Abstract
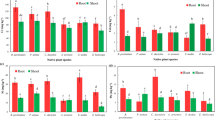
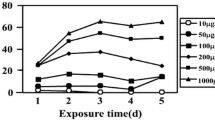
The stress tolerance of wetland plants is crucial for their appropriate application in constructed wetland (CW). Ammonia, one of the major pollutants in wastewater, is nutrition for plants at low concentrations but could be toxic at excess concentrations. This study aimed to investigate the effect of external ammonia at different concentrations (0, 1, 2, 4, 8, 10 mg L−1) to a specific submerged plant Potamogeton crispus (P. crispus), which has been used widely in CW. Results showed that the threshold value of ammonia for P. crispus was 4 mg L−1, under which no obvious variations from the control group were detected in all associated observations. When ammonia concentration exceeded 4 mg L−1, plants displayed significant increase in lipid peroxidation product contents (MDA, O2 − and H2O2), antioxidant enzyme activities (T-SOD, POD, and CAT), and a corresponding increase in the percentages of electrolyte leakage. However, external ammonia only had slight effect on the chlorophyll synthesis of P. crispus under the studied concentration range. Excess ammonia exposure (≥4 mg L−1) could affect the physiological responses of P. crispus, by inducing oxidative stress and by limitedly altering permeability of cell membrane and plant photosynthesis. The results of this study supplied useful information for the aquatic vegetation collocation in CW design, and it is suggested to take proper application of P. crispus in CW when treating eutrophication or other relatively heavily polluted water.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, M., Vajpayee, P., Tripathi, R., Rai, U., Kumar, A., Singh, N., Behl, H., & Singh, S. (2000). Mercury bioaccumulation induces oxidative stress and toxicity to submerged macrophyte Potamogeton crispus L. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 65, 573–582.
Asada, K. (1992). Ascorbate peroxidase—a hydrogen peroxide-scavenging enzyme in plants. Physiologia Plantarum, 85, 235–241.
Barata, C., Varo, I., Navarro, J. C., Arun, S., & Porte, C. (2005). Antioxidant enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation in the freshwater cladoceran Daphnia magna exposed to redox cycling compounds. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology, 140, 175–186.
Brix, H. (1997). Do macrophytes play a role in constructed treatment wetlands? Water Sci Technol, 35, 11–17.
Cao, T., Ni, L., & Xie, P. (2004). Acute biochemical responses of a submersed macrophyte, Potamogeton crispus L., to high ammonium in an aquarium experiment. J Freshwater Ecol, 19, 279–284.
Dewez, D., Geoffroy, L., Vernet, G., & Popovic, R. (2005). Determination of photosynthetic and enzymatic biomarkers sensitivity used to evaluate toxic effects of copper and fludioxonil in alga Scenedesmus obliquus. Aquatic Toxicology, 74, 150–159.
Dunne, E. J., Coveney, M. F., Hoge, V. R., Conrow, R., Naleway, R., Lowe, E. F., Battoe, L. E., & Wang, Y. (2015). Phosphorus removal performance of a large-scale constructed treatment wetland receiving eutrophic lake water. Ecol Eng, 79, 132–142.
Huang, L., Lu, Y., Gao, X., Du, G., Ma, X., Liu, M., Guo, J., & Chen, Y. (2013). Ammonium-induced oxidative stress on plant growth and antioxidative response of duckweed (Lemna minor L.). Ecol Eng, 58, 355–362.
Jampeetong, A., & Brix, H. (2009). Effects of NH +4 concentration on growth, morphology and NH +4 uptake kinetics of Salvinia natans. Ecol Eng, 35, 695–702.
Jampeetong, A., Brix, H., & Kantawanichkul, S. (2012). Response of Salvinia cucullata to high NH +4 concentrations at laboratory scales. Ecotox Environ Safe, 79, 69–74.
Jiao, L., Wang, S. & Jin, X. (2009). Physiological responses of Myriophyllum spicatum to ammonium nitrogen. Ying yong sheng tai xue bao= The journal of applied ecology/Zhongguo sheng tai xue xue hui, Zhongguo ke xue yuan Shenyang ying yong sheng tai yan jiu suo zhu ban, 20, 2283-2288.
Jin, X., Guo, J., Xu, Q., Hu, X., & Zhang, R. (2008). Effects of different concentrations of NH +4 on antioxidant system of Hydrilla verticillata and Myriophyllum spicatum. Ecology and Environment, 17, 1–5.
Li, C., Zhang, B., Zhang, J., Wu, H., Xie, H., Xu, J., & Qi, P. (2011). Physiological responses of three plant species exposed to excess ammonia in constructed wetland. Desalin Water Treat, 32, 271–276.
Lichtenthaler, H. K. (1987). Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Methods in enzymology, 148, 350–382.
Livingstone, D. (2003). Oxidative stress in aquatic organisms in relation to pollution and aquaculture. Revue de Medecine Veterinaire, 154, 427–430.
Manios, T., Stentiford, E. I., & Millner, P. A. (2003). The effect of heavy metals accumulation on the chlorophyll concentration of Typha latifolia plants, growing in a substrate containing sewage sludge compost and watered with metaliferus water. Ecol Eng, 20, 65–74.
Mates, J. (2000). Effects of antioxidant enzymes in the molecular control of reactive oxygen species toxicology. Toxicology, 153, 83–104.
Mittler, R. (2002). Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends in Plant Science, 7, 405–410.
Mittler, R., Vanderauwera, S., Gollery, M., & Van Breusegem, F. (2004). Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends in Plant Science, 9, 490–498.
Moran, J. F., Becana, M., Iturbe-Ormaetxe, I., Frechilla, S., Klucas, R. V., & Aparicio-Tejo, P. (1994). Drought induces oxidative stress in pea plants. Planta, 194, 346–352.
Nimptsch, J., & Pflugmacher, S. (2007). Ammonia triggers the promotion of oxidative stress in the aquatic macrophyte Myriophyllum mattogrossense. Chemosphere, 66, 708–714.
Nivala, J., Hoos, M. B., Cross, C., Wallace, S., & Parkin, G. (2007). Treatment of landfill leachate using an aerated, horizontal subsurface-flow constructed wetland. Sci Total Environ, 380, 19–27.
Ogawa, K. i., Kanematsu, S., & Asada, K. (1997). Generation of superoxide anion and localization of Cu Zn-superoxide dismutase in the vascular tissue of spinach hypocotyls: their association with lignification. Plant and Cell Physiology, 38, 1118–1126.
Rikans, L. E., & Hornbrook, K. R. (1997). Lipid peroxidation, antioxidant protection and aging. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis of Disease, 1362, 116–127.
Somashekaraiah, B., Padmaja, K., & Prasad, A. (1992). Phytotoxicity of cadmium ions on germinating seedlings of mung bean (Phaseolus vulgaris): involvement of lipid peroxides in chlorophyll degradation. Physiologia Plantarum, 85, 85–89.
Stottmeister, U., Wießner, A., