Abstract
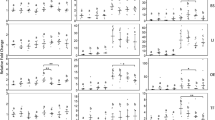
Copper is a common aqueous pollutant that is known to cause oxidative stress and disrupt the thyroid axis in amphibians. In the present study, tadpoles of the Chinese toad (Bufo gargarizans) were exposed to 1, 6.4, 32, and 64 μg L−1 of copper from Gosner stages 26 to 42. We aimed to examine the influence of copper on thyroid hormone-responsive and stress-associated gene expression in the hind-limb, tail, and liver of B. gargarizans tadpoles. Exposure to 64 μg L−1 copper decreased percent metamorphosis and increased length of both hind-limb and tail of B. gargarizans tadpoles at Gs 42. In addition, according to real-time PCR results, exposure to 64 μg L−1 copper induced downregulation of Dio2, Dio3, TRα, and TRβ mRNA levels in all tissues examined. We inferred that copper might induce a considerable reduction of TH levels through downregulation of Dio2 and Dio3 mRNA levels in peripheral tissues. Decreased TH levels may then decrease the expressions of TRα and TRβ. Also, HSP, SOD, and PHGPx transcript levels were measured to assess cellular stress which might affect TH signaling and metamorphosis. We found that copper significantly downregulated the level of HSP, SOD, and PHGPx transcripts in the hind-limb and tail. This demonstrates that high concentrations of copper could disrupt the antioxidant system of B. gargarizans tadpoles and increase oxidative damage. Therefore, we conclude that copper could disrupt the antioxidant system and cause thyroid hormone disruption in B. gargarizans tadpoles.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asagba, S. O., Eriyamremu, G. E., & Igberaese, M. E. (2008). Bioaccumulation of cadmium and its biochemical effects on selected tissues of the catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 34, 61–69.
Atli, G., & Canli, M. (2007). Enzymatic responses to metal exposures in a freshwater fish, Oreochromis niloticus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C. Toxicol. Pharmacol., 145, 282–287.
Barry, M. J. (2011). Effects of copper, zinc and dragonfly kairomone on growth rate and induced morphology of Bufo arabicus tadpoles. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 74, 918–923.
Bopp, S. K., Abicht, H. K., & Knauer, K. (2008). Copper-induced oxidative stress in rainbow trout gill cells. Aquatic Toxicology, 86, 197–204.
Brown, D. D., & Cai, L. (2007). Amphibian metamorphosis. Developmental Biology, 306, 20–33.
Brown, D. D., Wang, Z., Furlow, J. D., Kanamori, A., Schwartzman, R. A., Remo, B. F., & Pinder, A. (1996). The thyroid hormone-induced tail resorption program during Xenopus laevis metamorphosis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 93, 1924–1929.
Chai, L. H., Wang, H. Y., Deng, H. Z., Zhao, H. F., & Wang, W. K. (2014). Chronic exposure effects of copper on growth, metamorphosis and thyroid gland, liver health in Chinese toad, Bufo gargarizans tadpoles. Chemistry and Ecology, 30, 589–601.
Chen, T., Gross, J. A., & Karasov, W. H. (2007). Adverse effects of chronic copper exposure in larval northern leopard frogs (Rana pipiens). Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 26, 1470–1475.
Cheung, J., & Smith, D. F. (2000). Molecular chaperone interactions with steroid receptors: an update. Molecular Endocrinology, 14, 939–946.
Connors, K. A., Korte, J. J., Anderson, G. W., & Degitz, S. J. (2010). Characterization of thyroid hormone transporter expression during tissue-specific metamorphic events in Xenopus tropicalis. Gen. Comp. Endocr., 168, 149–159.
Craig, E. A. (1985). The heat shock response. CRC Critical Reviews in Biochemistry, 18, 239–280.
Csermely, P., Schnaider, T., Soti, C., Prohaszka, Z., & Nardai, G. (1998). The 90-kDa molecular chaperone family: structure, function, and clinical applications. A comprehensive review. Pharmacol. Ther., 79, 129–168.
