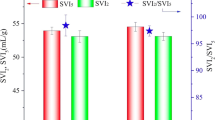
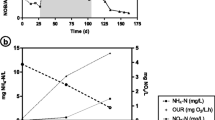
Abstract
Aeration strategy is an important factor for the formation and maintenance of aerobic granular sludge (AGS), but aeration is also the most energy-consuming part in the biological wastewater treatment system. In order to optimize the aeration strategy of AGS reactor at low temperature, short- and long-term effects of dissolved oxygen (DO) concentration and aeration intensity (AI) were investigated at 10 ℃ in this study. The results showed that the carbon and phosphorus removal performance of AGS exhibited high resistance to the short-term changes of DO and AI, while the nitrogen removal was greatly influenced. The optimum DO and AI were 4 mg/L and 0.25 cm/s, corresponding to 82.7% and 81.4% of total inorganic nitrogen removal efficiencies, respectively. Long-term operation experiment showed that the properties of AGS kept stable under 4 mg/L DO concentration, but the overgrowth of filamentous bacteria and reduction of extracellular polymeric substance under 0.25 cm/s AI led to a large amount of granule disintegration, which could not be recovered with the prolonged operation. These findings might provide guidance for the operation optimization of AGS system at low temperature.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. In, American Public Health Association, Washington, DC, New York.
Barr, J. J., Cook, A. E., & Bond, P. L. (2010). Granule formation mechanisms within an aerobic wastewater system for phosphorus removal. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 76(22), 7588–7597.
Beun, J. J., Loosdrecht, M. C. M., & v. and Heijnen J. J. (2000). Aerobic granulation. Water Science and Technology, 41, 41–48.
Burdon, J. (2001). Are the traditional concepts of the structures of humic substances realistic? Soil Science, 166, 752–769.
Campo, R., Corsino, S. F., Torregrossa, M., & Di Bella, G. (2018). The role of extracellular polymeric substances on aerobic granulation with stepwise increase of salinity. Separation and Purification Technology, 195, 12–20.
Carvalheira, M., Oehmen, A., Carvalho, G., Eusébio, M., & Reis, M. A. M. (2014). The impact of aeration on the competition between polyphosphate accumulating organisms and glycogen accumulating organisms. Water Research, 66, 296–307.
Castellanos, R. M., Dias, J. M. R., Dias, B. I., Dezotti, M., & Bassin, J. P. (2021). Effect of sludge age on aerobic granular sludge: Addressing nutrient removal performance and biomass stability. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 149, 212–222.
Chen, Y., Lan, S., Wang, L., Dong, S., Zhou, H., Tan, Z., & Li, X. (2017). A review: Driving factors and regulation strategies of microbial community structure and dynamics in wastewater treatment systems. Chemosphere, 174, 173–182.
Chiu, Z. C., Chen, M. Y., Lee, D. J., Wang, C. H., & Lai, J. Y. (2007). Oxygen diffusion and consumption in active aerobic granules of heterogeneous structure. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 75(3), 685–691.
de Sousa, R. S. L., Mendes, B. A., & R., Milen Firmino P. I. and Bezerra Dos Santos A. (2018). Aerobic granular sludge: Cultivation parameters and removal mechanisms. Bioresour Technol, 270, 678–688.
Frølund, B., Palmgren, R., Keiding, K., & Nielsen, P. H. (1996). Extraction of extracellular polymers from activated sludge using a cation exchange resin. Water Research, 30, 1749–1758.
Franca, R. D. G., Pinheiro, H. M., van Loosdrecht, M. C. M., & Lourenco, N. D. (2018). Stability of aerobic granules during long-term bioreactor operation. Biotechnology Advances, 36(1), 228–246.
Gao, D. W., Liu, L., & Liang, H. (2013). Influence of aeration intensity on mature aerobic granules in sequencing batch reactor. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 97(9), 4213–4219.
Garcia-Ochoa, F., & Gomez, E. (2009). Bioreactor scale-up and oxygen transfer rate in microbial processes: An overview. Biotechnology Advances, 27(2), 153–176.
Gerhardt, P., Murray, R. G. E., Wood, W. A., & Krieg, N. R. (1994). Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology.
Guimarães, L. B., Mezzari, M. P., Daudt, G. C., & da Costa, R. H. R. (2017). Microbial pathways of nitrogen removal in aerobic granular sludge treating domestic wastewater. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 92(7), 1756–1765.
He, J., & Xu, J. (2018). The characteristics of heat-driven ammonium adsorption in aerobic granular sludge. Water Science and Technology, 78(7), 1466–1475.
