Abstract
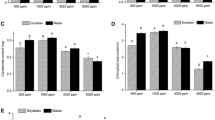
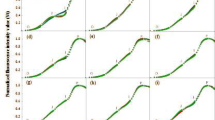
To investigate the effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 concentrations ([CO2]) on autumnal phenology and end of season photosynthesis of different bud-break leaves of trees, we fumigated 2-year-old red maple seedlings with 800, 600, and 400 μL L−1 [CO2] in nine continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR) chambers. Leaves were subdivided into first (B1), second (B2), and third bud-break (B3) leaves. The results indicated that (1) autumnal leaf senescence, including the beginning date, end date, and duration of leaf abscission of all three bud-break leaf groups, was not affected by elevated [CO2]; (2) elevated [CO2] increased leaf photosynthesis of B1, B2, and B3 leaves throughout the whole of the growing season; (3) elevated [CO2] significantly increased whole plant photosynthesis only for B2 leaves, accounting for 41.2–54.7% of the whole plant photosynthesis, due to the larger whole leaf area of B2. In conclusion, enhanced seasonal carbon gain in response to atmospheric CO2 enrichment is the result of strong stimulation of photosynthesis throughout the growing season, especially for B2 leaves but not by extending or shortening the growing season in autumn.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- P Nsat :
-
leaf light-saturated net photosynthetic rate
- P Nsatw :
-
whole plant light-saturated photosynthetic rate
References
Ainsworth, E. A., & Long, S. P. (2005). What have we learned from 15 years of free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE)? A meta-analytic review of the responses of photosynthesis, canopy properties and plant production to rising CO2. New Phytologist, 165, 351–372. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.01224.x.
Asshoff, R., Zotz, G., & Koerner, C. (2006). Growth and phenology of mature temperate forest trees in elevated CO2. Global Change Biology, 12, 848–861. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2006.01133.x.
Bigras, F. J., & Bertrand, A. (2006). Responses of picea mariana to elevated CO2 concentration during growth, cold hardening and dehardening: phenology, cold tolerance, photosynthesis and growth. Tree Physiology, 26, 875–888. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/26.7.875.
Borchert, R., Robertson, K., Schwartz, M. D., & Williams-Linera, G. (2005). Phenology of temperate trees in tropical climates. International Journal of Biometeorology, 50(1), 57–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-005-0261-7.
Elagöz, V., Han, S. S., & Manning, W. J. (2006). Acquired changes in stomatal characteristics in response to ozone during plant growth and leaf development of bush beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) indicate phenotypic plasticity. Environmental Pollution, 140, 395–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.08.024.
Gunderson, C. A., Norby, R. J., & Wullschleger, S. D. (1993). Foliar gas exchange responses of two deciduous hardwoods during 3 years of growth in elevated CO2: no loss of photosynthetic enhancement. Plant, Cell & Environment, 16(7), 797–807. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.1993.tb00501.x.
Herrick, J. D., & Thomas, R. B. (2003). Leaf senescence and late-season net photosynthesis of sun and shade leaves of overstory sweetgum (Liquidambar styraciflua) grown in elevated and ambient carbon dioxide concentrations. Tree Physiology, 23, 109–118. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/23.2.109.
Hoel, B. O., & Solhaug, K. A. (1998). Effect of irradiance on chlorophyll estimation with the Minolta SPAD-502 leaf chlorophyll meter. Annals of Botany, 82, 389–392. https://doi.org/10.1006/anbo.1998.0683.
Kikuzawa, K., & Lechowicz, M. J. (2011). “Ecology of leaf longevity”in Ecological research monographs, 1st ed. (Tokyo: Springer). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-53918-6.
Koike, T. (1990). Autumn coloring, photosynthetic performance and leaf development of deciduous broad-leaved trees in relation to forest succession. Tree Physiology, 7, 21–32. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/7.1-2-3-4.21.
Körner, C., & Basler, D. (2010). Phenology under global warming. Science, 327, 1461–1462.
Li, L., Xiaoke, W., & Manning, W. J. (2019a). Effects of elevated CO2 on leaf senescence, leaf nitrogen resorption, and late-season photosynthesis in Tilia americana L. Frontiers in Plant Science, 10, 1217. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01217.
Li, J. H., Dijkstra, P., Hymus, G. J., Wheeler, R. M., & Drake, B. G. (2000). Leaf senescence of Quercus myrtifolia as affected by long-term CO2 enrichment in its native environment. Global Change Biology, 6, 727–733. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2486.2000.00347.x.
Li, L., Manning, W. J., & Xiaoke, W. (2018). Autumnal leaf abscission of sugar maple is not delayed by atmospheric CO2 enrichment. Photosynthetica, 56, 1134–1139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-018-0802-z.
Li, L., Manning, W. J., & Xiaoke, W. (2019b). Elevated CO2 increases root mass and leaf nitrogen resorption in red maple (Acer rubrum L.) for more N demand. Forests, 10, 420.
Manning, W. J., & Krupa, S. V. (1992). Experimental methodology for studying the effects of ozone on crops and trees. In R. B. Flagler (Ed.), Surface level ozone exposures and their effects on vegetation (pp. 93–156). Lewis Publishers, Inc: Chelsea.
McConnaughay, K. D. M., Bassow, S. L., Berntson, G. M., & Bazzaz, A. F. (1996). Leaf senescence and decline of end of season gas exchange in five temperate deciduous tree species grown in elevated CO2 concentrations. Global. Global Change Biology, 2, 25–33. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.1996.tb00046.x.
