Abstract
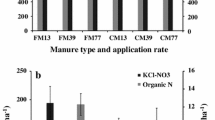
Livestock manure and compost are commonly used to supply nutrients for crops and improve soil quality. However, excess application may increase the risk of nutrient loss and eutrophication. We investigated the potential leaching losses of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and non-purgeable organic carbon (NPOC) over 105 days in the laboratory. Soils were amended with four treatments: (1) manure (BM) and (2) compost (BC) from cattle fed a typical finishing diet, (3) manure (DDGSM), and (4) compost (DDGSC) from cattle fed diets containing 60 % wheat dried distillers’ grains with solubles (DDGS) replacing barley grain. A non-amended control soil was included for comparison. Leachate samples were collected 0, 7, 21, 42, 70, and 105 days after amendment application. Amendment application significantly increased leaching loss of total nitrogen (TN), NO3 −-N, NH4 +-N, total phosphorus (TP), ortho-P (PO4 3−-P), and NPOC from soils by 2.2 to 154.8 times compared with the control. Regardless of whether DDGS was included in cattle diet, cumulative leaching losses of TN, NO3 −-N, TP, and PO4 3−-P were significantly higher, while NH4 +-N and NPOC were lower from compost-amended soil than manure-amended soil. The proportion of cumulative N leaching losses relative to the total N applied was greater with DDGSM and DDGSC than BM and BC, while a greater proportion of total P was leached from DDGSM and DDGSC than BM. Based on the results, more attention should be paid to the potential risk of soil nutrient leaching posed after applying manure and compost, and the higher risk of N and P leaching losses from soil amended with DDGS manure and compost than manure from beef cattle fed typical finishing diets.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson, H., Bergström, L., Djodjic, F., Ulén, B., & Kirchmann, H. (2013). Topsoil and subsoil properties influence phosphorus leaching from four agricultural soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 42(2), 455–463.
Aronsson, H., Liu, J., Ekre, E., Torstensson, G., & Salomo, E. (2014). Effects of pig and dairy slurry application on N and P leaching from crop rotations with spring cereals and forage leys. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 98(3), 281–293.
Ashworth, D., & Alloway, B. (2004). Soil mobility of sewage sludge-derived dissolved organic matter, copper, nickel and zinc. Environmental Pollution, 127(1), 137–144.
Basso, B., & Ritchie, J. T. (2005). Impact of compost, manure and inorganic fertilize on nitrate leaching and yield for a 6-year maize-alfalfa rotation in Michigan. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 108(4), 329–341.
Benke, M. B., Hao, X., Caffyn, P., Schoenau, J. J., & McAllister, T. A. (2010). Using manure from cattle fed dried distillers’ grains with solubles (DDGS) as fertilizer: effects on nutrient accumulation in soil and uptake by barley. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 139(4), 720–727.
Berger, L. L., & Good, D. L. (2007). Distillers dried grains plus solubles utilization by livestock and poultry, in corn-based ethanol in Illinois and the US: a report from the Department of Agricultural and Consumer Economics (pp. 97–111). Illinois: University of Illinois.
Brady, N. C., & Weil, R. R. (2012). The nature and properties of soils. New Delhi: Dorling Kindersley (India) Pvt. Ltd.
Canh, T. T., Aarnink, A. J. A., Schutte, J. B., Sutton, A., Langhout, D. J., & Werstegen, M. W. A. (1998). Dietary protein affects nitrogen excretion and ammonia emission from slurry of growing finishing pigs. Livestock Production Science, 56(3), 181–191.
Chadwick, D. R., John, F., Pain, B. F., Chambers, B. J., & Williams, J. (2000). Plant uptake of nitrogen from the organic nitrogen fraction of animal manures: a laboratory experiment. Journal of Agricultural Science, 134(2), 159–168.
Cooperband, L., Bollero, G., & Coale, F. (2002). Effect of poultry litter and composts on soil nitrogen and phosphorus availability and corn production. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 62(2), 185–194.
Deluca, T. H., & Deluca, D. K. (1997). Composting for feedlot manure management and soil quality. Journal of Production Agriculture, 10(2), 235–241.
Duong, T. T. T., Verma, S. L., Penfold, C., & Marschner, P. (2013). Nutrient release from composts into the surrounding soil. Geoderma, 195–196, 42–47.
Eghball, B., Binford, G. D., & Baltensperger, D. D. (1996). Phosphorus movement and adsorption in a soil receiving long-term manure and fertilizer application. Journal of Environmental Quality, 25(6), 1339–1343.
