Abstract
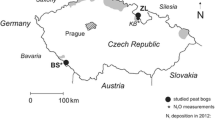
Under low nitrogen (N) input into rain-fed peat bogs, Sphagnum moss efficiently filters incoming N, preventing invasion of vascular plants and peat oxygenation. Elevated atmospheric N deposition, in combination with climatic warming, may cause retreat of bryophytes and degradation of peat deposits. There are concerns that higher emissions of greenhouse gases, accompanying peat thinning, will accelerate global warming. Breakthrough of deposited N below living moss has been quantified for two Central European peat bogs dominated by Sphagnum magellanicum. In the 1990s, the northern site, ZL, received three times more atmospheric N (> 40 kg ha−1 year−1) than the southern site, BS. Today, atmospheric N inputs at both sites are comparable (15 and 11 kg ha−1 year−1, respectively). Replicated peat cores were collected from the wet central segments of both study sites, 15N-NO3− tracer was applied on the moss surface, and the peat cores were incubated under water-logged conditions. After 40 weeks, the rate of downcore leaching of the 15N tracer was assessed. The recent history of high N pollution at ZL did not accelerate 15N penetration into deeper peat layers, relative to BS. At both sites, less than 3% of the 15N tracer reached the shallow depth of 9 cm. Analysis of control peat cores, along with a 210Pb chronology, revealed removal of the “excess” N from the ZL peat profiles prior to sampling. Following a decrease of atmospheric N pollution in the past two decades, efficient filtering of atmospheric N by Sphagnum at ZL has been renewed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biester, H., Knorr, K. H., Schellekens, J., Basler, A., & Hermanns, Y. M. (2014). Comparison of different methods to determine the degree of peat decomposition in peat bogs. Biogeosciences, 11(10), 2691–2707.
Blodau, C., Basiliko, N., Mayer, B., & Moore, T. R. (2006). The fate of experimentally deposited nitrogen in mesocosms from two Canadian peatlands. Science of the Total Environment, 364, 215–228.
Bohdalkova, L., Curik, J., Kubena, A. A., & Buzek, F. (2013). Dynamics of methane fluxes from two peat bogs in the Ore Mountains, Czech Republic. Plant Soil Environment, 1, 14–21.
Bohdalkova, L., Novak, M., Stepanova, M., Fottova, D., Chrastny, V., Mikova, J., & Kubena, A. A. (2014a). The fate of atmospherically derived Pb in Central European catchments: insights from spatial and temporal pollution gradients and Pb isotope ratios. Environmental Science & Technology, 48(8), 4336–4343.
Bohdalkova, L., Novak, M., Buzek, F., Kreisinger, J., Bindler, R., Pazderu, K., & Pacherova, P. (2014b). The response of a mid- and high latitude peat bog to predicted climate change: methane production in a 12-month peat incubation. Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change, 19(7), 997–1010.
Bragazza, L., & Limpens, J. (2004). Dissolved organic nitrogen dominates in European bogs under increasing atmospheric N deposition. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 18(4), GB4018.
Bragazza, L., Tahvanainen, T., Kutnar, L., Rydin, H., Limpens, J., Hajek, M., et al. (2004). Nutritional constraints in ombrotrophic Sphagnum plants under increasing atmospheric nitrogen deposition in Europe. New Phytologist, 163(3), 609–616.
Bragazza, L., Limpens, J., Gerdol, R., Grosvernier, P., Hajek, M., Hajek, T., et al. (2005). Nitrogen concentration and δ15N signature of ombrotrophic Sphagnum mosses at different N deposition levels in Europe. Global Change Biology, 11(1), 106–114.
Bragazza, L., Freeman, C., Jones, T., Rydin, H., Limpens, J., Fenner, N., et al. (2006). Atmospheric nitrogen deposition promotes carbon loss from peat bogs. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(51), 19386–19389.
Breeuwer, A., Heijmans, M., Robroek, B. J. M., Limpens, J., & Berendse, F. (2008). The effect of increased temperature and nitrogen deposition on decomposition in bogs. Oikos, 117(8), 1258–1268.
Broder, T., Blodau, C., Biester, H., & Knorr, K. H. (2012). Peat decomposition records in three pristine ombrotrophic bogs in southern Patagonia. Biogeosciences, 9(4), 1479–1491.
