Abstract
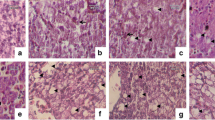
The aim of this study was to evaluate the acute and chronic effects caused by exposure to the 2,4 dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D)-based commercial herbicide Amina Zamba® on Physalaemus albonotatus tadpoles from Gosner stage 25. The lethal concentration (LC50) was determined after exposure to different concentrations of Amina Zamba® (350 to 2400 mg/L) at 96 h. Sublethal effects were evaluated after chronic exposure to four fractions of the LC5096h obtained (12.5, 25, 50, and 75% of LC5096h) and a control. The biological responses analyzed included survival, growth and development, morphological abnormalities, and histological changes in the liver. The LC50 values of Amina Zamba® at 48, 72, and 96 h were 1040.2, 754.2, and 350 mg/L, respectively. The chronic exposure to the herbicide altered the survival of exposed tadpoles and caused several morphological abnormalities and liver histological alterations, mainly at the highest concentrations tested. Oral disc malformations and intestinal abnormalities were the most frequent abnormalities in all treated tadpoles. Histological alterations observed in the liver structure included hepatocyte vacuolization, enlargement of sinusoids, dilation of blood vessels, and a significant increase in the number of melanomacrophages in tadpoles exposed to 25, 50, and 75% LC5096h with respect to control (P < 0.05). Furthermore, the treated tadpoles showed an accelerated development rate, reaching Gosner stages 38 and 42 before controls. These results demonstrate that the chronic exposure to this commercial formulation affects the survival, accelerates metamorphosis, and induces morphological abnormalities and liver damage in P. albonotatus tadpoles.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agius, C., & Roberts, R. J. (2003). Melano-macrophage centres and their role in fish pathology. Journal of Fish Diseases, 26(9), 499–509.
Alford, R. A., & Richards, S. J. (1999). Global amphibian declines: a problem in applied ecology. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 30, 133–165.
Aronzon, C. M., Sandoval, M. T., Herkovits, J., & Perez-Coll, C. S. (2011). Stage-dependent toxicity of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic on the embryonic development of a South American toad Rhinella arenarum. Environmental Toxicology, 26, 373–381.
ASIH, HL, SSAR, (2004). American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists. Guidelines for use of live amphibians and reptiles in field and laboratory research. http://asih.org/sites/default/files/documents/resources/guidelinesherpsresearch2004.pdf/. Accessed 20 May 2018.
Attademo, A. M., Peltzer, P. M., Lajmanovich, R. C., Cabagna, M., & Fiorenza, G. (2007). Plasma B-esterases and glutathione S-transferase activities in the toad Chaunus schneideri (Amphibia, Anura) inhabiting rice agroecosystems of Argentina. Ecotoxicology, 16(8), 533–539.
Attademo, A. M., Peltzer, P. M., Lajmanovich, R. C., Cabagna-Zenklusen, M., Junges, C. M., Lorenzatti, E., Aró, C., & Grenón, P. (2015). Biochemical changes in certain enzymes of Lysapsus llimellum (Anura: Hylidae) exposed to chlorpyrifos. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 113, 287–294.
Bach, N. C., Marino, D. J. G., Natale, G. S., & Somoza, G. M. (2018). Effects of Glyphosate and its commercial formulation, Roundup® Ultramax, on liver histology of tadpoles of the Neotropical frog, Leptodactylus latrans (Amphibia: Anura). Chemosphere, 202, 289–297.
Barni, S., Bertone, V., Croce, A. C., Bottiroli, G., Bernini, F., & Gerzeli, G. (1999). Increase in liver pigmentation during natural hibernation in some amphibians. Jornal of Anatomy, 195, 19–25.
Berger, G., Graef, F., & Pfeffer, H. (2013). Glyphosate applications on arable fields considerably coincide with migratins amphibians. Scientific Reports, 3, 2622.
Bernet, D., Schmidt, H., Meier, W., Burkhardt-Holm, P., & Wahli, T. (1999). Histopathology in fish: proposal for a protocol to assess aquatic pollution. Journal of Fish Diseases, 22(1), 25–34.