Denver, R. J., Hu, F., Scanlan, T. S., & Furlow, J. D. (2009). Thyroid hormone receptor subtype specificity for hormone-dependent neurogenesis in Xenopus laevis. Developmental Biology, 326, 155–168.
Doyotte, A., Cossu, C., Jacquin, M., Babut, M., & Vasseur, P. (1997). Antioxidant enzymes, glutathione and lipid peroxidation as relevant biomarkers of experimental or field exposure in the gills and the digestive gland of the freshwater bivalve Unio tumidus. Aquatic Toxicology, 39, 93–110.
Eliceiri, B. P., & Brown, D. D. (1994). Quantitation of endogenous thyroid hormone receptors alpha and beta during embryogenesis and metamorphosis in Xenopus laevis. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 269, 24459–24465.
Forrest, D., & Visser, T. J. (2013). Thyroid hormone signaling. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1830, 3859.
Furlow, J. D., & Neff, E. S. (2006). A developmental switch induced by thyroid hormone: Xenopus laevis metamorphosis. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism, 17, 40–47.
Gaetke, L. M., & Chow, C. K. (2003). Copper toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidant nutrients. Toxicology, 189, 147–163.
Gao, Q., Zhao, J., Song, L., Qiu, L., Yu, Y., Zhang, H., & Ni, D. (2008). Molecular cloning, characterization and expression of heat shock protein 90 gene in the haemocytes of bay scallop Argopecten irradians. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 24, 379–385.
Gechev, T., Gadjev, I., Van Breusegem, F., Inzé, D., Dukiandjiev, S., Toneva, V., & Minkov, I. (2002). Hydrogen peroxide protects tobacco from oxidative stress by inducing a set of antioxidant enzymes. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 59, 708–714.
Gereben, B., Zavacki, A. M., Ribich, S., Kim, B. W., Huang, S. A., Simonides, W. S., Zeold, A., & Bianco, A. C. (2008). Cellular and molecular basis of deiodinase-regulated thyroid hormone signaling. Endocrine Reviews, 29, 898–983.
Gosner, K. L. (1960). A simplified table for staging anuran embryos and larvae with notes on identification. Herpetologica, 16, 183–190.
Gravato, C., Teles, M., Oliveira, M., & Santos, M. A. (2006). Oxidative stress, liver biotransformation and genotoxic effects induced by copper in Anguilla anguilla L.: the influence of pre-exposure to β-naphthoflavone. Chemosphere, 65, 1821–1830.
Gultekin, F., Delibas, N., Yasar, S., & Killinc, I. (2001). In vivo changes in antioxidant systems and protective role of melatonin and a combination of vitamin C and vitamin E on oxidative damage in erythrocytes induced by chlorpyrifos-ethyl in rats. Archives of Toxicology, 75, 88–96.
Haywood, L. K., Alexander, G. J., Byrne, M. J., & Cukrowska, E. (2004). Xenopus laevis embryos and tadpoles as models for testing for pollution by zinc, copper, lead, and cadmium. African Zoology, 39, 163–174.
Huang, H., Marsh-Armstrong, N., & Brown, D. D. (1999). Metamorphosis is inhibited in transgenic Xenopus laevis tadpoles that overexpress type III deiodinase. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 96, 962–967.
Itoh, K., Watanabe, K., Wu, X., & Suzuki, T. (2010). Three members of the iodothyronine deiodinase family, dio1, Dio2 and Dio3, are expressed in spatially and temporally specific patterns during metamorphosis of the flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Zoological Science, 27, 574–580.
Jiang, J., Shi, Y., Shan, Z., Yang, L., Wang, X., & Shi, L. (2012). Bioaccumulation, oxidative stress and HSP70 expression in Cyprinus carpio L. exposed to microcystin-LR under laboratory conditions. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol, 155, 483–490.
Kanamori, A., & Brown, D. D. (1992). The regulation of thyroid hormone receptor β genes by thyroid hormone in Xenopus laevis. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 267, 739–745.
