Abstract
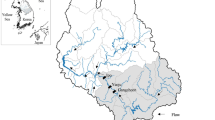
The dynamics of phosphorus (P) reactions in stream water are important because of their potential to trigger eutrophication. This study aimed to explore the nature of P in sediments associated with Walnut Creek, Jasper County, Iowa. The Walnut Creek watershed supports row crop production, grazing, and riparian buffer zones. The alluvial cross section is composed of a sequence of sediments that contribute differentially to the amounts and forms of P entering the stream. Twenty-five sediment samples collected near Walnut Creek (classified as bank, in-stream, and floodplain deposits) were sequentially extracted for P. Across all 25 samples, the inorganic P (Pi) fractions followed the order Fe-bound Pi > Ca-bound Pi > reductant-soluble Pi > Al-bound Pi > soluble and loosely bound Pi. For the organic (Po) fractions, the order was nonlabile Po > fulvic acid-bound Po > humic acid-bound Po > labile Po > moderately labile Po. The ranges of total P (TP), Mehlich-3-extractable P (P-M3), and ammonium oxalate-extractable P (Pox) were 386 to 1134, 5 to 85, and 60 to 823 mg kg−1, respectively. Among the sample groups, the highest concentrations of TP, P-M3, and Pox were measured in in-stream deposits. Total P was significantly correlated with Fe oxides, clay, and soil organic matter, especially in the bank and floodplain deposits. Because of the potential release of P from these sediments, we can speculate that changes in land use within the riparian areas may, at least initially, have little direct effect on soluble or particulate P loads in Walnut Creek.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, R. B., Smith, R. A., Schwarz, G. E., Boyer, E. W., Nolan, J. V., & Brakebill, J. W. (2008). Differences in phosphorus and nitrogen delivery to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River basin. Environmental Science and Technology, 42, 822–830.
Baker, R. G., Bettis 3rd, E. A., Schwert, D. P., Horton, D. G., Chumbley, C. A., Gonzalez, L. A., & Reagan, M. K. (1996). Holocene paleoenvironments of northeast Iowa. Ecological Monographs, 66, 203–234.
Bianchi, T. S., DiMarco, S. F., Cowan Jr., J. H., Hetland, R. D., Chapman, P., Day, J. W., & Allison, M. A. (2010). The science of hypoxia in the northern Gulf of Mexico: a review. Science of the Total Environment, 408, 1471–1484.
Cross, W. F., Benstead, J. P., Frost, P. C., & Thomas, S. A. (2005). Ecological stoichiometry in freshwater benthic systems: recent progress and perspectives. Freshwater Biology, 50, 1895–1912.
D’Angelo, E., Crutchfield, J., & Vandiviere, M. (2001). Rapid, sensitive, microscale determination of phosphate in water and soil. Journal of Environmental Quality, 30, 2206–2209.
Dalal, R. C. (1977). Soil organic phosphorus. Advances in Agronomy, 29, 85–117.
Deng, Y., & Dixon, J. B. (2002). Soil organic matter and organic–mineral interactions. In J. B. Dixon & D. G. Schulze (Eds.), Soil mineralogy with environmental applications (pp. 69–107). Madison: Soil Science Society of America.
Haggard, B. E., Smith, D. R., & Brye, K. R. (2007). Variations in stream water and sediment phosphorus among select Ozark catchments. Journal of Environmental Quality, 36, 1725–1734.
Hedley, M. J., Stewart, J. W. B., & Chauhan, B. S. (1982). Changes in inorganic and organic soil phosphorus fractions induced by cultivation practices and by laboratory incubations. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 46, 970–976.
Holford, I. C. R. (1997). Soil phosphorus: its measurement, and its uptake by plants. Australian Journal of Soil Research, 35, 227–239.
Hong, J. K., & Yamane, I. (1980). Inositol phosphate and inositol humic acid and fulvic acid fractions extracted by three methods. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 26, 491–496.
Hongthanat, N., Kovar, J. L., & Thompson, M. L. (2011). Sorption indices to estimate risk of soil phosphorus loss in the Rathbun Lake watershed, Iowa. Soil Science, 176, 237–244.
Hongthanat, N., Kovar, J. L., Thompson, M. L., Russell, J. R., & Isenhart, T. M. (2016). Phosphorus source–sink relationships of stream sediments in the Rathbun Lake watershed in southern Iowa, USA. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188, 453–467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5437-6
Huanxin, W., Presley, B. J., & Velinsky, D. J. (1997). Distribution and sources of phosphorus in tidal river sediments in the Washington, DC, area. Environmental Geology, 30, 224–230.
