Abstract
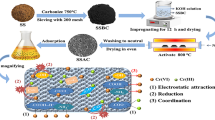
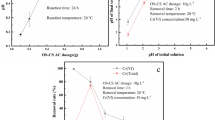
In the study, an activated carbon was prepared by co-pyrolyzing rice straw and sewage sludge with ZnCl2 activation (SS-RS AC) and used to remove Cr(VI) from wastewater. Firstly, for the preparation of SS-RS AC, the yield and iodine number were used to determine the appropriate addition percentage of rice straw. Then, a series of batch experiments including initial pH, adsorption kinetics and isotherms, and ionic strength as well as Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) analysis of SS-RS AC before and after adsorption were performed to explore the Cr(VI) adsorption removal behavior and mechanism of SS-RS AC prepared from sewage sludge with the appropriate rice straw addition percentage. The results showed that the appropriate addition percentage of rice straw was 20%. For the Cr(VI) adsorption removal with SS-RS AC, the initial pH of solution significantly influenced the removal efficient. The highest efficiency of Cr(VI) adsorption removal (97.7%) could be attained at pH 2.0. The adsorption kinetics and isotherm data were best fitted by the pseudo-second-order model and the Langmuir-Freundlich model, respectively. The prepared SS-RS AC had the maximum Cr(VI) adsorption removal capacity of 138.69 mg/g at 40 °C. The main mechanisms for the Cr(VI) removal with SS-RS AC involve the electrostatic attraction and the reduction of Cr(VI). Carboxy, amine, and hydroxyl groups were found to act as electron donor groups, contributing to the reduction of Cr(VI). The ionic strength had an adverse effect on the Cr(VI) removal. Overall, the prepared SS-RS AC can be used as an alternative and low-cost adsorbent for the removal of Cr(VI).








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai, L., Zhang, C., Liao, F., Wang, Y., Li, M., Meng, L., & Jiang, J. (2011). Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution with magnetite loaded multi-wall carbon nanotube: kinetic, isotherm and mechanism analysis. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 198, 282–290.
Altun, T., & Pehlivan, E. (2012). Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions by modified walnut shells. Food Chemistry, 132, 693–700.
Bhattcharya, A. K., & Venkobachar, C. (1984). Removal of cadmium(II) by low cost adsorbents. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 110, 110–122.
Chakravarty, R., & Banerjee, P. C. (2012). Mechanism of cadmium binding on the cell wall of an acidophilic bacterium. Bioresource Technology, 108, 176–183.
Chen, H., Yan, S. H., Ye, Z. L., Meng, H. J., & Zhu, Y. G. (2012a). Utilization of urban sewage sludge: Chinese perspectives. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 19, 1454–1463.
Chen, C. X., Huang, B., Li, T., & Wu, G. F. (2012b). Preparation of phosphoric acid activated carbon from sugarcane bagasse by mechanochemical processing. Bioresources, 4, 5109–5116.
Chen, T., Zhang, Y., Wang, H., Lu, W., Zhou, Z., Zhang, Y. Z., & Ren, L. (2014). Influence of pyrolysis temperature on characteristics and heavy metal adsorptive performance of biochar derived from municipal sewage sludge. Bioresource Technology, 164, 47–54.
Chen, T., Zhou, Z., Xu, S., Wang, H., & Lu, W. (2015). Adsorption behavior comparison of trivalent and hexavalent chromium on biochar derived from municipal sludge. Bioresource Technology, 190, 388–394.
Crini, G., & Badot, P. M. (2008). Application of chitosan, a natural aminopolysaccharide, for dye removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption processes using batch studies: A review of recent literature. Progress in Polymer Science, 33, 399–447.
Dada, A. O., Olalekan, A. P., Olatunya, A. M., & Dada, O. (2012). Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin--Radushkevich isotherms studies of equilibrium sorption of Zn2+ unto phosphoric acid modified rice husk. IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry, 3, 38–45.
Dong, X., Ma, L. Q., & Li, Y. (2011). Characteristics and mechanisms of hexavalent chromium removal by biochar from sugar beet tailing. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 190, 909–915.
Drake, L. R., Lin, S., Rayson, G. D., & Jackson, P. J. (1995). Chemical modification and metal binding studies of Datura innoxia. Environmental Science and Technology, 30, 110–114.
Dula, T., Siraj, K., & Kitte, S. A. (2014). Adsorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution using chemically activated carbon prepared from locally available waste of bamboo (Oxytenanthera abyssinica). ISRN Environmental Chemistry, 2014, 1–9.
Elangovan, R., Philip, L., & Chandraraj, K. (2008). Biosorption of hexavalent and trivalent chromium by palm flower (Borassus aethiopum). Chemical Engineering Journal, 141, 99–111.
Fan, L., Zhou, X., Liu, Q., Wan, Y., Cai, J., Chen, W., Chen, F., Ji, L., Cheng, L., & Luo, H. (2019). Properties of Eupatorium adenophora Spreng (Crofton weed) biochar produced at different pyrolysis temperatures. Environmental Engineering Science. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2019.0028.