Kawahara, A., Baker, B. S., & Tata, J. R. (1991). Developmental and regional expression of thyroid hormone receptor genes during Xenopus metamorphosis. Development, 112, 933–943.
Kawahara, A., Gohda, Y., & Hikosaka, A. (1999). Role of type III iodothyronine 5-deiodinase gene expression in temporal regulation of Xenopus metamorphosis. Development, Growth & Differentiation, 41, 365–373.
Kesheri, M., Kanchan, S., Richa, & Sinha, R. P. (2014). Isolation and in silico analysis of Fe-superoxide dismutase in the cyanobacterium Nostoc commune. Gene, 553, 117–125.
Kuiper, G. G., Klootwijk, W., Morvan, D. G., Destree, O., Darras, V. M., Van der Geyten, S., Demeneix, B., & Visser, T. J. (2006). Characterization of recombinant Xenopus laevis type I iodothyronine deiodinase: substitution of a proline residue in the catalytic center by serine (Pro132Ser) restores sensitivity to 6–propyl–2-thiouracil. Endocrinology, 147, 3519–3529.
Lance, S. L., Erickson, M. R., Flynn, R. W., Mills, G. L., Tuberville, T. D., & Scott, D. E. (2012). Effects of chronic copper exposure on development and survival in the southern leopard frog (Lithobates [Rana] sphenocephalus). Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 7, 1587–1594.
Lee, H., Kang, C., Yoo, Y. S., Hah, D. Y., Kim, C. H., Kim, E., & Kim, J. S. (2013). Cytotoxicity and the induction of the stress protein HSP 70 in Chang liver cells in response to zearalenone-induced oxidative stress. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 36, 732–740.
Li, C., Shi, L., Chen, D., Ren, A., Gao, T., & Zhao, M. (2015). Functional analysis of the role of glutathione peroxidase (GPx) in the ROS signaling pathway, hyphal branching and the regulation of ganoderic acid biosynthesis in Ganoderma lucidum. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 82, 168–180.
Lin, Y. C., Vaseeharan, B., & Chen, J. C. (2008). Identification of the extracellular copper–zinc superoxide dismutase (ecCuZnSOD) gene of the mud crab Scylla serrata and its expression following beta-glucan and peptidoglycan injections. Molecular Immunology, 5, 1346–1355.
Liu, H., Chen, H., Jing, J., & Ma, X. (2012). Cloning and characterization of the HSP90 beta gene from Tanichthys albonubes Lin (Cyprinidae): effect of copper and cadmium exposure. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 38, 745–756.
Loro, V. L., Jorge, M. B., Silva, K. R., & Wood, C. M. (2012). Oxidative stress parameters and antioxidant response to sub-lethal waterborne zinc in a euryhaline teleost Fundulus heteroclitus: protective effects of salinity. Aquatic Toxicology, 110-111, 187–193.
Lushchak, V. I. (2011). Environmentally induced oxidative stress in aquatic animals. Aquatic Toxicology, 101, 13–30.
Mathieu-Denoncourt, J., Martyniuk, C. J., de Solla, S. R., Balakrishnan, V. K., & Langlois, V. S. (2014). Sediment contaminated with the Azo Dye disperse yellow 7 alters cellular stress- and androgen-related transcription in Silurana tropicalis larvae. Environmental Science & Technology, 48, 2952–2961.
Miyata, K., & Ose, K. (2012). Thyroid hormone-disrupting effects and the amphibian metamorphosis assay. Toxicologic Pathology, 25, 1–9.
Mullur, R., Liu, Y. Y., & Brent, G.A. (2014). Thyroid hormone regulation of metabolism. Physiological Reviews, 94, 355–382.
Muthukumar, K., Rajakumar, S., Sarkar, M. N., & Nachiappan, V. (2011). Glutathione peroxidase3 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae protects phospholipids during cadmium-induced oxidative stress. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 99, 761–771.