Miao, F. A., & Bazzazs, L. (1993). Successional status, seed size, and responses of tree seedlings to CO2, light, and nutrients. Ecology, 74(1), 104–112.
Michael, T., Dananjali, G., Naoki, H., Anke, M., & Saman, S. (2017). Effects of elevated carbon dioxide on photosynthesis and carbon partitioning: a perspective on root sugar sensing and hormonal crosstalk. Frontiers in Physiology, 8, 578. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00578.
Moore, B. D., Cheng, S. H., Sims, D., & Seeman, J. R. (1999). The biochemical and molecular basis for photosynthetic acclimation to elevated atmospheric CO2. Plant, Cell & Environment, 22, 567–582. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3040.1999.00432.x.
Moors, E. J. (2010). Influence of spring and autumn phenological transitions on forest ecosystem productivity. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 365, 3227–3246. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2010.0102.
Norby, R. J., Wullschleger, S. D., Johnson, D. W., & Ceulemans, R. (1999). Tree responses to rising CO2 in field experiments: implications for the future forest. Plant, Cell & Environment, 22, 683–714. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3040.1999.00391.x.
Norby, R. J., Sholtis, J. D., Gunderson, C. A., & Jawdy, S. S. (2003a). Leaf dynamics of a deciduous forest canopy: no response to elevated CO2. Oecologia (Berlin), 136, 574–584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-003-1296-2.
Norby, R. J., Hartz-Rubin, J. S., & Verbrugge, M. J. (2003b). Phenological responses in maple to experimental atmospheric warming and CO2 enrichment. Global Change Biology, 9, 1792–1801. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2003.00714.x.
Norby, R. J., Warren, J. M., Iversen, C. M., Medlyn, B. E., & Mcmurtrie, R. E. (2010). CO2 enhancement of forest productivity constrained by limited nitrogen availability. PNAS, 107, 19368–19373. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1006463107.
Overdieck, D. (2016). CO2, temperature, and trees (pp. 84–Singapore, 85). Springer Singapore.
Polgar, C. A., & Primack, R. B. (2011). Leaf-out phenology of temperate woody plants: from trees to ecosystems. New Phytologist, 191, 926–941. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03803.x.
Rae, A. M., Ferris, R., Tallis, M. J., & Taylor, G. (2006). Elucidating genomic regions determining enhanced leaf growth and delayed senescence in elevated CO2. Plant, Cell & Environment, 29, 1730. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2006.01545.x.
Reich, P. B., Ellsworth, D. S., Walters, M. B., Vose, J. M., Grewham, C., Volin, J. C., et al. (1999). Generality of leaf trait relationships: a test across six biomes. Ecology, 80, 1955–1969. https://doi.org/10.2307/176671.
Sharwood, R. E., Crous, K. Y., Whitney, S. M., Ellsworth, D. S., Ghannoum, O. (2017). Linking photosynthesis and leaf allocation under future elevated CO2, and climate warming in Eeucalyptus globulus. Journal of Experimental Botany, erw484. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erw484.
Sigurdsson, B. (2001). Elevated CO2 and nutrient status modified leaf phenology and growth rhythm of young Populus trichocarpa trees in a 3-year field study. Trees, 15, 403–413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004680100121.
Springer, C. J., & Ward, J. K. (2007). Flowering time and elevated atmospheric CO2. New Phytologist, 176, 243–255. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02196.x.
Tallis, M. J., Lin, Y., Rogers, A., Zhang, J., Street, N. R., Miglietta, F., et al. (2010). The transcriptome of populus in elevated CO2 reveals increased anthocyanin biosynthesis during delayed autumnal senescence. New Phytologist, 186, 415–428. https://doi.org/10.2307/27797564.
Taylor, G., Tallis, M. J., Giardina, C. P., Percy, K. E., Miglietta, F., Gupta, P. S., et al. (2008). Future atmospheric CO2 leads to delayed autumnal senescence. Global Change Biology, 14, 264–275. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2007.01473.x.
Urban, O., Hrstka, M., Zitová, M., Holisová, P., Sprtová, M., Klem, K., et al. (2012). Effect of season, needle age and elevated CO2 concentration on photosynthesis and rubisco acclimation in picea abies. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 58, 135–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2012.06.023.
Wargo, P. M. (1978). Correlations of leaf area with length and width measurements of leaves of black oak, white oak, and sugar maple. Northeastern Forest Experiment Station: Forest Service Research Note.
Warren, J. M., Norby, R. J., & Wullschleger, S. D. (2011). Elevated CO2 enhances leaf senescence during extreme drought in a temperate forest. Tree Physiology, 31, 117–130. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpr002.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate Professor Michelle DaCosta in UMass, Amherst, for loaning us the LI-Cor 6400 photosynthesis system and giving us many kind suggestions during the experiment, Professors David Ratkowsky (Tasmanian Institute of Agriculture) and Bo Larson (University of Copenhagen) helped greatly with English polishing and suggestions for revision. We thank anonymous reviewers for their time and efforts in improving this paper.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science for Youth Foundation of China (31700439) and China Postdoctoral Foundation (2018M631595).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, William Manning; methodology, William Manning and Li Li; formal analysis, Li Li; investigation, Li Li; data curation, Li Li; writing–original draft preparation, Li Li; writing–review and editing, Wang Xiaoke; project administration, William Manning; funding acquisition, William Manning and Li Li.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Manning, W. & Wang, X. Effects of Elevated CO2 Concentrations on Leaf Senescence and Late-Season Net Photosynthesis of Red Maple (Acer rubrum). Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 467 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04828-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04828-z