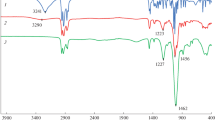
Abstract
Among the main contributors of water pollution are heavy metals. By being a component of the structure of enzymes, these metals, which are extremely harmful to both human health and the environment, exhibit toxic effects in living things. In this work, we aimed to prepare three phenolic-oxime derivatives (T1-oxime/T3-oxime) for liquid–liquid extraction of Cu(II) ions. The phenolic-oximes (T1-oxime/T3-oxime) were characterized by FT-IR, 1H-NMR and UV–Vis spectroscopy and the element percentages in their structures were determined by elemental analysis. Synthesized oxime compounds were subjected to liquid–liquid extraction of Cu(II) ion from the aqueous solution. The effect of pH, time and initial metal ion concentration on the extraction of Cu(II) ion was investigated. Within a short time (less than 30 min), all three oxime compounds showed 80% extraction of Cu(II) ion at pH = 4. The substitute groups at the meta position with respect to the oxime group affected the extraction of Cu(II) ion at pH = 1–2 range. The compounds were also found showed very quick extraction Cu(II) from aqueous solution to the organic phase (CHCl3) via coordination to the phenolic oxime compounds. Finally, the oxime compounds showed highly selective Cu(II) extraction in the presence of an interfering Pb(II), Ni(II) and Fe(II) ions.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Abdel Maksoud, M. I. A., Elgarahy, A. M., Farrell, C., Al-Muhtaseb, A. H., Rooney, D. W., & Osman, A. I. (2020). Insight on water remediation application using magnetic nanomaterials and biosorbents. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 403, 213096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2019.213096
Ahmed, M. J. K., & Ahmaruzzaman, M. (2016). A review on potential usage of industrial waste materials for binding heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 10, 39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2016.01.014
Bakalár, T., Búgel, M., & Gajdošová, L. (2009). Heavy metal removal using reverse osmosis. Acta Montanistica Slovaca, 14(3), 250–253.
Barnard, K. R., Nealon, G. L., Ogden, M. I., & Skelton, B. W. (2010). Crystallographic determination of three Ni-α-hydroxyoxime-carboxylic acid synergist complexes. Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 28(6), 778–792. https://doi.org/10.1080/07366299.2010.515169
Borba, C. E., Guirardello, R., Silva, E. A., Veit, M. T., & Tavares, C. R. G. (2006). Removal of nickel(II) ions from aqueous solution by biosorption in a fixed bed column: Experimental and theoretical breakthrough curves. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 30(2), 184–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2006.04.001
Cabir, B., Avar, B., Gulcan, M., Kayraldiz, A., & Kurtoglu, M. (2013). Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, and genotoxicity of a new group of azo-oxime metal chelates. Turkish Journal of Chemistry, 37(3), 422–438. https://doi.org/10.3906/kim-1210-57
Cheng, C. Y. (2006). Solvent extraction of nickel and cobalt with synergistic systems consisting of carboxylic acid and aliphatic hydroxyoxime. Hydrometallurgy, 84(1–2), 109–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2006.05.002
Chiarizia, R., & Danesi, P. R. (1981). Kinetic and thermodynamic separation of Cu(II) and Fe(III) by liquid-liquid extraction with a β-hydroxy-oxime in toluene. Separation Science and Technology, 16(9), 1181–1191. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496398108057606
Eren, T., Kose, M., Sayin, K., McKee, V., & Kurtoglu, M. (2014). A novel azo-aldehyde and its Ni (II) chelate; synthesis, characterization, crystal structure and computational studies of 2-hydroxy-5-{(E)-[4-(propan-2-yl)phenyl]diazenyl}benzaldehyde. Journal of Molecular Structure, 1065, 191–198.
