Abstract
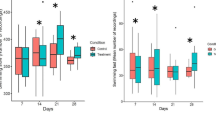
Behavioral changes have been considered as appropriate to evaluate sublethal effects of pollutants. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of a mixture of pesticides, with glyphosate and 2,4-D (Gly + 2,4-D) as active ingredients, on the zooplankton evasion behavior from the fish Cnesterodon decemmaculatus. An increase in the evasion behavior was observed for copepods at two different concentrations of the Gly + 2,4-D mixture, for cladocerans at the lowest pesticide concentration, and for rotifers at the highest pesticide concentration. The response time to the fish signals also differed, being copepods faster than cladocerans and rotifers. All the exposed organisms showed higher variability in their distribution over time than those of controls (without pesticides). Our results suggest that the Gly + 2,4-D mixture formulations may have a mimetic effect with the fish alarm signals. The potential consequences of maladaptive responses triggered by pesticides, as well as the increased swimming activity, are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen, H. R., Wollenberger, L., Halling-Sørensen, B., & Kusk, K. O. (2001). Development of copepod nauplii to copepodites—a parameter for chronic toxicity including endocrine disruption. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 20(12), 2821–2829.
Brooks, J. L., & Dodson, S. I. (1965). Predation, body size, and composition of plankton. Science, 150(3692), 28–35.
Brooks, A. C., Gaskell, P. N., & Maltby, L. L. (2009). Sublethal effects and predator-prey interactions: Implications for ecological risk assessment. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 28(11), 2449–2457.
Chang, K. H., Sakamoto, M., & Hanazato, T. (2005). Impact of pesticide application on zooplankton communities with different densities of invertebrate predators: an experimental analysis using small-scale mesocosms. Aquatic Toxicology, 72(4), 373–382.
Coors, A., & De Meester, L. (2008). Synergistic, antagonistic and additive effects of multiple stressors: predation threat, parasitism and pesticide exposure in Daphnia magna. Journal of Applied Ecology, 45(6), 1820–1828.
Diggle, A. J., Neve, P. B., & Smith, F. P. (2003). Herbicides used in combination can reduce the probability of herbicide resistance in finite weed populations. Weed Research, 43(5), 371–382.
Dodson, S. I. (1988). The ecological role of chemical stimuli for the zooplankton: predator-avoidance behavior in Daphnia. Limnology and Oceanography, 33(6;2), 1431–1439.
Dodson, S. I., Lillie, R. A., & Will-Wolf, S. (2005). Land use, water chemistry, aquatic vegetation, and zooplankton community structure of shallow lakes. Ecological Applications, 15(4), 1191–1198.
Forbes, V. E. (2000). Is hormesis an evolutionary expectation? Functional Ecology, 14, 12–24.
Frontier, S. (1981) Cálculo del error en el recuento de organismos zooplanctónicos. En Boltovskoy D (ed.), Atlas del Zooplancton del Atlántico Sudoccidental y métodos de trabajo con el zooplancton marino. INIDEP, Mar del Plata, Argentina, pp. 163–167.
Gliwicz, Z. M. (1994). Relative significance of direct and indirect effects of predation by planktivorous fish on zooplankton. Hydrobiologia, 272, 201–210.
Gutierrez, M. F., Gagneten, A. M., & Paggi, J. C. (2011). Microcrustaceans escape behavior as an early bioindicator of copper, chromium and endosulfan toxicity. Ecotoxicology, 21(2), 428–438.
Gutierrez, M. F., Paggi, J. C., & Gagneten, A. M. (2012). Infodisruptions in predator–prey interactions: xenobiotics alter microcrustaceans responses to fish infochemicals. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 81, 11–16.
Gutierrez, M. F., Andrade, V., Fanton, N., & Gagneten, A. M. (2016). Facing predation risk in aquatic systems: differential response of zooplankton and habituation to the false alarm. Fundamental and Applied Limnology., 184(4), 329–339.
Hanazato, T. (1999). Anthropogenic chemicals (insecticides) disturb natural organic chemical communication in the plankton community. Environmental Pollution, 105, 137–142.
Hanazato, T. (2001). Pesticide effects on freshwater zooplankton: an ecological perspective. Environmental Pollution, 112, 1–10.
Hanazato, T., & Dodson, S. I. (1992). Complex effects of a kairomone of Chaoborus and an insecticide on Daphnia pulex. Journal of Plankton Research, 14(12), 1743–1755.
Hanazato, T., & Dodson, S. I. (1993). Morphological responses of four species of cyclomorphic Daphnia to a short-term exposure to the insecticide carbaryl. Journal of Plankton Research, 15(9), 1087–1095.
Hanazato, T., & Dodson, S. I. (1995). Synergistic effects of low oxygen concentration, predator kairomone, and a pesticide on the cladoceran Daphnia pulex. Limnology and Oceanography, 40(4), 700–709.
Harmon, S. M., & Wiley, F. E. (2011). Effects of pollution on freshwater organisms. Water Environment Research, 83(10), 1733–1788.
Jergentz, S., Mugni, H., Bonetto, C., & Schulz, R. (2005). Assessment of insecticide contamination in runoff and stream water of small agricultural streams in the main soybean area of Argentina. Chemosphere, 61, 817–826.
José de Paggi, S. B., & Devercelli, M. (2011). Land use and basin characteristics determine the composition and abundance of the microzooplankton. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 218, 93–108.