Blaustein, A. R., & Kiesecker, J. M. (2002). Complexity in conservation: lessons from the global decline of amphibian populations. Ecology Letters, 5, 597–608.
Boone, M. D. (2008). Examining the single and interactive effects of three insecticides on amphibian metamorphosis. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 27(7), 1561–1568.
Brodeur, J. C., Sassone, A., Hermida, G. N., & Codugnello, N. (2013). Environmentally-relevant concentrations of atrazine induce non-monotic acceletarion of developmental rate and increased size at metamorphosis in Rhinella arenarum tadpoles. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 92, 10–17.
Bruhl, C. A., Schmidt, T., Pieper, S., & Alscher, A. (2013). Terrestrial pesticide exposure of amphibians: an underestimated cause of global decline? Scientific Reports, 3, 1135.
Cakici, O. (2015). Histopathologic changes in liver and kidney tiasues induced by carbaryl in Bufotestes variabilis (Anura: Bufonidae). Experimental and Toxicology Pathology, 67, 237–343.
Canadian Water Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life (Freshwater, Marine). (2014). Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment. http://st-ts.ccme.ca/en/index.html. Accesed 02 Febrary 2018.
Carey, C., & Bryant, C. J. (1995). Possible interrelations among environmental toxicants, amphibian development, and decline of amphibian populations. Environmental Health Perspectives, 103, 13–17.
Cattaneo, R., Loro, V. L., Spanevello, R., Silveira, F. A., Luz, L., Miron, D. S., Fonseca, M. B., Moraes, B. S., & Clasen, B. (2008). Metabolic and histological parameters on silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) exposed to commercial formulation of 2,4-diclorophenooxiacetic acid (2,4D) herbicide. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 92, 133–137.
Charles, J. M., Hanley, T. R. J., Wilson, R. D., van Ravenzwaay, B., & Bus, J. S. (2001). Developmental toxicity studies in rats and rabbits on 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and its forms. Toxicology Science, 60(1), 121–131.
Cheek, A. O., Ide, C. F., Bollinger, J. E., Rider, C. V., & McLachlan, J. A. (1999). Alteration of leopard frog (Rana pipiens) metamorphosis by the herbicide acetochlor. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 37(1), 70–77.
Chelgren, N. D., Rosenberg, D. K., Heppel, S. S., & Gitelman, A. I. (2006). Carryover aquatic effects on survival of metamorphic frogs during pond migrations. Ecological Applications, 16(1), 250–261.
Coady, K., Marino, T., Thomas, J., Sosinski, L., Neal, B., & Hammond, L. (2013). An evaluation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in the amphibian metamorphosis assay and the fish short-term Reproductionn assay. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 90, 143–150.
Coady, K. K., Murphy, M. B., Vulleneuve, D. L., Hecker, M., Jones, P. D., Carr, J. A., Salomon, K. R., Smith, E. E., Van der Kraak, G., Kendall, R. J., & Giesy, J. P. (2004). Effects of atrazine on metamorphosis, growth, and gonadal development in the Green Frog (Rana clamitans). Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health A, 67, 91–957.
Cooke, A. S. (1972). The effect of DDT, Dieldrin and 2,4D on amphibian spawn and tadpoles. Evironmental Pollution, 3(1), 51–68.
Crump, D., Werry, K., Veldhoen, N., Van Aggelen, G., & Helbing, C. C. (2002). Exposure to the herbicide acetochlor alters thyroid hormone-dependent gene expression and metamorphosis in Xenopus laevis. Environmental Health Perspectives, 110(12), 1199–1205.
Dann, A.B., (2009). The effects of Triclosan, 2,4-d, and their by-products on the adrenocortical cells of rainbow trout. Thesis submitted to the School of Graduate Studies of the University of Lethbridge in partial fulfillment of the requirements of the degree. Department of Biological Sciences University of Lethbridge, Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada. https://www.uleth.ca/dspace/bitstream/handle/10133/3154/dann,%20andrea.pdf;sequence=1
Das, B. C., Thapa, P., Karki, R., Das, S., Mahapatra, S., Liu, T., Torregroza, P., Wallace, D. P., Kambhampati, S., & Van eldhuizen, P., Verma, A., Ray, S.K., Evans, T. (2014). Retinoic acid signaling pathways in development and diseases. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 22(2), 673–683.