Gorzin, F., & Bahri Rasht Abadi, M. M. (2017). Adsorption of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by adsorbent prepared from paper mill sludge: kinetics and thermodynamics studies. Adsorption Science & Technology, 36, 149–169.
Gupta, V. K., Agarwal, S., & Saleh, T. A. (2011). Chromium removal by combining the magnetic properties of iron oxide with adsorption properties of carbon nanotubes. Water Research, 45, 2207–2212.
Han, R., Wang, Y., Yu, W., Zou, W., Shi, J., & Liu, H. (2007). Biosorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution by rice husk in a fixed-bed column. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 141, 713–718.
He, J., & Chen, J. P. (2014). A comprehensive review on biosorption of heavy metals by algal biomass: materials, performances, chemistry, and modeling simulation tools. Bioresource Technology, 160, 67–78.
Ho, Y. S., Ng, J. C. Y., & Mckay, G. (2000). Kinetics of pollutant sorption by biosorbents: review. Separation and Purification Reviews, 29, 189–232.
Hsu, N. H., Wang, S. L., Liao, Y. H., Huang, S. T., Tzou, Y. M., & Huang, Y. M. (2009). Removal of hexavalent chromium from acidic aqueous solutions using rice straw-derived carbon. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 171, 1066–1070.
Jeppu, G. P., & Clement, T. P. (2012). A modified Langmuir-Freundlich isotherm model for simulating pH-dependent adsorption effects. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 129-130, 46–53.
Jin, J., Li, Y., Zhang, J., Wu, S., Cao, Y., Liang, P., Zhang, J., Wong, M. H., Wang, M., Shan, S., & Christie, P. (2016). Influence of pyrolysis temperature on properties and environmental safety of heavy metals in biochars derived from municipal sewage sludge. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 320, 417–426.
Jin, J., Wang, M., Chao, Y., Wu, S., Liang, P., Li, Y., Zhang, J., Zhang, J., Wong, M. H., Shan, S., & Christie, P. (2017). Cumulative effects of bamboo sawdust addition on pyrolysis of sewage sludge: biochar properties and environmental risk from metals. Bioresource Technology, 228, 218–226.
Jung, C., Heo, J., Han, J., Her, N., Lee, S. J., Oh, J., Ryu, J., & Yoon, Y. (2013). Hexavalent chromium removal by various adsorbents: Powdered activated carbon, chitosan, and single/multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Separation and Purification Technology, 106, 63–71.
Kotaś, J., & Stasicka, Z. (2000). Chromium occurrence in the environment and methods of its speciation. Environmental Pollution, 107, 263–283.
Kousalya, G. N., Gandhi, R. M., & Meenakshi, S. (2010). Sorption of chromium(VI) using modified forms of chitosan beads. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 47, 308–315.
Kumar, A., & Jena, H. M. (2017). Adsorption of Cr(VI) from aqueous phase by high surface area activated carbon prepared by chemical activation with ZnCl2. Process Safety and Environment Protection, 109, 63–71.
Li, W., Yue, Q., Tu, P., Ma, Z., Gao, B., Li, J., & Xu, X. (2011). Adsorption characteristics of dyes in columns of activated carbon prepared from paper mill sewage sludge. Chemical Engineering Journal, 178, 197–203.
Li, Y., Li, Y., Li, L., Shi, X., & Wang, Z. (2016). Preparation and analysis of activated carbon from sewage sludge and corn stalk. Advanced Powder Technology, 27, 684–691.
Liu, H., Liang, S., Gao, J., Ngo, H. H., Guo, W., Guo, Z., Wang, J., & Li, Y. (2014). Enhancement of Cr(VI) removal by modifying activated carbon developed from Zizania caduciflora with tartaric acid during phosphoric acid activation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 246, 168–174.
Lu, H., Zhang, W., Wang, S., Zhuang, L., Yang, Y., & Qiu, R. (2013). Characterization of sewage sludge-derived biochars from different feedstocks and pyrolysis temperatures. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 102, 137–143.
Lv, X., Hu, Y., Tang, J., Sheng, T., Jiang, G., & Xu, X. (2013). Effects of co-existing ions and natural organic matter on removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solution by nanoscale zero valent iron (nZVI)-Fe3O4 nanocomposites. Chemical Engineering Journal, 218, 55–64.
Malwade, K., Lataye, D., Mhaisalkar, V., Kurwadkar, S., & Ramirez, D. (2016). Adsorption of hexavalent chromium onto activated carbon derived from Leucaena leucocephala waste sawdust: kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 13, 2107–2116.
Mianowski, A., Owczarek, M., & Marecka, A. (2007). Surface area of activated carbon determined by the iodine adsorption number. Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects, 29, 839–850.
Miretzky, P., & Cirelli, A. F. (2010). Cr(VI) and Cr(III) removal from aqueous solution by raw and modified lignocellulosic materials: a review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 180, 1–19.
Mohan, D., Singh, K. P., & Singh, V. K. (2006). Trivalent chromium removal from wastewater using low cost activated carbon derived from agricultural waste material and activated carbon fabric cloth. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 135, 280–295.