Elmi, A., Madani, A., Gordon, R., MacDonald, P., & Stratton, G. W. (2005). Nitrate nitrogen in the soil profile and drainage water as influenced by manure and mineral fertilizer application in a barley-carrot production system. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 160(1), 119–132.
European Environment Agency (EEA). (2000). Groundwater quality and quantity in Europe. Environmental assessment report no 3. Copenhagen: European Environment Agency.
Fierer, N., & Schimel, J. P. (2002). Effects of drying-rewetting frequency on soil carbon and nitrogen transformations. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 34(6), 777–787.
Frossard, E., Skrabal, P., Sinaj, S., Bangerter, F. S., & Traoré, O. (2002). Forms and exchangeability of inorganic phosphate in composted solid organic wastes. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 62(2), 103–113.
Gagnon, B., & Simard, R. R. (1999). Nitrogen and phosphorus release from on-farm and industrial composts. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 79(3), 481–489.
Glæsner, N., Kjaergaard, C., Rubæk, G. H., & Magid, J. (2011). Interactions between soil texture and placement of dairy slurry application: II, leaching of phosphorus forms. Journal of Environmental Quality, 40(2), 344–351.
González, C. E. A., Gil, E., Fernández-Falcón, M., & Hernández, M. M. (2009). Water leachates of nitrate nitrogen and cations from poultry manure added to an alfisol udalf soil. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 202(1), 273–288.
Hao, X., Benke, M. B., Gibb, D., Stronks, A., Travis, G., & McAllister, T. A. (2009). Effects of dried distillers’ grains with solubles (wheat-based) in feedlot cattle diets on feces and manure composition. Journal of Environmental Quality, 38(4), 1709–1718.
Hao, X., Benke, M., Larney, F. J., & McAllister, T. A. (2011). Greenhouse gas emissions when composting manure from cattle fed wheat dried distillers’ grains with solubles. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 89(1), 105–114.
Hao, X., Hill, B., Caffyn, P., Travis, G., Olson, A. F., Larney, F. J., McAllister, T., & Alexander, T. (2014). Co-composting of beef cattle feedlot manure with construction and demolition waste. Journal of Environmental Quality, 43(5), 1799–1808.
Jardine, P. M., Mayes, M., Mulholland, P. J., Hanson, P. J., Tarver, J. R., Luxmoore, R. J., McCarthy, J. F., & Wilson, G. V. (2006). Vadose zone flow and transport of dissolved organic carbon at multiple scales in humid regimes. Vadose Zone Journal, 5(1), 140–152.
Kindler, R., Siemens, J., Kaiser, K., Walmsley, D. C., Bernhofer, C., Buchmann, N., Cellier, P., Eugster, W., Gleixner, G., Grunwald, T., Heim, A., Ibrom, A., Jones, S. K., Jones, M., Klumpp, K., Kutsch, W., Steenberg, L. K., Lehuger, S., Loubet, B., McKenzie, R., Moors, E., Osborne, B., Pilegaard, K., Rebmann, C., Saunders, M., Schmidt, M. W. I., Schrumpf, M., Seyfferth, J., Skiba, U., Soussana, J. F., Sutton, M. A., Tefs, C., Vowinckel, B., Zeeman, M. J., & Kaupenjohann, M. (2011). Dissolved carbon leaching is a major component of net ecosystem carbon balances. Global Change Biology, 17(2), 1167–1185.
Klopfenstein, T. J., Erikson, G. E., & Bremer, V. R. (2008). Board-invited review: use of distillers by-products in the beef cattle feeding industry. Journal of Animal Science, 86(5), 1223–1231.
Lai, D. Y. F. (2014). Phosphorus fractions and fluxes in the soils of a free surface flow constructed wetland in Hong Kong. Ecological Engineering, 73, 73–79.
Lang, M., Li, P., Han, X. Z., Qiao, Y. F., & Miao, S. J. (2016). Gross nitrogen transformations in black soil under different land uses and management systems. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 52(2), 233–241.
Larney, F. J., Buckley, K. E., Hao, X., & McCaughey, W. P. (2006). Fresh, stockpiled, and composted beef cattle feedlot manure: nutrient levels and mass balance estimates in Alberta and Manitoba. Journal of Environmental Quality, 35(6), 1844–1854.
Liang, L., & Singer, P. C. (2003). Factors influencing the formation and relative distribution of haloacetic acids and trihalomethanes in drinking water. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(13), 2920–2928.