Davidson, C., Shaffer, H. B., & Jennings, M. R. (2002). Spatial tests of the pesticide drift, habitat destruction, UV-B, and climate-change hypotheses for California amphibian declines. Conservation Biology, 16(6), 1588–1601.
Davidson, C., & Knapp, R. A. (2007). Multiple stressors and amphibian declines: dual impacts of pesticides and fish on yellow-legged frogs. Ecological Applications, 17(2), 587–597.
Denver, R. J. (2009). Stress hormones mediate environment-genotype interactions during amphibian development. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 164, 20–31.
Denver, R. J. (2013). Neuroendocrinoloy of amphibian metamorphosis. Current Topics in Developmental Biology, 103, 195–227.
Fairchild, J.F., Allert, A., Sappington, L.S., Nelson, K.J., Valle, J., (2008). Using accelerated life testing procedures to compare the relative sensitivity of rainbow trout and the threatened bull trout to three commonly-used rangeland herbicides (picloram, 2,4-D and clopyralid). Environmental Toxicology Chemistry, 27(3), 623 630.
Fairchild, J. F., Feltz, K. P., Allert, A. L., Sappington, L. C., Nelson, K. J., & Valle, J. A. (2009). An ecological risk assessment of the exposure and effects of 2,4-D acid to rainbow trout (Onchorhyncus mykiss). Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 56, 754–760.
Figueredo, J., & de Jesus Rodrigues, D. (2014). Effects of four types of pesticides on survival, time and size to metamorphosis of two species of tadpoles (Rhinella marina and Physalaemus centralis) from the southern Amazon, Brazil. Herpetological Journal, 24, 7–15.
Franco, A., & Trapp, S. (2010). A multimedia activity model for ionizable compounds: validation study with 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, aniline, and trimethoprim. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 29, 789–799.
Gonzalez, J. M., Smith, D. R., Livingston, S., Warnemuende-Pappas, E., & Zwonitzer, M. (2016). Blind inlets: conservation practices to reduce herbicide losses from closed depressional areas. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 16, 1921–1932.
Gosner, K. L. (1960). A simplified table for staging anuran embryos and larvae, with notes on identification. Herpetologica, 16, 183–190.
Glozier, N. E., Struger, J., Cessna, A. J., Gledhill, M., Rondeau, M., Ernst, W. R., Sekela, M. A., Cagampan, S. J., Sverko, E., & Murphy, C. (2012). Occurrence of glyphosate and acidic herbicides in select urban rivers and streams in Canada, 2007. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 19, 821–834.
Hailey, A., Sooko, N., Mohammed, A., & Khan, A. (2006). Factors affecting tadpoles growth: develompent of rearing system for the Neotropical leptodactylid Physalaemus pustulosus for ecotoxicological studies. Applied Herpetology, 3, 111–128.
Hall, J., & Guyton, A. (2011). Textbook of medical physiology (12th ed.). Philadelphia: Saunders/Elservier.
Hamilton, M. A., Russo, R. C., & Thurston, R. V. (1977). Trimmed Spearman–Karber method for estimating median lethal concentrations in toxicity bioassays. Environmental Science & Technology, 11, 714–719.
Harraez, M. P., & Zapata, A. G. (1986). Structure and function of the melano-macrophage centres of the goldfish Carassius auratus. Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology, 12(1–4), 117–126.
Hayes, T. B., Collins, A., Lee, M., Mendoza, M., Noriega, N., Stuart, A. A., & Vonk, A. (2002). Hermaphroditic, demasculinized frogs after exposure to the herbicide atrazine at low ecologically relevant doses. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 99(8), 5476–5480.
Hayes, T., Haston, K., Tsui, M., Hoang, A., Haeffele, C., & Vonk, A. (2003). Atrazine induced hermaphroditism at 0.1 ppb in American leopard frogs (Rana pipiens): laboratory and field evidence. Environmental Health Perspectives, 111(4), 568–575.
Hayes, T. B., Stuart, A. A., Mendoza, M., Collins, A., Noriega, N., Vonk, A., Johnston, G., Liu, R., & Kpodzo, D. (2006a). Characterization of atrazine-induced gonadal malformations in African clawed frogs (Xenopus laevis) and comparisons with effects of an androgen antagonist (cyproterone acetate) and exogenous estrogen (17 b-estradiol): support for the demasculinization/feminization hypothesis. Environmental Health Perspectives, 114, 134–141.
Hayes, T. B., Case, P., Chui, S., Chung, D., Haeffele, C., Haston, K., Lee, M., Phoung Mai, V., Marjuoa, Y., Parker, J., & Tsui, M. (2006b). Pesticide mixtures, endocrine disruption, and amphibian declines: are we underestimating the impact? Environmental Health Perspectives, 114(1), 40–50.
Hayes, T. B., & Wu, T. H. (1995). Role of corticosterone in anuran metamorphosis and potential role in stress-induced metamorphosis. Netherland Journal of Zoology, 45(1–2), 107–109.
Huespe, I., Cabagna-Zenklusen, M., Curi, L. M., Peltzer, P. M., Attademo, M. A., Villafañe, N., & Lajmanovich, R. C. (2017). Liver melanomacrophages and gluthation S-transferase activity in Leptodactylus chaquensis (Anura: Leptodactylidae) as biomarkers of oxidative stress due to Chlorpirifos exposition. Acta Biologica Colombiana, 22(2), 234–237.
IARC. International Agency for Research on Cancer, (2015). Monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risk of chemicals to man. Some organochlorine insecticides and some chlorphenoxy herbicides. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon. https://monographs.iarc.fr/. Accesed 08 March 2018.
Inoue, D., Sei, K., & Ike, M. (2010). Disruption of retinoic acid receptor signaling by environmental pollutants. Journal of Health Science, 56(3), 221–230.
IUCN (2017), The IUCN red list of threatened species. Version 2017-3. http://www.iucnredlist.org. Accesed 12 December 2017.
Islam, F., Wang, J., Muhammad, F., Jhan, M. A., Xu, M. S. S., Zhu, L., Zhao, J., Muños, M., Li, S., & Zhou, Q. X. W. (2018). Potential impact of the herbicide 2,4-diclorophenoxyacetic acid on human and ecosystems. Environment International, 111, 332–351.
Jantawongsri, K., Thammachoti, P., Kitana, J., Khonsue, W., Varanusupakul, P., & Kitana, N. (2013). Altered immune response of the rice frog Fejervarya limnocharis living in agricultural area with intensive herbicide utilization at Nan Province, Thailand. Environmental Asia, 8(1), 68–74.
Krishnamurthy, S. V., & Smith, G. R. (2011). Combined effects of malathion and nitrate on early growth, abnormalities, and mortality of wood frog (Ranas sylvatica) tadpoles. Ecotoxicology, 20(6), 1361–1367.
Lajmanovich, R. C., Sandoval, M. T., & Peltzer, P. M. (2003a). Induction of mortality and malformation in Scinax nasicus tadpoles exposed by glyphosate formulations. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 70(3), 612–618.
Lajmanovich, R. C., Lorenzatti, E., Maitre, M. I., Enrique, S., & Peltzer, P. M. (2003b). Comparative acute toxicity of the comercial herbicides glyphosate to neotropical tadpoles Scinax nasicus (Anura: Hylidae). Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 12(4), 364–367.
Lajmanovich, R. C., Attademo, M. A., Peltzer, P. M., Junges, C. M., & Cabagna, M. C. (2011). Toxicity of four herbicide formulations with glyphosate on Rhinella arenarum (Anura: Bufonidae) tadpoles: B-esterases and glutathione S-transferase inhibitors. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 60(4), 681–689.
Lajmanovich, R. C., Attademo, A. M., Simoniello, M. F., Poletta, G. L., Junges, C. M., Peltzer, P. M., Grenon, P., & Cabagna-Zenklusen, M. C. (2015). Harmful effects of the dermal intake of commercial formulations containing chlorpyrifos, 2, 4-D, and glyphosate on the common toad Rhinella arenarum (Anura: Bufonidae). Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 36, 226–427.