Core Team, R. (2017). R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for statistical computing http://www.R-projetc.org.
Chiwa, M., Sheppard, L. J., Leith, I. D., Leeson, S. R., Tang, Y. S., & Cape, J. N. (2016). Sphagnum can ‘filter’ N deposition, but effects on the plant and pore water depend on the N form. Science of the Total Environment, 559, 113–120.
Clymo, R. S., Turunen, J., & Tolonen, K. (1998). Carbon accumulation in peatland. Oikos, 81, 368–388.
Dise, N. B., Ashmore, M., Belyazid, S., Bleeker, A., Bobbink, R., de Vries, W., et al. (2011). Nitrogen as threat to European terrestrial biodiversity. In M. A. Sutton, C. M. Howard, J. W. Erisman, G. Billen, A. Bleeker, P. Grennfelt, H. van Grinsven, & B. Grizetti (Eds.), The European Nitrogen Assessment (pp. 463–494). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Dohnal, Z., Kunst, M., Mejstrik, V., Raucina, S., & Vydra, V. (1965). Czechoslovak Peatlands. Czechoslovakia: Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences.
Erbanova, L., Novak, M., Fottova, D., & Dousova, B. (2008). Export of arsenic from forested catchments under easing atmospheric pollution. Environmental Science & Technology, 42(19), 7187–7192.
Esmeijer-Liu, A. J., Kurschner, W. M., Lotter, A. F., Verhoeven, J. T. A., & Goslar, T. (2012). Stable carbon and nitrogen isotopes in a peat profile are influenced by early stage diagenesis and changes in atmospheric CO2 and N deposition. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 223(5), 2007–2022.
Fisak, J., Tesar, M., Rezacova, D., Elias, V., Weignerova, V., & Fottova, D. (2002). Pollutant concentrations in fog and low cloud water at selected sites of the Czech Republic. Atmospheric Research, 64(1–4), 75–87.
Fottova, D. (1995). Regional evaluation of mass element fluxes - GEOMON network of small catchments. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 34(2), 215–221.
Fottova, D. (2003). Trends in sulphur and nitrogen deposition fluxes in the GEOMON network, Czech Republic, between 1994 and 2000. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 150(1–4), 73–87.
Fottova, D., & Skorepova, I. (1998). Changes in mass element fluxes and their importance for critical loads: GEOMON network, Czech Republic. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 105(1–2), 365–376.
Franzes, A. J., & Loiseau, P. (1999). The fate of mineral nitrogen in a fen with Sphagnum fallax klinggr. and Carex rostrata stokes (Massif central, France). Canadian Journal of Botany, 77, 1136–1143.
Fraser, C. J. D., Roulet, N. T., & Lafleur, M. (2001). Groundwater flow patterns in a large peatland. Journal of Hydrology, 246(1–4), 142–154.
Fritz, C., Lamers, L. P. M., Riaz, M., van den Berg, L. J. L., & Elzenga, T. J. T. M. (2014). Sphagnum mosses - masters of efficient N-uptake while avoiding intoxication. PLoS One, 9(1), 1–11.
Gabor, R. S., Hall, S. J., Eiriksson, D. P., Jameel, Y., Millington, M., Stout, T., et al. (2017). Persistent urban influence on surface water quality via impacted groundwater. Environmental Science & Technology, 51(17), 9477–9487.
Galloway, J. N., Dentener, F. J., Capone, D. G., Boyer, E. W., Howarth, R. W., Sitzinger, S. P., et al. (2004). Nitrogen cycles: past, present, future. Biogeochemistry, 70, 153–226.
Gorham, E. (1991). Northern peatlands: role in the carbon cycle and probable responses to climatic warming. Ecological Applications, 1, 182–195.
Granath, G., Limpens, J., Posch, M., Mücher, S., & de Vries, W. (2014). Spatio-temporal trends of nitrogen deposition and climate effects on Sphagnum productivity and European peatlands. Environmental Pollution, 187, 73–80.
Harmens, H., Schnyder, E., Thoni, L., Cooper, D. M., Mills, G., Leblond, S., et al. (2014). Relationship between site-specific nitrogen concentrations in mosses and measured wet bulk atmospheric nitrogen deposition across Europe. Environmental Pollution, 194, 50–59.
Heijmans, M. M. P. D., Klees, H., de Visser, W., & Berendse, F. (2002). Effects of increased nitrogen deposition on the distribution of 15N-labeled nitrogen between Sphagnum and vascular plants. Ecosystems, 5, 500–508.
Högberg, M. (1997). Tansley review no. 95. 15N abundance in soil-plant system. New Phytologist, 137, 179–203.
Hunova, I., Maznova, J., & Kurfurst, P. (2014). Trends in atmospheric deposition fluxes of sulphur and nitrogen in Czech forests. Environmental Pollution, 184, 668–675.
Inglett, P. W., Reddy, K. R., Newman, S., & Lorenzen, B. (2007). Increased soil stable nitrogen isotopic ratio following phosphorus enrichment: historical patterns and tests of two hypotheses in a phosphorus-limited wetland. Oecologia, 153(1), 99–109.
Jirousek, M., Hajek, M., & Bragazza, L. (2011). Nutrient stoichiometry in Sphagnum along a nitrogen deposition gradient in highly polluted region of Central-East Europe. Environmental Pollution, 159(2), 585–590.
Johnson, D. W., & Lindberg, S. E. (Eds.). (1992). Atmospheric deposition and forest nutrient cycling. Berlin Heidelberg New York: Springer.
Jones, M. C., Peteet, D. M., & Sambrotto, R. (2010). Late-glacial and Holocene δ15N and δ13C variation from a Kenai Peninsula, Alaska peatland. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 293(1–2), 132–143.
Kalbitz, K., & Geyer, S. (2002). Different effects of peat degradation on dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen. Organic Geochemistry, 33(3), 319–326.
Kohzu, A., Matsui, K., Yamada, T., & Sugimoto, A. (2003). Significance of rooting depth in mire plants: evidence from natural 15N abundance. Ecological Research, 18(3), 257–266.
Kopacek, J., & Posch, M. (2011). Anthropogenic nitrogen emissions during the Holocene and their possible effect on remote ecosystems. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 25(GB2017), 1–16.
Kopacek, J., & Vesely, J. (2005). Sulfur and nitrogen emissions in the Czech Republic and Slovakia from 1850 till 2000. Atmospheric Environment, 39(12), 2179–2188.
Kopacek, J., Vesely, J., & Stuchlik, E. (2001). Sulphur and nitrogen fluxes and budgets in the Bohemian Forest and Tatra Mountains during the Industrial Revolution (1850–2000). Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 5(3), 391–405.
Kruger, J. P., Leifeld, J., Glatzel, S., Szidat, S., & Alewell, C. (2015). Biogeochemical indicators of peatland degradation—a case study of a temperate bog in northern Germany. Biogeosciences, 12(10), 2861–2871.
Kuhry, P., & Vitt, D. H. (1996). Fossil carbon/nitrogen ratios as a measure of peat decomposition. Ecology, 77, 271–275.
Lamers, L. P. M., Bobbing, R., & Roelofs, J. G. M. (2000). Natural nitrogen filter fails in polluted raised bogs. Global Change Biology, 6, 583–586.
Larmola, T., Leppanen, S. M., Tuitila, E.-S., Aarva, M., Merila, P., Fritze, H., & Tiirola, M. (2014). Methanotrophy induces nitrogen fixation during peatland development. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(2), 734–739.
Li, Y. H., & Vitt, D. H. (1997). Patterns of retention and utilization of aerially deposited nitrogen in boreal peatlands. Ecoscience, 4, 106–116.
Limpens, J., Berendse, F., & Klees, H. (2003). N deposition affects N availability in interstitial water, growth of Sphagnum and invasion of vascular plants in bog vegetation. New Phytologist, 157, 339–347.
Limpens, J., Berendse, F., & Klees, H. (2004). How P affects the impact of N deposition on Sphagnum and vascular plants in bogs. Ecosystems, 7, 793–804.
Manninen, S., Kivimäki, S., Leith, I. D., Leeson, S. R., & Sheppard, L. J. (2016). Nitrogen deposition does not enhance Sphagnum decomposition. Science of the Total Environment, 571, 314–322.
Mihaljevic, M., Zuna, M., Ettler, V., Chrastny, V., Sebek, O., Strnad, L., & Kyncl, T. (2008). A comparison of tree rings and peat deposit geochemical archives in the vicinity of a lead smelter. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 188(1–4), 311–321.
