, M., Ortega-Azabache, B., Gonzalez-Martinez, A., & Bellido-Fernandez, A. (2021). Using excitation-emission matrix fluorescence to evaluate the performance of water treatment plants for dissolved organic matter removal. Spectrochim Acta, Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 249, 119298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2020.119298
Rothhaupt, K. O., & Gude, H. (1992). The influence of spatial and temporal concentration gradients on phosphate partitioning between different size fractions of plankton: Further evidence and possible causes. Limnology and Oceanography, 37, 739–749. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1992.37.4.0739
Scofield, A. E., Watkins, J. M., Osantowski, E., & Rudstam, L. G. (2020). Deep chlorophyll maxima across a trophic state gradient : A case study in the Laureentian Great Lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 65, 2460–2484. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.11464
Severiano, J. D. S., Moura, A. N. D., Magalhaes, E. M. D. M., & Almeida, V. L. S. (2012). Study about top-down and bottom-up controls in regulating the phytoplankton biomass in a eutrophic reservoir in Northeastern Brazil. Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 4(8), 616–621. https://doi.org/10.4236/jwarp.2012.48071
Shinfuku, Y., Takanashi, H., Nakajima, T., Ogura, A., Kitamura, H., & Akiba, M. (2020). Exploration of an odorous aldehydes and ketones produced by Uroglena americana using high resolution mass spectrometry, GC-Olfactometry, and multivariate analysis. Chemosphere, 257, 127174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127174
Shinfuku, Y., Takanashi, H., Nakajima, T., Kasuga, I., & Akiba, M. (2022). The status quo of casual substance exploration for fishy odor in raw water for taps. Journal of Water and Environment Technology, 20(2), 29–44. https://doi.org/10.2965/jwet.21-135
Thingstad, T. F., Havskum, H., Garde, K., & Riemann, B. (1996). On the strategy of eating your competitor: A mathematical analysis of algal mixotrophy. Ecology, 77, 2108–2118. https://doi.org/10.2307/2265705
Triki, H. Z., Daly-Yahia, O. K., Malouche, D., Komiha, Y., Deidun, A., Brahim, M., & Laabir, M. (2014). Distribution of resting cysts of the potentially toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium pseudogonyaulax in recently deposited sediment within Bizerte Lagoon (Mediterranean coast, Tunisia). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 84, 172–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.05.014
Urabe, J., Gurung, T. B., & Yoshida, T. (1999). Effects of phosphorus supply on phagotrophy by the mixotrophic alga Uroglena americana (Chrysophyceae). Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 18, 77–83. https://doi.org/10.3354/ame018077
Wang, Z. H., Fu, Y. H., Kang, W., Liang, J. F., Gu, Y. G., & Jiang, X. L. (2013). Germination of phytoplankton resting cells from surface sediments in two areas of the southern Chinese coastal waters. Marine Ecology, 34, 218–232. https://doi.org/10.1111/maec.12009
Watson, S. B., Satchwill, T., Dixon, E., & Maccauley, E. (2001). Under-ice blooms and source-water odour in a nutrient -poor reservoir: Biological, ecological and applied perspectives. Freshwater Biology, 46, 1553–1567. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2427.2001.00769.x
Watson, S. B., Whitton, B. A., Higgins, S. N., Paerl, H. W., Brooks, B. W., & Wehr, J. D. (2015). Harmful algal blooms. In J. D. Wehr, R. G. Sheath, & J. P. Kociolek (Eds.), Freshwater algae of North America (2nd ed., pp. 873–920). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-385876-4.00020-7
Yoshida, Y., Matsumoto, T., & Kadota, H. (1983). Studies on a freshwater red tide in lake Biwa-II, relation between occurrence of red tide and environmental factors. Japanese Journal of Limnology, 44(1), 28–35.
Yoshida, Y., Miyahara, K., & Nakahara, H. (1995). Relationships between the dominant phytoplankton and DIN:DIP ratios in inland waters. Fisheries Science, 61, 396–400. https://doi.org/10.2331/fishsci.61.396
Zhang, Y., Li, M., Dong, J., Yang, H., Zwieten, L. V., Lu, H., Alshameri, A., Zhan, Z., Chen, X., Jiang, X., Xu, W., Bao, Y., & Wang, H. (2021). A critical review of methods for analyzing freshwater eutrophication. Water, 13, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020225
Zhao, Y. Y., Yu, J. W., Su, M., An, W., & Yang, M. (2013). A fishy odor episode in a north China reservoir: Occurrence, origin, and possible odor causing compounds. Journal of Environmental Science, 25(12), 2361–2366. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(12)60317-9
Zhong, Y., Su, Y., Zhang, D., She, C., Chen, N., Chen, J., Yang, H., & Balaji-Prasath, B. (2022). The spatiotemporal variations in microalgae communities in vertical waters of a subtropical reservoir. Journal of Environmental Management., 317, 115379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115379
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interest
We declare that the manuscript consists of original and unpublished work which is not under consideration for publication in whole or in part elsewhere. All authors have approved the manuscript for publication. No conflict of interest is present in the submission of this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• The water temperature negatively correlated with U. americana.
• Total bacteria (16S rDNA) showed a strong positive correlation (r = 0.66, p = 0.05) with U. americana.
• The Peridinium sp was the dominant algal species and negatively correlated with U. americana.
• The Euglena sp showed a significant positive (r = 0.90, p = 0.01) correlation with U. americana.
• Humic-like substances increased before the proliferation of U. americana, whereas protein-like substances increased after its proliferation.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sarkar, K., Yandi, R., Sagita, N.D. et al. Spatiotemporal Variation of Fishy Smell-Causing Algae (Uroglena americana) and Its Correlation with Water Quality Factors in the Source Water of Drinking Water Treatment Plant. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 507 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06490-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06490-7