He, Q., Chen, L., Zhang, S., Chen, R., & Wang, H. (2019). Hydrodynamic shear force shaped the microbial community and function in the aerobic granular sequencing batch reactors for low carbon to nitrogen (C/N) municipal wastewater treatment. Bioresource Technology, 271, 48–58.
He, Q., Chen, L., Zhang, S., Wang, L., Liang, J., Xia, W., Wang, H., & Zhou, J. (2018). Simultaneous nitrification, denitrification and phosphorus removal in aerobic granular sequencing batch reactors with high aeration intensity: Impact of aeration time. Bioresource Technology, 263, 214–222.
Lee, H., & Yun, Z. (2014). Comparison of biochemical characteristics between PAO and DPAO sludges. Journal of Environmental Sciences (china), 26(6), 1340–1347.
Li, X. Y., & Yang, S. F. (2007). Influence of loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on the flocculation, sedimentation and dewaterability of activated sludge. Water Research, 41(5), 1022–1030.
Liu, Y., & Liu, Q. S. (2006). Causes and control of filamentous growth in aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactors. Biotechnology Advances, 24(1), 115–127.
Mosquera-Corral, A., de Kreuk, M. K., Heijnen, J. J., & van Loosdrecht, M. C. (2005). Effects of oxygen concentration on N-removal in an aerobic granular sludge reactor. Water Research, 39(12), 2676–2686.
Muhammad, K. S. K. (2015). Studies on the interactions of Ca2+ and Mg2+ with EPS and their role in determining the physicochemical characteristics of granular sludges in SBR system. Process Biochem, 50, 966–972.
Nguyen, Quoc B., Wei, S., Armenta, M., Bucher, R., Sukapanpotharam, P., Stahl, D. A., Stensel, H. D., & Winkler, M.-K.H. (2021). Aerobic granular sludge: Impact of size distribution on nitrification capacity. Water Res, 188, 116445.
Ni, L., Li, D., Rong, S., Su, L., Zhou, W., Wang, P., Wang, C., Li, S., & Acharya, K. (2017). Characterization of extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) fractions produced by Microcystis aeruginosa under the stress of linoleic acid sustained-release microspheres. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(26), 21091–21102.
Pronk, M., de Kreuk, M. K., de Bruin, B., Kamminga, P., Kleerebezem, R., & van Loosdrecht, M. C. (2015). Full scale performance of the aerobic granular sludge process for sewage treatment. Water Research, 84, 207–217.
Sadri Moghaddam, S., & AlaviMoghaddam, M. R. (2016). Aerobic granular sludge for dye biodegradation in a sequencing batch reactor with anaerobic/aerobic cycles. CLEAN - Soil, Air, Water, 44(4), 438–43.
Wang, J., Yang, H., Liu, X., Wang, J., & Chang, J. (2020). The impact of temperature and dissolved oxygen (DO) on the partial nitrification of immobilized fillers, and application in municipal wastewater. RSC Advances, 10, 37194–37201.
Wei, D., Li, M., Wang, X., Han, F., Li, L., Guo, J., Ai, L., Fang, L., Liu, L., Du, B., & Wei, Q. (2016). Extracellular polymeric substances for Zn (II) binding during its sorption process onto aerobic granular sludge. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 301, 407–415.
Winkler, M. K. H., Bassin, J. P., Kleerebezem, R., van der Lans, R. G. J. M., & van Loosdrecht, M. C. M. (2012). Temperature and salt effects on settling velocity in granular sludge technology. Water Research, 46(16), 5445–5451.
Xu, J., He, J., Wang, M., & Li, L. (2018). Cultivation and stable operation of aerobic granular sludge at low temperature by sieving out the batt-like sludge. Chemosphere, 211, 1219–1227.
Yang, S., & Yang, F. (2011). Nitrogen removal via short-cut simultaneous nitrification and denitrification in an intermittently aerated moving bed membrane bioreactor. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 195, 318–323.
Yuan, X., & Gao, D. (2010). Effect of dissolved oxygen on nitrogen removal and process control in aerobic granular sludge reactor. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 178(1–3), 1041–1045.
Zhu, L., Zhou, J., Yu, H., & Xu, X. (2015). Optimization of hydraulic shear parameters and reactor configuration in the aerobic granular sludge process. Environmental Technology, 36(13–16), 1605–1611.
Zitomer, D. H., Duran, M., Albert, R., & Guven, E. (2007). Thermophilic aerobic granular biomass for enhanced settleability. Water Research, 41(4), 819–825.
Funding
This research was supported financially by the Key Research and Development Program of Shandong Province (No. 2020CXGC011202) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2021QE274).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Ju, H., He, J. et al. The Performance of Aerobic Granular Sludge Under Different Aeration Strategies at Low Temperature. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 43 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05506-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05506-y