Hund, S. V., Brown, S., Lavkulich, L. M., & Oswald, S. E. (2013). Relating P lability in stream sediments to watershed land use via an effective sequential extraction scheme. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 224, 1643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1643-9
Jacobson, L. M., David, M. B., & Drinkwater, L. E. (2011). A spatial analysis of phosphorus in the Mississippi River basin. Journal of Environmental Quality, 40, 931–941.
Jarvie, H. P., Sharpley, A. N., Withers, P. J. A., Scott, J. T., Haggard, B. E., & Neal, C. (2013). Phosphorus mitigation to control river eutrophication: murky waters, inconvenient truths and ‘post-normal’ science. Journal of Environmental Quality, 42, 295–304.
Kettler, T. A., Doran, J. W., & Gilbert, T. L. (2001). Simplified method for soil particle-size determination to accompany soil-quality analyses. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 65, 849–852.
Kirkby, C. A., Kirkegaard, J. A., Richardson, A. E., Wade, L. J., Blanchard, C., & Batten, G. (2011). Stable soil organic matter: a comparison of C:N:P:S ratios in Australian and other world soils. Geoderma, 163, 197–208.
Kisand, A. (2005). Distribution of sediment phosphorus fractions in hypertrophic strongly stratified Lake Verevi. Hydrobiologia, 547, 33–39.
Kleinman, P. J. A., & Sharpley, A. N. (2002). Estimating soil phosphorus sorption saturation from Mehlich-3 data. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 33, 1825–1839.
Konen, M. E., Jacobs, P. M., Burras, C. L., Talaga, B. J., & Mason, J. A. (2002). Equations for predicting soil organic carbon using loss-on-ignition for north central U.S. soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 66, 1878–1881.
Kuo, S. (1996). Phosphorus. In D. L. Sparks (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis. Part 3. Chemical methods (pp. 869–919). Madison: Soil Science Society of America.
McDaniel, M. D., David, M. B., & Royer, T. V. (2009). Relationships between benthic sediments and water column phosphorus in Illinois streams. Journal of Environmental Quality, 38, 607–617.
McDowell, R. W., & Sharpley, A. N. (2001). A comparison of fluvial sediment phosphorus (P) chemistry in relation to location and potential to influence stream P concentrations. Aquatic Geochemistry, 7, 255–265.
McDowell, R. W., Sharpley, A. N., & Folmar, G. (2003). Modification of phosphorus export from an eastern USA catchment by fluvial sediment and phosphorus inputs. Agriculture Ecosystems and Environment, 99, 187–199.
McLaren, T. I., Smernik, R. J., McLaughlin, M. J., McBeath, T. M., Kirby, J. K., Simpson, R. J., Guppy, C. N., Doolette, A. L., & Richardson, A. E. (2015). Complex forms of soil organic phosphorus—a major component of soil phosphorus. Environmental Science & Technology, 49, 13238–13245.
Mehlich, A. (1984). Mehlich 3 soil extractant: a modification of Mehlich 2 extractant. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 15, 1409–1416.
Nelson, D. W., & Sommers, L. E. (1996). Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In D. L. Sparks (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis, part 3, Soil Science Society of America Book Series 5 (pp. 961–1010). Madison: SSSA.
Paing, J., Gomez, E., & Picot, B. (1999). Humic substances interactions with sedimentary phosphorus. Analusis, 27, 436–438.
Pettersson, K. (1998). Mechanisms for internal loading of phosphorus in lakes. Hydrobiologia, 373(374), 21–25.
Quintero, C. E., Boschetti, G. N., & Benavidez, R. A. (1999). Phosphorus retention in some soils of the Argentinean Mesopotamia. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 30, 1449–1461.
Rabalais, N. N., Turner, R. E., & Scavia, D. (2002). Beyond science into policy: Gulf of Mexico hypoxia and the Mississippi River. Bioscience, 52, 129–142.
Royer, T. V., David, M. B., & Gentry, L. E. (2006). Timing of riverine export of nitrate and phosphorus from agricultural watersheds in Illinois: Implications for reducing nutrient loading to the Mississippi river. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 4126–4131.
SAS Institute. (2012). SAS/STAT® 9.4 user’s guide (2nd ed.). Cary: SAS Institute.
Schilling, K. E., & Wolter, C. F. (2000). Application of GPS and GIS to map channel features in Walnut Creek, Iowa. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 36, 1423–1434.
Schilling, K. E., Zhang, Y. K., & Drobney, P. (2004). Water table fluctuations near an incised stream, Walnut Creek, Iowa. Journal of Hydrology, 286, 236–248.
Schilling, K. E., Hubbard, T., Luzier, J., & Spooner, J. (2006). Walnut Creek watershed restoration and water quality monitoring project: final report. Iowa City: Iowa Department of Natural Resources.