Mihaljevic, M., Zuna, M., Ettler, V., Sebek, O., Strnad, L., & Golias, V. (2006). Lead fluxes, isotopic and concentration profiles in a peat deposit near a lead smelter (Pribram, Czech Republic). Science of the Total Environment, 372(1), 334–344.
Nadelhoffer, K., & Fry, B. (1988). Controls on natural nitrogen-15 and carbon-13 abundances in forest soil organic matter. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 52, 1633–1640.
Nadelhoffer, K., Shaver, G., Fry, B., Giblin, A., Johnson, L., & McKane, R. (1996). N-15 natural abundances and N use by tundra plants. Oecologia, 107(3), 386–394.
Nordbakken, J. F., Ohlson, M., & Högberg, P. (2003). Boreal bog plants: Nitrogen sources and uptake of recently deposited nitrogen. Environmental Pollution, 126, 191–200.
Novak, M., Bottrell, S. H., Fottova, D., Buzek, F., Groscheova, H., & Zak, K. (1996). Sulfur isotope signals in forest soils of Central Europe along an air-pollution gradient. Environmental Science & Technology, 30(12), 3473–3476.
Novak, M., Buzek, F., & Adamova, M. (1999). Vertical trends in δ13C, δ15N and δ34S ratios in bulk Sphagnum peat. Soil Biology & Biogeochemistry, 31(9), 1343–1346.
Novak, M., Buzek, F., Jackova, I., Stepanova, M., & Prechova, E. (2017). Isotope constraints on microbial N2-fixation in ombrotrophic peat bogs. Annual Report, Czech Geological Survey, Prague. Grant project no. 16-18079S (Czech Science Foundation).
Novak, M., Emmanuel, S., Vile, M. A., Erel, Y., Veron, A., Paces, T., et al. (2003). Origin of lead in eight Central European peat bogs determined from isotope ratios, strengths and operation times of regional pollution sources. Environmental Science & Technology, 37, 437–445.
Novak, M., Erel, Y., Zemanova, L., Bottrell, S. H., & Adamova, M. (2008). A comparison of lead pollution record in Sphagnum peat with known historical Pb emission rates in the British Isles and the Czech Republic. Atmospheric Environment, 42, 8997–9006.
Novak, M., Gebauer, G., Thoma, M., Curik, J., Stepanova, M., Jackova, I., et al. (2015b). Denitrification at two nitrogen-polluted, ombrotrophic Sphagnum bogs in Central Europe: insights from porewater N2O-isotope profiles. Soil Biology & Biogeochemistry, 81, 48–57.
Novak, M., Jackova, I., Curik, J., Stepanova, M., Veselovsky, F., Buzek, F., et al. (2016). Contrasting δ15N values of atmospheric deposition and Sphagnum peat bogs: N fixation as a possible cause. Ecosystems, 19, 1037–1050.
Novak, M., Stepanova, M., Jackova, I., Vile, M. A., Wieder, R. K., Buzek, F., et al. (2014). Isotopic evidence for nitrogen mobility in peat bogs. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 133, 351–361.
Novak, M., Veselovsky, F., Curik, J., Stepanova, M., Fottova, D., Prechova, E., & Myska, O. (2015a). Nitrogen input into Sphagnum bogs via horizontal deposition: an estimate for N-polluted high-elevation sites. Biogeochemistry, 123(1–2), 307–312.
Novak, M., Wieder, R. K., & Schell, W. R. (1994). Sulfur during early diagenesis in Sphagnum peat: insights from δ34S ratio profiles in 210Pb-dated peat cores. Limnology and Oceanography, 39(5), 1172–1185.
Novak, M., Zemanova, L., Buzek, F., Jackova, I., Adamova, M., Komarek, A., et al. (2010). The effect of a reciprocal peat transplant between two contrasting Central European sites on C cycling and C isotope ratios. Biogeosciences, 7(3), 921–932.
Oulehle, F., Chuman, T., Hruska, J., Kram, P., McDowell, W. H., Myska, O., et al. (2017). Recovery from acidification alters concentrations and fluxes of solutes from Czech catchments. Biogeochemistry, 132(3), 251–272.
