Abstract
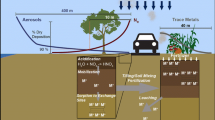
Roads and highways play an important function in the human-dominated Earth landscape and strongly affect the environment. Roadside ecosystems receive a number of pollutants, including deicing salt and inorganic nitrogen (N) from automobiles. We investigated how soil carbon (C) and N cycling were impacted by the application of salt (NaCl) and nitrate (NO3−) to experimental plots in a field that is adjacent to Interstate 81, in Binghamton, NY. Experimental plots were constructed on two parallel transects; one was adjacent to the highway (0-m) and the other 50 m away from the highway (50-m). We hypothesized that the 0-m transect was exposed to roadway-derived pollutants over a long-term period of time, while the 50-m transect was exposed to fewer pollutants due to its distance from the road. Soils were collected in July and November 2011 and June and October 2012. Salt significantly decreased the rates of soil C mineralization and in situ soil respiration in both 0- and 50-m transects (p < 0.001), though it did not discernibly affect the rates of N mineralization or nitrification. Applications of NO3− had no significant impact on soil C or N mineralization. The effects of roadway pollutants were reflected in higher soil conductivities and pH at the 0-m transect. Under experimental salt treatment, C mineralization was reduced by 75% in the 50-m transect, compared to 20% reduction in the 0-m transect. We conclude that microbial communities near roads might have evolved to better withstand the impacts of roadway pollutants. Nevertheless, roads and vehicle traffic have strong impacts on the environment, and the application of road salt has important environmental consequences.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Rahman, A. A. (1998). On the emissions from internal-combustion engines: A review. International Journal of Energy Research, 22, 483–513.
Aber, J. D., Goodale, C. L., Ollinger, S. V., Smith, M. L., Magill, A. H., Martin, M. E., Hallet, R. A., & Stoddard, J. L. (2003). Is nitrogen deposition altering the nitrogen status of northeastern forests? Bioscence, 53(4), 375–389.
Angold, P. G. (1997). The impact of a road upon adjacent heathland vegetation: Effects on plant species composition. Journal of Applied Ecology, 34, 409–417.
Asman, W. A. H., Sutton, M. A., & Schjorring, J. K. (1998). Ammonia: Emission, atmospheric transport and deposition. New Phytologist, 139, 27–48.
Bettez, N. D., Marino, R., Howarth, R. W., & Davidson, E. A. (2013). Roads as nitrogen deposition hot spots. Biogeochemistry, 114, 149–163.
Bignal, K. L., Ashmore M. R., Headley, A. D., Stewart, K., Weigert, K. (2007). Ecological impacts of air pollution from road transport on local vegetation. Applied Geochemistry, 22, 1265–1271.
Blomqvist, G., & Johansson, E. L. (1999). Airborne spreading and deposition of de-icing salt-a case study. Science of the Total Environment, 235, 161–168.
Bowden, R. D., Newkirk, K. M., & Rullo, G. M. (1998). Carbon dioxide and methane fluxes by a forest soil under laboratory-controlled moisture and temperature conditions. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 30(12), 1591–1597.
Brady, S. P., Monosson, E., Matson, C., Bickham, L. (2017). Evolutionary toxicology: Toward a unified understanding of life’s response to toxic chemicals. Evolutionary Applications: Special Issue, in press.
Bryson, G. M. & Barker, A. V. (2002). Sodium accumulation in soils and plants along Massachusetts roadsides. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 33(1&2), 67–78.
Butler, T. J., Likens, G. E., Vermeylen, F. M., & Stunder, B. J. B. (2003). The relation between NOx emissions and precipitation NO3 − in the eastern USA. Atmospheric Environment, 37, 2093–2104.
Cape, J. N., Tang, Y. S., van Dijk, N., Love, L., Sutton, M. A., & Palmer, S. C. F. (2004). Concentrations of ammonia and nitrogen dioxide at roadside verges, and their contribution to nitrogen deposition. Environmental Pollution, 132, 469–478.