Schilling, K. E., Isenhart, T. M., Palmer, J. A., Wolter, C. F., & Spooner, J. (2011). Impacts of land-cover change on suspended sediment transport in two agricultural watersheds. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 47, 672–686.
Shang, C., & Zelazny, L. W. (2008). Selective dissolution techniques for mineral analysis of soils and sediments. In A. L. Ulery & L. R. Dress (Eds.), Methods of soil analysis, part 5—mineralogical methods (pp. 33–80). Madison: Soil Science Society of America.
Sharpley, A. N., Daniel, T., Sims, T., Lemunyon, J., Stevens, R., & Parry, R. (2003). Agricultural phosphorus and eutrophication, 2 nd edition. USDA-ARS report 149. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
Sharpley, A., Jarvie, H. P., Buda, A., May, L., Spears, B., & Kleinman, P. (2013). Phosphorus legacy: overcoming the effects of past management practices to mitigate future water quality impairment. Journal of Environmental Quality, 42, 1308–1326.
Sinaj, S., Stamm, C., Toor, G. S., Condron, L. M., Hendry, T., Di, H. J., Cameron, K. C., & Frossard, E. (2002). Phosphorus exchangeability and leaching losses from two grassland soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 31, 319–330.
Sylvan, J. B., Dortch, Q., Nelson, D. M., Brown, A. F. M., Morrison, W., & Ammerman, J. W. (2006). Phosphorus limits phytoplankton growth on the Louisiana shelf during the period of hypoxia formation. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 7548–7553.
Tiessen, H., & Moir, J. O. (2008). Characterization of available P by sequential extraction. In M. R. Carter (Ed.), Soil sampling and analysis (2nd ed., pp. 293–306). New York: Canadian Society of Soil Science.
Turner, B. L., & Haygarth, P. M. (2000). Phosphorus forms and concentrations in leachate under four grassland soil types. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 64, 1090–1099.
van Rotterdam, A. M. D., Busssink, D. W., Temminghoff, E. J. M., & van Riemsdijk, W. H. (2012). Predicting the potential of soils to supply phosphorus by integrating soil chemical processes and standard soil tests. Geoderma, 189, 617–626.
Wang, Z., Lin, C., He, M., Quan, X., & Yang, Z. (2010). Phosphorus content and fractionation of phosphate in the surface sediments of the Dalio river system in China. Environmental Earth Science, 59, 1349–1357.
Watanabe, F. S., & Olsen, S. R. (1965). Test of an ascorbic acid method for determining phosphorus in water and NaHCO3 extracts from soil. Soil Science Society of America Proceedings, 29, 677–678.
Wilson, C. G., Kuhnle, R. A., Bosch, D. D., Steiner, J. L., Starks, P. J., Tomer, M. D., & Wilson, G. V. (2008). Quantifying relative contributions from sediment sources in conservation effects assessment project watersheds. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 63, 523–532.
Xu, D., Ding, S., Li, B., Bai, X., Fan, C., & Zhang, C. (2013). Speciation of organic phosphorus in a sediment profile of Lake Taihu I: chemical forms and their transformation. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 25, 637–644.
Yao, W., & Millero, F. J. (1996). Adsorption of phosphate on manganese dioxide in seawater. Environmental Science and Technology, 30, 536–541.
You, S. J., Thakali, S., & Allen, H. E. (2006). Characteristics of soil organic matter (SOM) extracted using base with subsequent pH lowering and sequential pH extraction. Environment International, 36, 101–105.
Zaimes, G. N., Schultz, R. C., & Isenhart, T. M. (2008). Streambank soil and phosphorus losses under different riparian land-uses in Iowa. Journal of American Water Resources Association, 44, 935–947.
Zhang, H., & Kovar, J. L. (2009). Fractionation of soil phosphorus. In J. L. Kovar & G. M. Pierzynski (Eds.), Methods of phosphorus analysis for soils, sediments, residuals, and waters (2nd ed., pp. 29–32). Southern Cooperative Series Bulletin 408). Blacksburg: Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University.
Acknowledgements
The senior author’s present address is Indonesian Oil Palm Research Institute, Medan, North Sumatra, Indonesia. The authors are grateful to Teresita Chua and Jay Berkey and for technical support. This research was supported by Agriculture & Food Research Initiative Competitive Grant no. 2013-67019-21393 from the USDA National Institute of Food & Agriculture. Mention of trade names does not imply recommendation or endorsement by Iowa State University or the USDA Agricultural Research Service.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 205 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahutomo, S., Kovar, J.L. & Thompson, M.L. Inorganic and Organic Phosphorus in Sediments in the Walnut Creek Watershed of Central Iowa, USA. Water Air Soil Pollut 229, 72 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3721-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3721-5