Oulehle, F., Evans, C. D., Hofmeister, J., Krejci, R., Tahovska, K., Persson, T., et al. (2011). Major changes in forest carbon and nitrogen cycling caused by declining sulphur deposition. Global Change Biology, 17(10), 3115–3129.
Oulehle, F., Kopacek, J., Chuman, T., Cernohous, V., Hunova, I., Hruska, J., et al. (2016). Predicting sulphur and nitrogen deposition using a simple statistical method. Atmospheric Environment, 140, 456–468.
Pinheiro, J. C., & Bates, D. (2000). Mixed-effects models in S and S-Plus. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Pinheiro, J. C., Bates, D., DebRoy, S., Sarkar, D., & R Core Team. (2016). Nlme: linear and nonlinear mixed effect models. R package version, 3, 1–128 http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=nlme.
Pinsonneault, A. J., Moore, T. R., & Roulet, N. T. (2016). Effects of long-term fertilization on peat stoichiometry and associated microbial enzyme activity in an ombrotrophic bog. Biogeochemistry, 129(1–2), 149–164.
Sheppard, L. J., Leith, I. D., Leeson, S. R., van Dijk, N., Field, C., & Levy, P. (2013). Fate of N in a peatland, Whim bog: immobilization in the vegetation and peat, leakage into pore water and losses as N2 depend on the form of N. Biogeosciences, 10, 149–160.
Song, Y., Song, C., Meng, H., Swarzenski, C. M., Wang, X., & Tan, W. (2017). Nitrogen additions affect litter quality and soil biochemical properties in a peatland of Northeast China. Ecological Engineering, 100, 175–185.
Sorrell, B. K., Chague-Goff, C., Basher, L. M., & Partridge, T. R. (2011). N:P ratios, δ15N fractionation and nutrient resorption along a nitrogen to phosphorus limitation gradient in an oligotrophic wetland complex. Aquatic Botany, 94(2), 93–101.
Tfaily, M. M., Cooper, W. T., Kostka, J. E., Chanton, P. R., Schadt, C. W., Hanson, P. J., et al. (2014). Organic matter transformations in the peat column at Marcell Experimental Forest: humification and vertical stratification. Journal of Geophysical Research – Biogeosciences, 119(4), 661–675.
Van den Elzen, E., Kox, M. A. R., Harpenslager, S. F., Hensgens, G., Fritz, C., Jetten, M. S. M., et al. (2017). Symbiosis revisited: phosphorus and acid buffering stimulate N2 fixation but not Sphagnum growth. Biogeosciences, 14(5), 1111–1122.
Vile, M. A., Wieder, R. K., & Novak, M. (2000). 200 years of Pb deposition throughout the Czech Republic: patterns and sources. Environmental Science & Technology, 34, 12–21.
Vile, M. A., Wieder, R. K., Zivkovic, T., Scott, K. D., Vitt, D. H., Hartsock, J. A., et al. (2014). N2-fixation by methanotrophs sustains carbon and nitrogen accumulation in pristine peatlands. Biogeochemistry, 121(2), 317–328.
Wieder, R. K., & Vitt, D. H. (Eds.). (2006). Boreal peatland ecosystems. Berlin Heidelberg New York: Springer.
Williams, B. L., Silcock, D. J., & Young, M. (1999). Seasonal dynamics of N in two Sphagnum moss species and the underlying peat treated with 15NH4 15NO3. Biogeochemistry, 45, 285–302.
Xing, Y., Bubier, J., Moore, T. R., Murphy, M., Basiliko, N., Wendel, S., & Blodau, C. (2011). The fate of 15N-nitrate in a northern peatland impacted by long term experimental nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilization. Biogeochemistry, 103, 281–296.
Zając, K., & Blodau, C. (2016). The fate of 15N-nitrate in mesocosms from five European peatlands differing in long-term nitrogen deposition rate. Biogeosciences, 13, 707–722.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Andrea Kucerova of the Botanical Institute of the Czech Academy of Sciences, Trebon, for a consultation on phosphorus cycling.
Funding
This work was funded by the Czech Science Foundation, Project No. 16-18079S to MN.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Novak, M., Stepanova, M., Buzek, F. et al. The Fate of 15N Tracer in Waterlogged Peat Cores from Two Central European Bogs with Different N Pollution History. Water Air Soil Pollut 229, 70 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3731-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3731-3