Owlad, M., Aroua, M. K., Daud, W. A. W., & Baroutian, S. (2009). Removal of hexavalent chromium-contaminated water and wastewater: a review. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 200, 59–77.
Pan, J., Jiang, J., & Xu, R. (2013). Adsorption of Cr(III) from acidic solutions by crop straw derived biochars. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 25, 1957–1965.
Park, J., Lee, Y., Ryu, C., & Park, Y. K. (2014). Slow pyrolysis of rice straw: analysis of products properties, carbon and energy yields. Bioresource Technology, 155, 63–70.
Park, J. A., Jung, S. M., Yi, I. G., Choi, J. W., Kim, S. B., & Lee, S. H. (2017). Adsorption of microcystin-LR on mesoporous carbons and its potential use in drinking water source. Chemosphere, 177, 15–23.
Phan, N. H., Rio, S., Faur, C., Coq, L. L., Cloirec, P. L., & Nguyen, T. H. (2006). Production of fibrous activated carbons from natural cellulose (jute, coconut) fibers for water treatment applications. Carbon, 44, 2569–2577.
Selvi, K., Pattabhi, S., & Kadirvelu, K. (2001). Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by adsorption onto activated carbon. Bioresource Technology, 80, 87–89.
Nethaji, S., Sivasamy, A., & Mandal, A. B. (2013). Preparation and characterization of corn cob activated carbon coated with nano-sized magnetite particles for the removal of Cr(VI). Bioresource Technology, 134, 94–100.
Smith, K. M., Fowler, G. D., Pullket, S., & Graham, N. J. (2009). Sewage sludge-based adsorbents: a review of their production, properties and use in water treatment applications. Water Research, 43, 2569–2594.
Sun, Y., Yue, Q., Mao, Y., Gao, B., Gao, Y., & Huang, L. (2014). Enhanced adsorption of chromium onto activated carbon by microwave-assisted H3PO4 mixed with Fe/Al/Mn activation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 265, 191–200.
Tang, L., Yang, G., Zeng, G., Cai, Y., Li, S., Zhou, Y., Pang, Y., Liu, Y., Zhang, Y., & Luna, B. (2014). Synergistic effect of iron doped ordered mesoporous carbon on adsorption-coupled reduction of hexavalent chromium and the relative mechanism study. Chemical Engineering Journal, 239, 114–122.
Tao, H. C., Zhang, H. R., Li, J. B., & Ding, W. Y. (2015). Biomass based activated carbon obtained from sludge and sugarcane bagasse for removing lead ion from wastewater. Bioresource Technology, 192, 611–617.
Tay, J. H., Chen, X. G., Jeyaseelan, S., & Graham, N. (2001). Optimising the preparation of activated carbon from digested sewage sludge and coconut husk. Chemosphere, 44, 45–51.
Vaiopoulou, E., & Gikas, P. (2012). Effects of chromium on activated sludge and on the performance of wastewater treatment plants: a review. Water Research, 46, 549–570.
Wong, S., Yac’Cob, N. A. N., Ngadi, N., Hassan, O., & Inuwa, M. (2018). From pollutant to solution of wastewater pollution: synthesis of activated carbon from textile sludge for dye adsorption. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 26, 870–878.
Worasuwannarak, N., Sonobe, T., & Tanthapanichakoon, W. (2007). Pyrolysis behaviors of rice straw, rice husk, and corncob by TG-MS technique. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 78, 265–271.
Worch, E. (2012). Adsorption technology in water treatment: fundamentals, processes, and modeling. Berlin: De Gruyter.
Wu, C., Song, M., Jin, B., Wu, Y., & Huang, Y. (2013). Effect of biomass addition on the surface and adsorption characterization of carbon-based adsorbents from sewage sludge. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 25, 405–412.
Yang, G., Zhang, G., & Wang, H. (2015). Current state of sludge production, management, treatment and disposal in China. Water Research, 78, 60–73.
Zhang, M., Liu, Y., Li, T., Xu, W., Zheng, B., Tan, X., Wang, H., Guo, Y., Guo, F., & Wang, S. (2015). Chitosan modification of magnetic biochar produced from Eichhornia crassipes for enhanced sorption of Cr(vi) from aqueous solution. RSC Advances, 5, 46955–46964.
Zietzschmann, F., Altmann, J., Ruhl, A. S., Dünnbier, U., Dommisch, I., Sperlich, A., Meinel, F., & Jekel, M. (2014). Estimating organic micro-pollutant removal potential of activated carbons using UV absorption and carbon characteristics. Water Research, 56, 48–55.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Undergraduate Innovation Training Program Funded Project of Sichuan Agricultural University (No. 201610626042) and the Scientific Research Innovation Team Project of Sichuan Provincial Department of Education (No. 16TD0006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, L., Wan, W., Wang, X. et al. Adsorption Removal of Cr(VI) with Activated Carbon Prepared by Co-pyrolysis of Rice Straw and Sewage Sludge with ZnCl2 Activation. Water Air Soil Pollut 230, 233 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4305-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4305-8