Klaschka, U. (2008). The infochemical effect—a new chapter in ecotoxicology. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 15(6), 452–462.
Lass, S., & Spaak, P. (2003). Chemically induced anti-predator defences in plankton: a review. Hydrobiologia, 491, 221–239.
McCormick, P. V., & Cairns, J. (1997). Algal indicators of aquatic ecosystem condition and change. In W. Wuncheng (Ed.), Plants for Environmental Studies (pp. 177–208). New York: Lewish Publishers.
Milam, C. D., Farris, J. L., Dwyer, F. J., & Hardesty, D. K. (2005). Acute toxicity of six freshwater mussel species (Glochidia) to six chemicals: implications for Daphnids and Utterbackia imbecillis as surrogates for protection of freshwater mussels (Unionidae). Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 48, 166–173.
Ohman, M. D. (1988). Behavioral responses of zooplankton to predation. Bulletin of Marine Science, 43(3), 530–550.
Pérez, G. L., Miranda, L., Vera, M. S. (2011). Effects of herbicide glyphosate and glyphosate-based formulations on aquatic ecosystems. INTECH Open Access Publisher.
Peruzzo, P. J., Porta, A. A., & Ronco, A. E. (2008). Levels of glyphosate in surface waters, sediments and soils associated with direct sowing soybean cultivation in north pampasic region of Argentina. Environmental Pollution, 156, 61–66.
Preston, B. J., Cecchine, G., & Snell, T. W. (1999). Effects of pentachlorophenol on predator avoidance behavior of the rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus. Aquatic Toxicology, 44, 201–212.
Relyea, R. A. (2009). A cocktail of contaminants: how mixtures of pesticides at low concentrations affect aquatic communities. Oecologia, 159(2), 363–376.
Relyea, R., & Hoverman, J. (2006). Assessing the ecology in ecotoxicology: a review and synthesis in freshwater systems. Ecology Letters, 9(10), 1157–1171.
Rico-Martínez, R., Pérez-Legaspi, I. A., Alvarado-Flores, J., Retes-Pruneda, J. L., Arias-Almeida, J. C. (2012). Adverse effects of herbicides on freshwater zooplankton in Hasaneen MN (ed) Herbicides—properties, synthesis and control of weeds. INTECH Open Access Publisher, pp. 405-434.
Rose, R. M., Warne, M. S. J., & Lim, R. P. (2001). Factors associated with fish modify life history traits of the cladoceran Ceriodaphnia dubia. Journal of Plankton Research, 23(1), 11–17.
Sakamoto, M., Chang, K. H., & Hanazato, T. (2006). Inhibition of development of anti-predator morphology in the small cladoceran Bosmina by an insecticide: impact of an anthropogenic chemical on prey–predator interactions. Freshwater Biology, 51(10), 1974–1983.
Sarikaya, R., & Yılmaz, M. (2003). Investigation of acute toxicity and the effect of 2, 4-D (2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid) herbicide on the behavior of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio L., 1758; Pisces, Cyprinidae). Chemosphere, 52(1), 195–201.
Schindler, D. W. (1987). Detecting ecosystem responses to anthropogenic stress. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, Ottawa, 44, 6–25.
Sharp, A. A., & Stearns, D. E. (1997). Sublethal effects of cupric ion activity on the grazing behaviour of three calanoid copepods. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 34, 1041–1048.
Snell, T. W., Moffat, B. D., Janssen, C., & Persoone, G. (1991). Acute toxicity tests using rotifers. IV. Effects of cyst age, temperature and salinity on the sensitivity of Brachionus calyciflorus. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 21, 308–317.
Sokal, R. R., Rohlf, F. J. (1969). Biometría. Principios y métodos estadísticos en la investigación biológica. Ed. H. Blume, Madrid. 832 pp.
Soltani, N., Shropshire, C., & Sikkema, P. H. (2009). Sensitivity of winter wheat to preplant and preemergence glyphosate tankmixes. Crop Protection, 28(5), 449–452.
Stearns, S. C. (1992). The evolution of life histories (Vol. 249, 247 pp). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Stewart, C. L., Nurse, R. E., Van Eerd, L. L., Vyn, R. J., & Sikkema, P. H. (2011). Weed control, environmental impact, and economics of weed management strategies in glyphosate-resistant soybean. Weed Technology, 25(4), 535–541.
Sullivan, B. K., Buskey, E., Miller, D. C., & Ritacco, P. J. (1983). Effects of copper and cadmium on growth, swimming and predator avoidance in Eurytemora affinis (Copepoda). Marine Biology, 77, 299–306.
Williamson, C. E. (1987). Predator-prey interactions between omnivorous diaptomid copepods and rotifers: the role of prey morphology and behavior. Limnology and Oceanography, 32(1), 167–177.
Acknowledgments
We thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Funding
This research was supported by the National University of the Littoral, (research Project CAI + D 2011: 50120110100215LI) and CONICET (PIP 2015: 11220150100395CO). V.A. was supported by the Universidad Nacional del Litoral through a research initiation scholarship (CIENTIBECA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andrade, V.S., Gutierrez, M.F., Fantón, N.I. et al. Shifts in Zooplankton Behavior Caused by a Mixture of Pesticides. Water Air Soil Pollut 229, 107 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3752-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3752-y