Lenkowski, J. R., Reed, J. M., Deininger, L., & McLaughlin, K. A. (2008). Perturbation of organogénesis by the herbicide atrazine in the amphibian Xenopus laevis. Environmental Health Perspectives, 116(2), 223–230.
Lenkowski, J.R., Sanchez-Bravo, G., McLaughlin, K.A., (2010). Low concentrations of atrazine, glyphosate, 2,4-dichloro phenoxy acetic acid,and triadimefon exposures have diverse effects on Xenopus laevis organ morphogenesis. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 22(9), 1305–1308.
Lenkowski, J. R., & McLaughlin, K. A. (2010). Acute atrazine exposure disrupts matrix metalloproteinasas and retinoid signaling during organ morphogenesis in Xenopus laevis. Journal of Applied Toxicology, 30(6), 582–589.
Lipscomb, K., Schmitt, C., Sablyak, A., Yoder, J. A., & Nascone-Yoder, N. (2006). Role for retinoid signaling in left-right asymmetric digestive organ morphogenesis. Developmental Dynamics, 235(8), 2266–2275.
Lilienfeld, D., & Gallo, M. (1989). 2,4,5-T, and 2,3,7,8-TCDD: an overview. Epidemiologic Reviews, 11, 28–36.
Loumbourdis, N. S., & Vogiatzis, A. K. (2002). Impact of cadmium on liver pigmentary system of the frog Rana ridibunda. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 53(1), 52–58.
Mann, R. M., Hyne, R. V., Choung, C. B., & Wilson, S. P. (2009). Amphibians and agricultural chemicals: Review of the risks in a complex environment. Environmental Pollution, 157(11), 2903–2927.
Marcato, A. C. C., Souza, C. P., & Fontanetti, C. S. (2017). Herbicide 2,4D: a review of toxicity on non-Trget organism. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 228, 120.
Marco, A., Cash, D., Belden, L. K., & Blaustein, A. R. (2001). Sensitivity to urea fertilization in three amphibian species. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 40, 406–409.
Meehan, W., Norris, L., & Sears, H. (1974). Toxicity of various formulations of 2,4-D to salmonids in southeast Alaska. Journal of the Fisheries Research Board of Canada, 31(4), 480–485.
Mesak, C., Oliveira Mendes, B., Oliveira Ferreira, R., & Malafaia, G. (2018). Mutagenic assessment of Lithobates catesbeianus tadpoles exposed to the 2,4D herbicide in a simulated realistic scenario. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(15), 15235–15244.
Metts, B. S., Hopkins, W. A., & Nestor, J. P. (2005). Interaction of an insecticide with larval density in pond-breeding salamanders (Ambystoma). Freshwater Biology, 50(4), 685–696.
Morgan, M. K., Scheuerman, P. R., Bishop, C. S., & Pyles, R. A. (1996). Teratogenic potential of antrazine and 2,4-D using FETAX. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, 48(2), 151–168.
Nikoloff, N., Natale, G. S., Marino, D., Solonesky, S., & Larramendy, M. (2014). Flurochloridone-based herbicides induced genotoxicity effects on Rhinella arenarum tadpoles (Anura: Bufonidae). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 100, 275–281.
Oztas, H., Ozdemir, C., & Kalipci, E. (2011). Investigation of ecotoxicological effects of 2,4-D acid herbicide on the ecosystem. World Applied Sciences Journal, 14, 126–135.
Palma, G., Sánchez, A., Olave, Y., Encina, F., Palma, R., & Barra, R. (2004). Pesticides levels in surface waters in an agricultural-forestry basin in Southern Chile. Chemosphere, 57, 763–770.
Passantino, L., Santamaria, N., Zupa, R., Pousis, C., Garofalo, R., Cianciotta, A., Jirillo, E., Acone, F., & Corriero, A. (2013). Liver melanomacrophage centres as indicators of Atlantic bluefin tuna, Thunnus thynnus L. well-being. Journal of Fish Diseases, 37(3), 241–250.
Paunescu, A., Ponepal, C. M., Drghici, O., & Marinescu, A. G. (2010). Liver histopathologic alterations in the frog Rana (Pelophylax) ridibunda induce by the action of Reldan 40EC insecticide. Analele Universitatii din Oradea Fascicula Biologie, 17(1), 166–169.