Nations, S., Long, M., Wages, M., Maul, J. D., Theodorakis, C. W., & Cobb, G. P. (2015). Subchronic and chronic developmental effects of copper oxide (CuO) nanoparticles on Xenopus laevis. Chemosphere, 135, 166–174.
Ni, D., Song, L., Gao, Q., Wu, L., Yu, Y., Zhao, J., Qiu, L., Zhang, H., & Shi, F. (2007). The cDNA cloning and mRNA expression of cytoplasmic Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene in scallop Chlamys farreri. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 23, 1032–1042.
Oksala, N. K., Ekmekçi, F. G., Ozsoy, E., Kirankaya, S., Kokkola, T., Emecen, G., Lappalainen, J., Kaarniranta, K., & Atalay, M. (2014). Natural thermal adaptation increases heat shock protein levels and decreases oxidative stress. Redox Biology, 3, 25–28.
Opitz, R., Lutz, I., Nguyen, N. H., Scanlan, T. S., & Kloas, W. (2006). Analysis of thyroid hormone receptor βA mRNA expression in Xenopus laevis tadpoles as a means to detect agonism and antagonism of thyroid hormone action. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 212, 1–13.
Ossana, N. A., Castañé, P. M., Poletta, G. L., Mudry, M. D., & Salibián, A. (2010). Toxicity of waterborne copper in premetamorphic tadpoles of Lithobates catesbeianus (Shaw, 1802). Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 84, 712–715.
Parris, M. J., & Baud, D. R. (2004). Interactive effects of a heavy metal and chytridiomycosis on gray treefrog larvae (Hyla chrysoscelis). Copeia, 2, 344–350.
Pechmann, J. H. K., Scott, D. E., Gibbons, J. W., & Semlitsch, R. D. (1989). Influence of wetland hydroperiod on diversity and abundance of metamorphosing juvenile amphibians. Wetlands Ecology and Management, 1, 3–11.
Pedrajas, J. R., Peinado, J., & López-Barea, J. (1995). Oxidative stress in fish exposed to model xenobiotics. Oxidatively modified forms of Cu, Zn-superoxide dismutase as potential biomarkers. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 3, 267–282.
Picard, D. (2002). Heat-shock protein 90, a chaperone for folding and regulation. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 59, 1640–1648.
Pritchard, K. A., Ackerman, A. W., Gross, E. R., Stepp, D. W., Shi, Y., Fontana, J. T., Baker, J. E., & Sessa, W. C. (2001). Heat shock protein 90 mediates the balance of nitric oxide and superoxide anion from endothelial nitric-oxide synthase. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276, 17621–17624.
Robert, J. (2003). Evolution of heat shock protein and immunity. Developmental and Comparative Immunology, 27, 449–464.
Shi, Y. B. (2000). Amphibian metamorphosis: from morphology to molecular biology. New York: Wiley-Liss.
Stephanou, A., & Latchman, D. S. (2011). Transcriptional modulation of heat-shock protein gene expression. Biochemistry Research International, 238601.
Stilborn, S. S., Manzon, L. A., Schauenberg, J. D., & Manzon, R. G. (2013). Thyroid hormone deiodinase type 2 mRNA levels in sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus) are regulated during metamorphosis and in response to a thyroid challenge. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 183, 63–68.
Sujiwattanarat, P., Pongsanarakul, P., Temsiripong, Y., Temsiripong, T., Thawornkuno, C., Uno, Y., Unajak, S., Matsuda, Y., Choowongkomon, K., & Srikulnath, K. (2016). Molecular cloning and characterization of Siamese crocodile (Crocodylus siamensis) copper, zinc superoxide dismutase (CSI-Cu,Zn-SOD) gene. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. Part A, Molecular & Integrative Physiology, 191, 187–195.
Troy, C. M., & Shelanski, M. L. (1994). Down-regulation of copper/zinc superoxide dismutase causes apoptotic cell death in PC12 neuronal cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 91, 6384–6387.
USEPA. (2007). Aquatic life ambient freshwater quality criteria for copper. In EPA-822-R-07-001. DC, U. S. A: Washington.
