Abstract
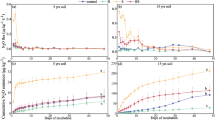
Leaching of phosphorus fertilizer from loose-structured subtropical soils is a major course of agricultural water pollution in southeastern USA. Soil amendments play a major role in the phosphorus retention in soil through different mechanisms. In the present study we tested the effect of two soil amendments; biochar and coal fly ash in immobilizing the soluble phosphorus fertilizer added to sandy Ultisol soils from subtropical USA. Column leaching tests were conducted with Ultisol soil added with biochar (from avocado branch cut biomass) and coal fly ash at 5 tons/ha rate, under simulated rainfall, to collect the leachate over five pore volumes. The leachate was analyzed for the phosphate phosphorus content. In the end, the soil columns were carefully extracted, sectioned and analyzed for the total phosphorus, after acid digestion. Results showed 50% and 6% drop of soluble phosphorus leaching loss in biochar and coal fly ash added soil respectively. Soil amendments have shifted the loosely bound phosphorus into the Ca/Mg bound and Al/Fe/Mn bound pools which are not readily water extractable. Addition of biochar and coal fly ash together showed a synergistic interaction effect in reducing the leaching loss of phosphorus which needs further investigation to understand the exact mechanism.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson, C. J., Fitzgerald, J. D., & Hipps, N. A. (2010). Potential mechanisms for achieving agricultural benefits from biochar application to temperate soils: a review. Plant and Soil, 337(1–2), 1–18.
Boman, B.J., Wilson, C.P. and Hebb, J. 2000. Water quality/quantity best management practices (BMPs) for Indian river area citrus groves. Florida Department of Agricultural and Consumer Services, Tallahassee.
Bouyoucos, G. J. (1936). Directions for making mechanical analysis of soils by the hydrometer method. Soil Science., 42(3), 225–230.
Callery, O., Brennan, R. B., & Healy, M. G. (2015). Use of amendments in a peat soil to reduce phosphorus losses from forestry operations. Ecological Engineering., 85, 193–200.
Chamberlain, R., & Hayward, D. (1996). Evaluation of water quality and monitoring in the St. Lucie Estuary. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 32, 681–696.
Chen, G. C., He, Z. L., Stoffella, P. J., Yang, X. E., Yu, S., & Calvert, D. (2006). Use of dolomite phosphate rock (DPR) fertilizers to reduce phosphorus leaching from sandy soil. Environmental Pollution., 139, 176–182.
Chintala, R., Schumacher, T. T., McDonald, L. M., Clay, D. E., Malo, D. D., Papiernik, S. K., Clay, S. A., & Julson, J. L. (2014). Phosphorus sorption and availability from biochars and soil/biochar mixtures. Clean Soil, Air, Water., 42(5), 626–634.
Elliott, H. A., O’Connor, G. A., & Brinton, S. (2002). Phosphorus leaching from biosolids-amended sandy soils. Journal of Environmental Quality., 31, 681–689.
Glaser, B., & Lehr, V. I. (2019). Biochar effects on P availability in agricultural soils: a meta-analysis. Science Reports, 9, 9338. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-45693-z.
Kim, H. Y., Lim, S. S., Kwak, J. H., Lee, S., Lee, D. S., Hao, X., Yoon, K. S., & Choi, W. J. (2011). Soil and compost type affect phosphorus leaching from inceptisol, ultisol, and andisol in a column experiment. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis., 42(18), 2188–2199.
Komatsuzaki, M., & Ohta, H. (2007). Soil management practices for sustainable agro-ecosystems. Sustainability Science., 2, 103–120.
Liang, B., Lehmann, J., Solomon, D., Kinyangi, J., Grossman, J., O’Neill, B., Skjemstad, J. O., Thies, J., Luizao, F. J., Petersen, J., & Neves, E. G. (2006). Black carbon increases cation exchange capacity in soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal., 70, 1719–1730.
Makoto, K., Shibata, H., Kim, Y. S., Satomura, T., Takagi, K., Nomura, M., Satoh, F., & Koike, T. (2012). Contribution of charcoal to short-term nutrient dynamics after surface fire in the humus layer of a dwarf bamboo-dominated forest. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-011-0657-y.
