Abstract
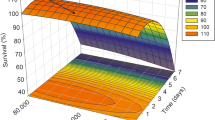
This work has investigated the effects of 17β-estradiol on the Enterobacteriaceae growth profile and whether they were antibiotic resistant. The experiments were performed in vitro with sixteen Enterobacteriaceae species exposed to 1, 10, and 100 ηg L−1 of E2, and antimicrobial resistance was evaluated for the five antibiotic classes. According to the antimicrobial profile, 12.5, 18.7, 18.7, and 50% of the Enterobacteriaceae strains were resistant to four, one, two, and three antibiotics, respectively. The bacteria response to the E2 was species-specific, where some strains grew up 99.99%, if compared to the negative control. Other bacteria had the growth inhibited, and others had not affected the growth profile by the hormone. These differences might be related to various mechanisms of each bacteria cell and its metabolism. Therefore, the impact of 17β-estradiol in the environment on pathogenic bacteria is of particular concern due to the increased human population and animal protein consumption, potentially resulting in a load of hormones and pathogens in the environment, becoming an invisible threat.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adeel, M., Song, X., Wang, Y., Francis, D., & Yang, Y. (2017). Environmental impact of estrogens on human, animal and plant life: A critical review. Environment International, 99, 107–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.12.010
An, J., Choi, K., Yang, S., & Nam, K. (2018). Estimation of human-origin estrone and 17β-estradiol concentrations in the Han River, Seoul, South Korea and its uncertainty-based ecological risk characterization. Science of the Total Environment, 633, 1148–1155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.248
Antunes, L. C. M., Arena, E. T., Menendez, A., Han, J., Ferreira, R. B. R., Buckner, M. M. C., et al. (2011). Impact of Salmonella infection on host hormone metabolism revealed by metabolomics. Infection and Immunity, 79(4), 1759–1769. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.01373-10
Armand-Lefèvre, L., Andremont, A., & Ruppé, E. (2018). Travel and acquisition of multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Médecine Et Maladies Infectieuses, 48(7), 431–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medmal.2018.02.005
Benson, R., Conerly, O. D., Sander, W., Batt, A. L., Boone, J. S., Furlong, E. T., et al. (2017). Human health screening and public health significance of contaminants of emerging concern detected in public water supplies. Science of the Total Environment, 579, 1643–1648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.03.146
Burkholder, J., Libra, B., Weyer, P., Heathcote, S., Kolpin, D., Thorne, P. S., & Wichman, M. (2007). Impacts of waste from concentrated animal feeding operations on water quality. Environmental Health Perspectives, 115(2), 308–312. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.8839
Caldwell, D. J., Mastrocco, F., Anderson, P. D., Länge, R., & Sumpter, J. P. (2012). Predicted-no-effect concentrations for the steroid estrogens estrone, 17β-estradiol, estriol, and 17α-ethinylestradiol. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 31(6), 1396–1406. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.1825
Church, N. A., & McKillip, J. L. (2021). Antibiotic resistance crisis: Challenges and imperatives. Biologia, 76(5), 1535–1550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-021-00697-x
Clark, D. T., & Soory, M. (2006). The metabolism of cholesterol and certain hormonal steroids by Treponema denticola. Steroids, 71(5), 352–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2005.11.006
Clark, D. T., & Soory, M. (2006). The influence of cholesterol, progesterone, 4-androstenedione and testosterone on the growth of Treponema denticola ATCC 33520 in batch cultures. Anaerobe, 12(5–6), 267–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anaerobe.2006.08.002
Clarke, R. M., & Cummins, E. (2015). Evaluation of “classic” and emerging contaminants resulting from the application of biosolids to agricultural lands: A review. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 21(2), 492–513. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2014.930295
Costa, M. E., & Machado, H. S. (2017). Evolution of antimicrobial resistance in Europe: A factual review. Journal of Allergy & Therapy, 8(250), 2. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6121.1000250
Dai, X., Qiu, L., Zhao, B., Gao, Y., Mu, Y., Chu, Z., et al. (2020). Melatonin ameliorates the fertilization capacity of oocytes exposed to 17α-ethynylestradiol. Reproductive Toxicology, 93, 61–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2020.01.004
Elkins, C. A., & Mullis, L. B. (2006). Mammalian steroid hormones are substrates for the major RND- and MFS-type tripartite multidrug efflux pumps of Escherichia coli. Journal of Bacteriology, 188(3), 1191–1195. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.188.3.1191-1195.2006
EUCAST - The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. (2020). Clinical breakpoints - breakpoints and guidance. https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Breakpoint_tables/v_10.0_Breakpoint_Tables.pdf. Accessed 15 Jan 2022.