Veldhoen, N., Skirrow, R.C., Osachoff, H., Wigmore, H., Clapson, D.J., Gunderson, M.P., et al., 2006a b. The bactericidal agent triclosan modulates thyroid hormone-associated gene expression and disrupts postembryonic anuran development. Aquatic Toxicology 80, 217–227.
Veldhoen, N., Skirrow, R.C., Ji, L., Domanski, D., Bonfield, E.R., Bailey, C.M., et al., 2006b a. Use of heterologous cDNA arrays and organ culture in the detection of thyroid hormone-dependent responses in a sentinel frog, Rana catesbeiana. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. D. Genomics Proteomics 1, 187–199.
Wang, Z., & Brown, D. D. (1993). Thyroid hormone-induced gene expression program for amphibian tail resorption. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 268, 16270–16278.
Wang, X. D., Matsuda, H., & Shi, Y. B. (2008). Developmental regulation and function of thyroid hormone receptors and 9-cis retinoic acid receptors during Xenopus tropicalis metamorphosis. Endocrinology, 149, 5610–5618.
Wang, C., Liang, G., Chai, L. H., & Wang, H. Y. (2016). Effects of copper on growth, metamorphosis and endocrine disruption of Bufo gargarizans larvae. Aquatic Toxicology, 170, 24–30.
Wei, K. Q., & Yang, J. X. (2015). Oxidative damage induced by copper and beta-cypermethrin in gill of the freshwater crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 113, 446–453.
Won, E. J., Rhee, J. S., Kim, R. O., Ra, K., Kim, K. T., Shin, K. H., & Lee, J. S. (2012). Susceptibility to oxidative stress and modulated expression of antioxidant genes in the copper-exposed polychaete Perinereis nuntia. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C. Toxicol. Pharmacol., 155, 344–351.
Xia, K., Zhao, H. F., Wu, M. Y., & Wang, H. Y. (2012). Chronic toxicity of copper on embryo development in Chinese toad, Bufo gargarizans. Chemosphere, 87, 1395–1402.
Yang, Y., Liu, B., Dai, J., Srivastava, P. K., Zammit, D. J., Lefrançois, L., & Li, Z. (2007). Heat shock protein gp96 is a master chaperone for toll-like receptors and is important in the innate function of macrophages. Immunity, 26, 215–226.
Yaoita, Y., & Brown, D. D. (1990). A correlation of thyroid hormone receptor gene expression with amphibian metamorphosis. Genes & Development, 4, 1917–1924.
Yologlu, E., & Ozmen, M. (2015). Low concentrations of metal mixture exposures have adverse effects on selected biomarkers of Xenopus laevis tadpoles. Aquatic Toxicology, 168, 19–27.
Zapata, M., Tanguy, A., David, E., Moraga, D., & Riquelme, C. (2009). Transcriptomic response of Argopecten purpuratus post-larvae to copper exposure under experimental conditions. Gene, 442, 37–46.
Zizza, M., Canonaco, M., & Facciolo, R. M. (2015). Neurobehavioral alterations plus transcriptional changes of the heat shock protein 90 and hypoxia inducible factor-1α in the crucian carp exposed to copper. Neurotoxicology, 52, 162–175.
Funding
The current work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41401570, No.31572222) and Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province, China (No. 2015JQ4098, No. 2016JM3009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Highlights
1. Copper could decrease percent metamorphosis of Bufo gargarizans larvae.
2. Copper increased tail length and hind-limb length of Bufo gargarizans larvae.
3. Sixty-four micrograms per liter copper downregulated transcripts of Dio2, Dio3, TRα, and TRβ in the hind-limb, tail, and liver.
4. Copper changed mRNA expressions of HSP, SOD, and PHGPx in the hind-limb and tail.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chai, L., Chen, A., Deng, H. et al. Inhibited Metamorphosis and Disruption of Antioxidant Defenses and Thyroid Hormone Systems in Bufo gargarizans Tadpoles Exposed to Copper. Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 359 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3548-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3548-5