Paunescu, A., Ponepal, C. M., Grigorean, V. T., & Popescu, M. (2012). Histopathological changes in the liver and kidney tissues of marsh frog (Pelophylax ridibundus) induced by the action of Talstar 10EC insecticide. Analele Universitatii din Oradea Fascicula Biologie, 19(1), 5–10.
Peltzer, P. M., Lajmanovich, R. C., Attademo, A. M., Junges, C. M., Cabagna, Z., Repetti, M. C., Sigrist, R., & Beldoménico, H. M. (2013). Effect of exposure to contaminated pond sediments on survival, development, and enzyme and blood biomarkers in veined tree frog (Trachycephalus typhonius) tadpoles. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 98, 142–151.
Peltzer, P. M., Lajmanovich, R. C., Sanchez-Hernandez, J. C., Cabagna, M., Attademo, A. M., & Bassó, A. (2008). Effects of agricultural pond eutrophication on survival and health status of Scinax nasicus tadpoles. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 70(1), 185–197.
Peltzer, P. M., Lajmanovich, R. C., Sanchez, L. C., Attademo, A. M., Junges, C. M., Bionda, C. L., Martino, A. L., & Bassó, A. (2011). Morphological abnormalities in wild amphibian populations from the mid-eastern of Argentina. Herpetological Conservation and Biology, 6, 432–442.
Pérez Iglesias, J. M., Franco-Belussi, L., Moreno, L., Tripole, S., De Oliveira, C., & Natale, G. S. (2016). Effects of glyphosate on hepatic tissue evaluating melanomacrophages and erythrocytes responses in Neotropical anuran Leptodactylus latinasus. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(10), 9852–9861.
Pérez Iglesias, J. M., Soloneski, S., Nikoloff, N., Natale, G. S., & Larramendy, M. L. (2015). Toxic and genotoxic effects of the imazethapyr-based herbicide formulation Pivot H ® on Montevideo tree frog Hypsiboas pulchellus larvae (Anura, Hylidae). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 119, 15–24.
Pereira de Paiva, P., Cruz Delcorso, M., Matheus, V. A., do Nascimento de Queiroz, S. C., Collares-Buzato, C. B., & Arana, S. (2017). Acute toxicity of commercial atrazine in Piaractus mesopotamicus: histopathological, ultrastructural, molecular, and genotoxic evaluation. Veterinary World, 10, 1008–1019.
Punzo, F. (2005). Effects of insecticide (Carbaryl) exposure on activity and swimming performance of tadpoles of the Rio Grande leopard frog, Rana berlandieri (Anura: Ranidae). Texas Journal of Science, 57(3), 263–272.
Relyea, R. A. (2005). The lethal impacts of Roundup and predatory stress on six species of North American tadpoles. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 48(3), 351–357.
Relyea, R. A., & Hoverman, J. T. (2006). Assessing the ecology in ecotoxicology: a review and synthesis in freshwater systems. Ecology Letters, 9(10), 1157–1171.
Rodriguez, E. M., & Amin, O. A. (1991). Acute toxicity of parathion and 2,4-D to larval and juvenile stage of Chasmagnatuthus granulata (Decapoda, Brachyura). Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 47, 634–640.
Rowe, C. L., Kinney, O. M., Fiori, A. P., & Congdon, J. D. (1996). Oral deformities in tadpoles (Rana catesbeiana) associated with coal ash deposition: effects on grazing ability and growth. Freshwater Biology, 36, 723–730.
Ruiz de Arcaute, C., Soloneski, S., & Larramendy, M. L. (2016). Toxic and genotoxic effects of the2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D)-based herbicide on the Neotropical fish Cnesterodon decemmaculatus. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 128, 222–229.
Ryan, T. J., Scott, C. M., & Douthitt, B. A. (2007). Sub-lethal effects of 2,4-D exposure on golf course amphibians. USGA Turfgrass and Environmental Research Online., 5, 1–14.