O’connor, G. A., Brinton, S., & Silveria, M. L. (2005). Evaluation and selection of soil amendments for field testing to reduce P losses. Soil Science, 57, 96–102.
Ouyang, L., Wang, F., Tang, J., Yu, L., & Zhang, R. (2013). Effects of biochar amendment on soil aggregates and hydraulic properties. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition., 13(4), 991–1002.
Parfitt, R. L. (1979). Anion adsorption by soils and soil materials. Advances in Agronomy., 30, 1–50.
Pathan, S. 2003. Fly ash amendment of sandy soils to improve water and nutrient use in Turf. PhD thesis. Agriculture and Plant Sciences: University of Western Australia.
Rashmi, I., Biswas, A. K., Shinogi, K. C., & Kala, S. (2017). Phosphorus movement and vertical distribution in four soil orders of India: column leaching experiment. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences., 6(4), 1919–1930.
Rennesona, M., Vardenberghe, C., Dufey, J., Marcoen, J. M., Bocka, L., & Colnet, G. (2015). Degree of phosphorus saturation in agricultural loamy soils with a near-neutral pH. European Journal of Soil Science., 66, 33–41.
Sharpley, A. N., & Rekolainen, S. (1997). Phosphorus in agriculture and its environmental implications. In H. Tunney, O. T. Carton, P. C. Brookes, & A. E. Johnston (Eds.), Phosphorus loss from soil to water (pp. 1–54). Wallingford: CABI Publ..
Sharpley, A. N., Smith, S. J., Jones, O. R., Berg, W. A., & Coleman, G. A. (1992). The transport of bioavailable phosphorus in agricultural runoff. Journal of Environmental Quality., 21, 30–35.
Simard, R. R. (2000). Potential for preferential pathways of phosphorus transport. Journal of Environmental Quality., 29, 97–105.
Tryon, E. H. (1948). Effect of charcoal on certain physical. Chemical, and Biological Properties of Forest Soils., 18(1, 81–115.
Xu, J., Yao, W., & Jiang, Z. W. (2014). Non-ureolytic bacterial carbonate precipitation as a surface treatment strategy on cementitious materials. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering., 26, 983–991. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0000906.
Yang, J., He, Z., Yang, Y., Stoffella, P., Yang, X., Banks, D., & Mishra, S. (2007). Use of amendments to reduce leaching loss of phosphorus and other nutrients from a sandy soil in Florida. Environmental Science and Pollution Research., 14(4), 266–269.
Yao, Y., Gao, B., Zhang, M., Inyang, M., & Zimmerman, A. R. (2012). Effect of biochar amendment on sorption and leaching of nitrate, ammonium, and phosphate in a sandy soil. Chemosphere., 89(2012), 1467–1471.
Zhang, M. K. (2008). Effects of soil properties on phosphorus subsurface migration in sandy soils. Pedosphere., 18(5), 599–610.
Zhang, X., Wang, H., He, L., Lu, K., Sarmah, A., Li, J., Bolan, N. S., Pei, J., & Huang, H. (2013). Using biochar for remediation of soils contaminated with heavy metals and organic pollutants. Environmental Science and Pollution Research., 20(12), 8472–8483.
Zhao, M., Chen, X., Shi, Y., Zhou, Q., & Lu, C. (2009). Phosphorus vertical migration in aquic brown soil and light chernozem under different phosphorous application rate: a soil column leaching experiment. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology., 82(1), 85–89.
Zhou, L., Xu, D., Li, Y., Pan, Q., Wang, J., Xue, L., & Howard, A. (2019). P and nitrogen adsorption capacities of biochars derived from feedstocks at different pyrolysis temperatures. Water., 11, 1559. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081559.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ukwattage, N.L., Li, Y., Gan, Y. et al. Effect of Biochar and Coal Fly Ash Soil Amendments on the Leaching Loss of Phosphorus in Subtropical Sandy Ultisols. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 56 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-4393-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-4393-5