Liu, J., Aronsson, H., Bergström, L., & Sharpley, A. (2012). Phosphorus leaching from loamy sand and clay loam topsoils after application of pig slurry. SpringerPlus, 1(1), 53–63.
Masaka, J., Wuta, M., Nyamangara, J., & Mugabe, F. T. (2013). Effect of manure quality on nitrate leaching and groundwater pollution in wetland soil under field tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum, Mill var. Heinz) rape (Brassica napus, L var. Giant). Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 96(2), 149–170.
Miller, J. J., Beasley, B. W., Drury, C. F., Hao, X., & Larney, F. J. (2013). Transport of residual nitrogen and carbon through intact soil cores amended with stockpiled feedlot manure with wood-chip or straw bedding. Journal of Environmental Quality, 42(6), 1881–1888.
Moshi, A. O., Wild, A., & Greenland, D. J. (1974). Effect of organic matter on the charge and phosphate adsorption characteristics of kikuyu red clay from Kenya. Geoderma, 11(4), 275–285.
Nest, T. V., Vandecasteele, B., Ruysschaert, G., Cougnon, M., Merckx, R., & Reheul, D. (2014). Effect of organic and mineral fertilizers on soil P and C levels, crop yield and P leaching in a long term trial on a silt loam soil. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 197, 309–317.
Parkinson, J. A., & Allen, S. E. (1975). A wet oxidation procedure suitable for the determination of nitrogen and mineral nutrients in biological material. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 6(1), 1–11.
Parvage, M. M., Ulén, B., & Kirchmann, H. (2015a). Are horse paddocks threatening water quality through excess loading of nutrients? Journal of Environmental Management, 147, 306–313.
Parvage, M. M., Ulén, B., & Kirchmann, H. (2015b). Nutrient leaching from manure-amended topsoils (Cambisols and Histosols) in Sweden. Geoderma Regional, 5, 209–214.
Qian, P., & Schoenau, J. J. (2002). Availability of nitrogen in solid manure amendments with different C:N ratios. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 82(2), 219–225.
Schelde, K., de Jonge, L. W., Kjaergaard, C., Laegdsmand, M., & Rubaek, G. H. (2006). Effects of manure application and plowing on transport of colloids and phosphorus to tile drains. Vadose Zone Journal, 5(1), 445–458.
Spiehs, M. J., Whitney, M. H., & Shurson, G. C. (2002). Nutrient database for distillers dried grains with solubles produced from new ethanol plants in Minnesota and South Dakota. Journal of Animal Science, 80(10), 2639–2645.
Tong, Y. A., Emteryd, O., Lu, D. Q., & Grip, H. (1997). Effect of organic manure and chemical fertilizer on nitrogen uptake and nitrate leaching in a Eum-orthic anthrosols profile. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 48(3), 225–229.
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). (1990). National pesticide survey. Summary results of EPA’s national survey of pesticide in drinking water well. Draft 31 October 1990. Washington, DC: USEPA.
USEPA. (1992). National water inventory, report to US congress.
USEPA. (1993). Determination of total kjeldahl nitrogen and phosphorus in water. Cincinnati, OH: USEPA.
USEPA. (1996). Environmental indicators of water quality in the United States (USEPA 841-R-96–002. USEPA, Office of Water (4503F)). Washington, D.C.: US Gov. Print. Office.
Van Gaelen, N., Verschoren, V., Clymans, W., Poesen, J., Govers, G., Vanderborght, J., & Diels, J. (2014). Controls on dissolved organic carbon export through surface runoff from loamy agricultural soils. Geoderma, 226–227, 387–396.
Webb, J., Sørensen, P., Velthof, G., Amon, B., Pinto, M., Rodhe, L., Salomon, E., Hutchings, N., Burczyk, P., & Reid, J. (2013). An assessment of the variation of manure nitrogen efficiency throughout Europe and an appraisal of means to increase manure-N efficiency. Advances in Agronomy, 119, 371–442.
World Health Organization (WHO). (2004). Guidelines for drinking water quality (3rd ed.). Geneva: WHO.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by Agricultural Bioproducts Innovation Program (ABIP), Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41301345, 41101284), the China Government Scholarship (201409040013), and the Jiangsu Government Scholarship for Overseas Studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Lang, M., Li, C. et al. Nutrient Leaching from Soil Amended with Manure and Compost from Cattle Fed Diets Containing Wheat Dried Distillers’ Grains with Solubles. Water Air Soil Pollut 227, 393 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3094-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3094-6