Compton, J. E., Watrud, L. S., Porteous, L. A., & DeGrood, S. (2004). Response of soil microbial biomass and community composition to chronic nitrogen additions at Harvard forest. Forest Ecology and Management, 196, 143–158.
Councell, T. B., Duckenfield, K. U., Landa, E. R., & Callender, E. (2004). Tire-wear particles as a source of zinc to the environment. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 4206–4214.
Cunningham, M. A., Snyder, E., Yonkin D., Ross, M., Elsen, T. (2008). Accumulation of deicing salts in soils in an urban environment. Urban Ecosystems, 11, 17–31.
Davidson, E. A., Savage, K. E., Bettez, N. D., Marino, R., & Howarth, R. W. (2009). Nitrogen in runoff from residential roads in a coastal area. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0218-2.
Fay, L., & Shi, X. (2012). Environmental impacts of chemicals for snow and ice control: State of the knowledge. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 223, 2751–2770.
Fierer, N., Allen, A. S., Schimel, J. P., & Holden, P. A. (2003). Controls on microbial CO2 production: A comparison of surface and subsurface soil horizons. Global Change Biology, 9, 1322–1332.
Findlay, S. E. G., & Kelly, V. R. (2011). Emerging indirect and long-term road salt effects on ecosystems. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1223, 58–68.
Green, S. M., & Cresser, M. S. (2008). Nitrogen cycle disruption through the application of de-icing salts on upland highways. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 188, 139–153.
Green, S. M., Machin, R., & Cresser, M. S. (2008). Effect of long-term changes in soil chemistry induced by road salt applications on N-transformations in roadside soils. Environmental Pollution, 152, 20–31.
Heeb, N. V., Forss, A. M., Bruhlmann, S., Luscher, R., Saxer, C. J., & Hug, P. (2006). Three-way catalyst induced formation of ammonia—Velocity- and acceleration-dependent emission factors. Atmospheric Environment, 40, 5986–5997.
Heintzman, R. L., Titus, J. E., & Zhu, W. X. (2015). Effects of roadside deposition on growth and pollutant accumulation by willow (Salix miyabeana). Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 226, 11.
Hjortenkrans, D. S. T., Bergback, B. G., & Haggerud, A. V. (2008). Transversal immission patterns and leachability of heavy metals in road side soils. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 10, 739–746.
Johansson, C., Norman, M., & Burman, L. (2009). Road traffic emission factors for heavy metals. Atmospheric Environment, 43, 4681–4688.
Kaushal, S. S., Groffman, P. M., Likens, G. E., Belt, K. T., Stack, W. P., Kelly, V. R., Band, L. E., & Fisher, G. T. (2005). Increased salinization of fresh water in the northeastern United States. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 102(38), 13517–13520.
Kaye, J. P., Groffman, P. M., Grimm, N. B., Baker, L. A., & Pouyat, R. V. (2006). A distinct urban biogeochemistry? Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 21(4), 192–199.
Kelly, V. R., Lovett, G. M., Weathers, K. C., Findlay, S. E. G., Strayer, D. L., Burns, D. J., & Likens, G. E. (2008). Long-term sodium chloride retention in a rural watershed: Legacy effects of road salt on streamwater concentration. Environmental Science and Technology, 42(2), 410–415.
Kincaid, D. W., & Findlay, S. E. G. (2009). Sources of elevated chloride in local streams: Groundwater and soils as potential reservoirs. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 203, 335–342.
Lovett, G. M., Traynor, M. M., Pouyat, R. V., Carreiro, M. M., Zhu, W.-X., & Baxter, J. W. (2000). Atmospheric deposition to oak forests along an urban-rural gradient. Environmental Science and Technology, 34, 4294–4300.
Lundmark, A., & Olofsson, B. (2007). Chloride deposition and distribution in soils along a deiced highway—Assessment using different methods of measurement. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 182, 173–185.
Magill, A. H., Aber, J. D., Hendricks, J. J., Bowden, R. D., Melillo, J. M., & Steudler, P. A. (1997). Biogeochemical response of forest ecosystems to simulated chronic nitrogen deposition. Ecological Applications, 7(2), 402–415.