Sánchez, L. C., Lajmanovich, R. C., Peltzer, P. M., Manzano, A. S., Junges, C. M., & Attademo, A. M. (2014). First evidence of the effects of agricultural activities on gonadal form and function of Rhinella fernandezae and Dendropsophus sanborni (Amphibia: Anura) from Entre Rios, Province, Argentina. Acta Herpetologica, 9, 75–88.
Santos, L. R. S., Franco-Belussi, L., Zieri, R., Borges, R. E., & Oliveira, C. (2014). Effects of thermal stress on hepatic melanomacrophages of Eupemphix nattereri (Anura). Anatomical Research, 297(5), 864–875.
Sarikaya, M., & Yilmaz, M. (2003). Investigation of acute toxicity and the effect of 2,4-D (2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid) herbicide on the behavior of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio L., 1758; Pisces, Cyprinidae). Chemosphere, 52, 195–201.
Semlitsch, R., Bridges, C. M., & Welch, A. M. (2000). Genetic variation and a fitness tradeoff in the tolerance of gray treefrog (Hyla versicolor) tadpoles to the insecticide Carbaryl. Oecologia, 125, 179–185.
Sayed, A. H., & Younes, H. A. M. (2017). Melanomacrophage centers in Clarias gariepinus as an immunological biomarker for toxicity of silver nanoparticles. Journal of Microscopy and Ultrastructure, 5, 97–104.
Scalia, M., Geremia, E., Corsaro, C., Santoro, C., Baratta, D., & Sichel, G. (1990). Lipid peroxidation in pigmented and unpigmented liver tissue: protective role of melanin. Pigment Cell Research, 3(2), 115–119.
Spolyarich, N., Hyne, R., Wilson, S., Palmer, C., & Byrne, M. (2010). Growth, development and sex ratios of Spotted Mars Frog (Limnodynastes tasmaniensis) larvae exposed to atrazine and an herbicide mixture. Chemosphere, 78, 807–813.
Stebbins-Boaz, B., Fortner, K., Frazier, J., Piluso, S., Pullen, S., Rasar, M., Reid, W., Sinclair, K., & Winger, E. (2004). Oocyte Maturtion in Xenopus laevis is blocked by the hormonal herbicide, 2,4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid. Molecular Reproduction and Development, 67(2), 233–242.
Steinel, N. C., & Bolnick, D. I. (2017). Melanomacrophage centers as a histological indicator of immune function in fish and other poikilotherms. Frontiers in Immunology, 8, 827.
Stentiford, G. D., Longshaw, M., Lyons, B. P., Jones, G., Green, M., & Feist, S. W. (2003). Histopathological biomarkers in estuarine fish species for the assessment of biological effects of contaminants. Marine Environmental Research, 55(2), 137–159.
Storrs, S. I., & Semlitsch, R. D. (2008). Variation in somatic and ovarian development: predicting susceptibility of amphibians to estrogenic contaminants. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 156(3), 524–530.
Stuart, S. N., Chanson, J. S., Cox, N. A., Young, B. E., Rodrigues, A. S. L., Fischman, D. L., & Waller, R. W. (2004). Status and trends of amphibian declines and extinctions worldwide. Science, 306(5702), 1783–1786.
Stuart, S.N., Hoffmann, M., Chanson, J.S., Cox, N.A., Berridge, R.J., Ramani, P., Young, B.E., (2008). Threatened amphibians of the world. Lynx editions, Barcelona; IUCN, Gland, Switzerland; and Conservation International, Arlington, Virginia, USA.
Teplitsky, C., Piha, H., Laurila, A., & Merila, J. (2005). Common pesticide increases costs of antipredator defenses in Rana temporaria tadpoles. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(16), 6079–6085.
USEPA. United States Environmental Protection Agency., (2005). Reregistration eligibility decision for 2,4-D.). EPA 738-R-05-002. http:// nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPDF.cgi/2000E8DY.PDF?Dockey¼2000E8DY. Accesed 11 November 2017.
Van der Oost, R., Beyer, J., & Vermeulen, N. P. (2003). Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environmetal Toxicology and Pharmacology, 13(2), 57–149.
Velásquez, T. M. T., Montes Rojas, C. M., & Bernal Bautista, M. H. (2013). Efectos letales y subletales del Glifosayo (Roundup® activo) en embriones de anuros colombianos. Acta Biologica Colombiana, 18, 271–278.