Ferreira, C., Jensen, P., Ottosen, L., & Ribeiro, A. (2005). Removal of selected heavy metals from MSW fly ash by the electrodialytic process. Engineering Geology, 77(3–4), 339–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2004.07.024
García-Niño, W. R., & Pedraza-Chaverrí, J. (2014). Protective effect of curcumin against heavy metals-induced liver damage. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 69, 182–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2014.04.016
Karabörk, M., Ersöz, A., Denizli, A., & Say, R. (2008). Polymer−clay nanocomposite iron traps based on intersurface ion-imprinting. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 47(7), 2258–2264. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie070885o
Karabörk, M., Kırpık, H., Sayın, K., & Köse, M. (2019). New diazo-containing phenolic oximes: Structural characterization, computationalstudies, and solvent extraction of Cu(II), Ni(II), and Zn(II) ions. TURKISH JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY, 43(1), 197–212. https://doi.org/10.3906/kim-1807-139
Khoutoul, M., Djedouani, A., Lamsayah, M., Abrigach, F., & Touzani, R. (2016). Liquid-liquid extraction of metal ions, DFT and TD-DFT analysis for some pyrane derivatives with high selectivity for Fe(II) and Pb(II). Separation Science and Technology, 51(7), 1112–1123. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2015.1107583
Kose, R., Gungor, S. A., Erkan Kariper, S., Kose, M., & Kurtoglu, M. (2017). The new O, O and N, O type ligands and their Cu(II) and Ni(II) complexes: Crystal structure, absorption-emission properties and superoxide dismutase mimetic studies. Inorganica Chimica Acta, 462, 130–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2017.03.022
Krupa, M., Wieszczycka, K., Wojciechowska, A., & Olszanowski, A. (2015). Selective removal of cobalt from nickel sulphate solutions using oxime of 1-(2-pyridyl)tridecan-1-one. Separation Science and Technology, 50(5), 654–660. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2014.957312
Kukushkin, V. Y., Tudela, D., & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (1996). Metal-ion assisted reactions of oximes and reactivity of oxime-containing metal complexes. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 156, 333–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-8545(95)01234-6
Mason, K., Chang, J., Prescimone, A., Garlatti, E., Carretta, S., Tasker, P. A., & Brechin, E. K. (2012). Linking [MIII3] triangles with “double-headed” phenolic oximes. Dalton Transactions, 41(29), 8777. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2dt30189j
Milios, C. J., Stamatatos, T. C., & Perlepes, S. P. (2006). The coordination chemistry of pyridyl oximes. Polyhedron, 25(1), 134–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2005.07.022
Morizono, H., Oshima, T., & Baba, Y. (2011). Liquid–liquid extraction of transition metal ions with an alkylhistidine extractant. Separation and Purification Technology, 80(2), 390–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2011.05.026
Petrov, S., & Nenov, V. (2004). Removal and recovery of copper from wastewater by a complexation-ultrafiltration process. Desalination, 162, 201–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-9164(04)00043-8
Qasem, N. A. A., Mohammed, R. H., & Lawal, D. U. (2021). Author correction: Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: a comprehensive and critical review. npj Clean Water, 4(1), 52. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-021-00144-z
Qin, H., Hu, T., Zhai, Y., Lu, N., & Aliyeva, J. (2020). The improved methods of heavy metals removal by biosorbents: a review. Environmental Pollution, 258, 113777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113777
Shen, Y. F., Tang, J., Nie, Z. H., Wang, Y. D., Ren, Y., & Zuo, L. (2009). Preparation and application of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles for wastewater purification. Separation and Purification Technology, 68(3), 312–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2009.05.020
Shi, C., Jing, Y., Xiao, J., Wang, X., & Jia, Y. (2017). Liquid-liquid extraction of lithium using novel phosphonium ionic liquid as an extractant. Hydrometallurgy, 169, 314–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2017.02.015
Silva, J. E., Paiva, A. P., Soares, D., Labrincha, A., & Castro, F. (2005). Solvent extraction applied to the recovery of heavy metals from galvanic sludge. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 120(1–3), 113–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.12.008
Smith, A. (2003). The structures of phenolic oximes and their complexes. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 241(1–2), 61–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-8545(02)00310-7
Taseidifar, M., Makavipour, F., Pashley, R. M., & Rahman, A. F. M. M. (2017). Removal of heavy metal ions from water using ion flotation. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 8, 182–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2017.07.002
Tasker, P. A., Tong, C. C., & Westra, A. N. (2007). Co-extraction of cations and anions in base metal recovery. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 251(13–14), 1868–1877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2007.03.014
Upadhyay, J. B., & Parekh, H. M. (2020). Resorcin [4] arene Schiff base derivatives: Synthesis, characterization, and extraction studies. Journal of Chemical Research, 44(11–12), 660–666. https://doi.org/10.1177/17475198209158
Wei, G.-T., Yang, Z., & Chen, C.-J. (2003). Room temperature ionic liquid as a novel medium for liquid/liquid extraction of metal ions. Analytica Chimica Acta, 488(2), 183–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(03)00660-3
Werlinger, F., & Rojas, R. S. (2020). Evaluation of novel imino-phenol ligands in divalent metal ion extraction/recovery processes from leaching solutions. Separation and Purification Technology, 252, 117451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117451
Wilson, A. M., Bailey, P. J., Tasker, P. A., Turkington, J. R., Grant, R. A., & Love, J. B. (2014). Solvent extraction: The coordination chemistry behind extractive metallurgy. Chemical Society Reviews, 43(1), 123–134. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CS60275C
Zamora-Ledezma, C., Negrete-Bolagay, D., Figueroa, F., Zamora-Ledezma, E., Ni, M., Alexis, F., & Guerrero, V. H. (2021). Heavy metal water pollution: a fresh look about hazards, novel and conventional remediation methods. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 22, 101504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101504
Zou, Y., Wang, X., Khan, A., Wang, P., Liu, Y., Alsaedi, A., et al. (2016). Environmental remediation and application of nanoscale zero-valent iron and its composites for the removal of heavy metal ions: A review. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(14), 7290–7304. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b01897
Funding
The authors thank Kahramanmaras Sutcu Imam University for financial support (Project Number: 2018/2-10YLS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Karabörk, M., Kırveli, E., Kırpık, H. et al. Competitive Liquid–Liquid Extraction of Cu(II) Ion from Aqueous Using New Diazo-Compounds. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 130 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06092-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06092-3