Fahrbach, M., Kuever, J., Remesch, M., Huber, B. E., Kampfer, P., Dott, W., & Hollender, J. (2008). Steroidobacter denitrificans gen nov., sp. nov., a steroidal hormone-degrading gammaproteobacterium. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 58(9), 2215–2223. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.65342-0
Fonseca, T. G., Motta, E. A., Mass, A. P., Fongaro, G., Ramos, F. M., Machado, M. S., et al. (2021). Toxicity and Enterobacteriaceae profile in water in different hydrological events: A case from South Brazil. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 232(7), 278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05208-x
Fujitani, T., Fujii, Y., Lyu, Z., Harada Sassa, M., & Harada, K. H. (2021). Urinary equol levels are positively associated with urinary estradiol excretion in women. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 19532. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-98872-2
García-Gómez, E., González-Pedrajo, B., & Camacho-Arroyo, I. (2013). Role of sex steroid hormones in bacterial-host interactions. BioMed Research International, 2013, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/928290
Glass, T. L., Saxerud, M. H., & Casper, H. H. (1991). Properties of a 4-ene-3-ketosteroid-5α-reductase in cell extracts of the intestinal anaerobe, Eubacterium sp. strain 144. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 39(3), 367–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/0960-0760(91)90048-A
Göhler, A., Xiong, G., Paulsen, S., Trentmann, G., & Maser, E. (2008). Testosterone-inducible regulator is a kinase that drives steroid sensing and metabolism in Comamonas testosteroni. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 283(25), 17380–17390. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M710166200
Hudzicki, J. (2009). Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion susceptibility test protocol. American Society for Microbiology. https://www.asm.org/Protocols/Kirby-Bauer-Disk-Diffusion-Susceptibility-Test-Pro. Accessed 28 November 2022
Jeong, I. S., & Song, J. Y. (2022). Epidemiological characteristics of carbapenemase producing carbapenem-resISTANT Enterobacteriaceae colonization. Asian Nursing Research, 16(3), 134–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anr.2022.05.002
Jürgens, M. D., Holthaus, K. I. E., Johnson, A. C., Smith, J. J. L., Hetheridge, M., & Williams, R. J. (2002). The potential for estradiol and ethinylestradiol degradation in English rivers. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 21(3), 480–488. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620210302
Kidd, K. A., Blanchfield, P. J., Mills, K. H., Palace, V. P., Evans, R. E., Lazorchak, J. M., & Flick, R. W. (2007). Collapse of a fish population after exposure to a synthetic estrogen. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104(21), 8897–8901. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0609568104
Kisiela, M., Skarka, A., Ebert, B., & Maser, E. (2012). Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (HSDs) in bacteria – a bioinformatic perspective. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 129(1–2), 31–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2011.08.002
Kita, E., Takahashi, S., Yasui, K., & Kashiba, S. (1985). Effect of estrogen (17 beta-estradiol) on the susceptibility of mice to disseminated gonococcal infection. Infection and Immunity, 49(1), 238–243. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.49.1.238-243.1985
Kita, E., Yagyu, Y., Nishikawa, F., Hamuro, A., Oku, D., Emoto, M., et al. (1989). Alterations of host resistance to mouse typhoid infection by sex hormones. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 46(6), 538–546. https://doi.org/10.1002/jlb.46.6.538
Klein, S. L. (2000). The effects of hormones on sex differences in infection: From genes to behavior. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 24(6), 627–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0149-7634(00)00027-0
Kornman, K. S., & Loesche, W. J. (1982). Effects of estradiol and progesterone on Bacteroides melaninogenicus and Bacteroides gingivalis. Infection and Immunity, 35(1), 256–263. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.35.1.256-263.1982
Lennette, E. H., Balows, A., Hausler Jr, W. J., & Truant, J. P. (1980). Manual of clinical. Microbiology. Washington, DC: American Society for Microbiology, pp. 195–219.
Li, X., Liu, X., Jia, Z., Wang, T., & Zhang, H. (2021). Screening of estrogenic endocrine-disrupting chemicals in meat products based on the detection of vitellogenin by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Chemosphere, 263, 128251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128251
Lv, Y.-Z., Yao, L., Wang, L., Liu, W.-R., Zhao, J.-L., He, L.-Y., & Ying, G.-G. (2019). Bioaccumulation, metabolism, and risk assessment of phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals in specific tissues of wild fish. Chemosphere, 226, 607–615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.03.187
Marlatt, V. L., Bayen, S., Castaneda-Cortès, D., Delbès, G., Grigorova, P., Langlois, V. S., et al. (2022). Impacts of endocrine disrupting chemicals on reproduction in wildlife and humans. Environmental Research, 208, 112584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112584
Nakamura-Silva, R., Dias, L. L., Sousa, R. C., Fujimoto, R. Y., & Pitondo-Silva, A. (2022). Multidrug-resistant and potentially pathogenic Enterobacteriaceae found in a tertiary hospital sewage in southeastern Brazil. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 194(10), 782. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10454-5
Nie, M., Yan, C., Dong, W., Liu, M., Zhou, J., & Yang, Y. (2015). Occurrence, distribution and risk assessment of estrogens in surface water, suspended particulate matter, and sediments of the Yangtze Estuary. Chemosphere, 127, 109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.01.021
Ojanotko-Harri, A., Nikkari, T., Harrl, M.-P., & Paunio, K. (1990). Metabolism of progesterone and testosterone by Bacillus cereus strain Socransky 67 and Streptococcus mutans strain Ingbritt. Oral Microbiology and Immunology, 5(4), 237–239. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-302X.1990.tb00653.x
Payus, C., Payus, A. O., & Yan, M. P. (2021). Steroid hormones assay on estrogen and progesterone group occurrences fate and pathway distributions in river and coastal environment. Journal of Sustainability Science and Management, 16(3), 103–115. https://doi.org/10.46754/jssm.2021.04.009
Pung, O. J., Tucker, A. N., Vore, S. J., & Luster, M. I. (1985). Influence of estrogen on host resistance: Increased susceptibility of mice to Listeria monocytogenes correlates with depressed production of interleukin 2. Infection and Immunity, 50(1), 91–96. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.50.1.91-96.1985
Pung, O. J., & Luster, M. I. (1986). Toxoplasma gondii: Decreased resistance to infection in mice due to estrogen. Experimental Parasitology, 61(1), 48–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-4894(86)90134-7
Sang, Y., Xiong, G., & Maser, E. (2011). Steroid degradation and two steroid-inducible enzymes in the marine bacterium H5. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 191(1–3), 89–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2011.01.027
Shine, W. E., Robert, S., & McCulley, J. P. (1993). Relation of cholesterol-stimulated Staphylococcus aureus growth to chronic blepharitis. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science, 34(7), 2291–3229.