Waite, D. T., Cessna, A. J., Grover, R., Kerr, L. A., & Snihura, A. D. (2002). Environmental concentrations of agricultural herbicides: 2,4-dd and triallate. Journal of Environmental Quality, 31(1), 129–144.
Wauchope, R. D., Buttler, T. M., Hornsby, A. G., Augustijn-Beckers, P. W., & Burt, J. P. (1992). The SCS/ARS/CES pesticide properties database for environmental decision-making. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 123, 1–55.
Wake, D.B., Vredenburg, V.T., (2008). Are we in the midst of the sixth mass extinction? A view from the world of amphibians. Proceedings of the National Academic of Sciences, 105, 11466–11473.
Widder, P. D., & Bidwell, J. (2008). Tadpole size, cholinesterase activity, and swim speed in four frog species after exposure to sub-lethal concentrations of chlorpyrifos. Aquatic Toxicology, 88(1), 9–18.
Wilson, R. D., Geronimo, J., & Armbruster, J. A. (1997). 2,4-D dissipation in field soils after applications of 2,4-D dimethylamine salt and 2,4-D 2-ethylhexyl ester. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 16, 1239–1246.
WHO. World Health Organization, International Programme on Chemical Safety & WHO Task Group on Environmental Health Criteria for 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid (2,4-D: Environmental Aspects)., (1989). 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D : environmental aspects / published under the joint sponsorship of the United Nations Environment Programme, the International Labour Organisation, and the World Health Organization. Geneva: World Health Organization. http://www.who.int/iris/handle/10665/40019. Accesed 15 March 2018.
WHO. World Health Organization., (2009). The WHO recommended classification of pesticides by Hazard 1. World Health Organization, Geneva, Italy. http://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/44271?locale=es. Accesed 15 March 2018.
Woudneh, M. B., Sekela, M., Tuominen, T., & Gledhill, M. (2007). Acidic herbicides in surface waters of Lower Fraser Valley, British Columbia, Canada. Journal of Chromatografy A, 1139(1), 121–129.
Xie, L., Thrippleton, K., Irwin, M. A., Siemering, G. S., Mekebri, A., Crane, D., Berry, K., & Schlenk, D. (2005). Evaluation of estrogenic activities of aquatic herbicides and surfactants using a rainbow trout vitellogenin assay. Toxicologicl Sciences, 87(2), 391–398.
Zaya, R. M., Amini, Z., Whitaker, A. S., Kohler, S. L., & Ide, C. F. (2011). Atrazine exposure affects growth, body condition and liver health in Xenopus laevis tadpoles. Aquatic Toxicology, 104(3–4), 243–253.
Zimdahl, R. L. (1993). Fundamentals of weed science (fourth ed.). San Diego CA: Academic Press.
Zar, J. H. (1999). Biostatistical analysis (4th ed.). Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall.
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to Dra. Victoria Eusebi for English review. We also thank to Dra. Cristina S. Zalazar (Institute of Technological Development for the Chemical Industry (INTEC)) for the chemical analysis of 2,4-D commercial formulation. To the Direccción de Recursos Naturales de la provincia de Corrientes for providing the collection permits. We also thank the anonymous reviewer for many valuable comments and suggestions.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Project Course of Action for Research and Science Promotion (CAI+D project N° 045, 2012), National Council for Scientific and Technical Research (CONICET, project PIP N° 036, 2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Standards
Animals used in this research were treated according to the norms of ASIH-American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists (2004), and the bioethics protocol and bioethical evaluations proposed by the Animal Ethical Committee of the Facultad de Bioquímica y Ciencias Biológicas, Universidad Nacional del Litoral (Res. N°: 388/06). http://wwwfbcb.unl.edu.ar/pages/investigacion/comite-de-etica.php.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Curi, L.M., Peltzer, P.M., Sandoval, M.T. et al. Acute Toxicity and Sublethal Effects Caused by a Commercial Herbicide Formulated with 2,4-D on Physalaemus albonotatus Tadpoles. Water Air Soil Pollut 230, 22 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-4073-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-4073-x