Magill, A. H., Aber, J. D., Berntson, G. M., McDowell, W. H., Nadelhoffer, K. J., Melillo, J. M., & Steudler, P. (2000). Long-term nitrogen additions and nitrogen saturation in two temperate forests. Ecosystems, 3, 238–253.
McCormick, R. W., & Wolfe, D. C. (1980). Effect of sodium chloride on CO2 evolution, ammonification and nitrification in a Sassafras sandy loam. Soil Biology and Biogeochemistry, 12, 153–157.
Mo, J., Zhang, W., Zhu, W. X., Gundersen, P., Fang, Y., Li, D., & Wang, H. (2007). Nitrogen addition reduces soil respiration in mature tropical forest in southern China. Global Change Biology, 14, 1–10.
New York State Department of Transportation (2010). 2010 Traffic volume report. https://www.dot.ny.gov/divisions/engineering/technical-services/hds-respository/Traffic%20Volume%20Report%202010.pdf. Accessed 30 August 2014.
Padgett, P. E., Allen, E. B., Bytnerowicz, A., & Minich, R. A. (1999). Changes in soil inorganic nitrogenous pollutants in southern California. Atmospheric Environment, 33, 769–781.
Phoenix, G., Emmett, B., Britton, A., Caporn, S., Dise, N., Helliwell, R., Jones, L., Leake, J., Leith, I., Sheppard, L., Sowerby, A., Pilkington, M., Rowe, E., Ashmore, M., & Power, S. (2012). Impacts of atmospheric nitrogen deposition: Responses of multiple plant and soil parameters across contrasting ecosystems in long-term field experiments. Global Change Biology, 18, 1197–1215.
Pouyat, R. V., & Turechek, W. W. (2001). Short- and long-term effect of site factors on net N-mineralization and nitrification rates along an urban-rural gradient. Urban Ecosystems, 5, 159–178.
Pouyat, R. V., Szlavecz, K., Yesilonis, I. D., Groffman, P. M., & Schwarz, K. (2010). Chemical, physical and biological characteristics of urban soils. In J. Aitkenhead-Peterson & A. Volder (Eds.), Urban ecosystem ecology (pp. 119–152). Madison: American Society of Agronomy.
R Core Team. 2016. R: A language and environment for statistical Computing R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna.
Redling, K., Elliot, E., Bain, D., & Sherwell, J. (2013). Highway contributions to reactive nitrogen deposition: Tracing the fate of vehicular NOx using stable isotopes and plant biomonitors. Biogeochemistry, 116, 261–274.
Scott, T. J., Craig, S. C., & Zhu, W. X. (2011). The effects of simulated nitrogen and salt deposition on nitrogen mineralization and soil chemistry in a roadside ecosystem. Bulletin of the New Jersey Academy of Sciences, 56(2), 9–11.
United States Department of Transportation, Federal Highway Administration (2013). Highway statistics series: Highway statistics 2013, Table HM-12. http://www.fhwa.dot.gov/policyinformation/statistics.cfm. Accessed September 30, 2015.
Yesilonis, I. D., Pouyat, R. V., & Neerchal, N. K. (2008). Spatial distribution of metals in soils in Baltimore, Maryland: Role of native parent material, proximity to major roads, housing age and screening guidelines. Environmental Pollution, 156, 723–731.
Zhu, W. X., & Carreiro, M. M. (2004). Temporal and spatial variations in nitrogen cycling in deciduous forest ecosystems along and urban-rural gradient. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 36, 267–278.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Tim Scott, Megan Larson, Jonathan Schmitkons, Joseph Graney, John Titus, and other students and faculty from the Center for Integrated Watershed Studies (CIWS) at Binghamton University for the help and support of this project, and funding support from the Wallace Research Foundation. We would also like to thank the highly professional review that had improved the quality of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Craig, S., Zhu, W. Impacts of Deicing Salt and Nitrogen Addition on Soil Nitrogen and Carbon Cycling in a Roadside Ecosystem. Water Air Soil Pollut 229, 187 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3838-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3838-6