Soory, M. (1995). Bacterial steroidogenesis by periodontal pathogens and the effect of bacterial enzymes on steroid conversions by human gingival fibroblasts in culture. Journal of Periodontal Research, 30(2), 124–131. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0765.1995.tb01261.x
Varsha, M., Senthil Kumar, P., & Senthil Rathi, B. (2022). A review on recent trends in the removal of emerging contaminants from aquatic environment using low-cost adsorbents. Chemosphere, 287, 132270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132270
Viancelli, A., Michelon, W., Rogovski, P., Cadamuro, R. D., de Souza, E. B., Fongaro, G., et al. (2020). A review on alternative bioprocesses for removal of emerging contaminants. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 43(12), 2117–2129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-020-02410-9
vom Steeg, L. G., & Klein, S. L. (2017). Sex steroids mediate bidirectional interactions between hosts and microbes. Hormones and Behavior, 88, 45–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2016.10.016
Wasko, C., Westra, S., Nathan, R., Orr, H. G., Villarini, G., Villalobos Herrera, R., & Fowler, H. J. (2021). Incorporating climate change in flood estimation guidance. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society a: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 379(2195), 20190548. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2019.0548
Watanabe, M., Phillips, K., & Chen, T. (1973). Steroid-receptor in pseudomonas testosteroni released by osmotic shock. Journal of Steroid Biochemistry, 4(6), 613–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-4731(73)90036-8
Webber, M. A. (2003). The importance of efflux pumps in bacterial antibiotic resistance. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 51(1), 9–11. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkg050
Williams, R. J., Keller, V. D. J., Johnson, A. C., Young, A. R., Holmes, M. G. R., Wells, C., et al. (2009). A national risk assessment for intersex in fish arising from steroid estrogens. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 28(1), 220. https://doi.org/10.1897/08-047.1
Willyard, C. (2017). The drug-resistant bacteria that pose the greatest health threats. Nature, 543(7643), 15–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature.2017.21550
Wise, A., O’Brien, K., & Woodruff, T. (2011). Are oral contraceptives a significant contributor to the estrogenicity of drinking water? Environmental Science & Technology, 45(1), 51–60. https://doi.org/10.1021/es1014482
Xiong, G., & Maser, E. (2001). Regulation of the steroid-inducible 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/carbonyl reductase gene in Comamonas testosteroni. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276(13), 9961–9970. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M010962200
Ying, G.-G., Kookana, R. S., & Ru, Y.-J. (2002). Occurrence and fate of hormone steroids in the environment. Environment International, 28(6), 545–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(02)00075-2
Zhang, C., Li, Y., Wang, C., Niu, L., & Cai, W. (2016). Occurrence of endocrine disrupting compounds in aqueous environment and their bacterial degradation: A review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 46(1), 1–59. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2015.1061881
Zhang, H., Wang, L., Li, Y., Wang, P., & Wang, C. (2019). Background nutrients and bacterial community evolution determine 13C–17β-estradiol mineralization in lake sediment microcosms. Science of the Total Environment, 651, 2304–2311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.098
Zhao, X., Wang, Y., Xu, X., Tian, K., Zhou, D., Meng, F., et al. (2020). Genomics analysis of the steroid estrogen-degrading bacterium Serratia nematodiphila DH-S01. Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment, 34(1), 430–440. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2020.1764388
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support provided by FAPESC CP 48/2021and Governo do Estado de Santa Catarina.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.A. and W.M — conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, writing — original draft, writing — review and editing; P.R.J., D.M.A., and P.R.S.M — methodology, formal analysis; M.P.S. and N.D — writing — review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Viancelli, A., Avalos, D.M., Reis, P. et al. The Impact of 17β-estradiol (E2) on the Growth Profile of Environmental Enterobacteriaceae. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 20 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-06036-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-06036-3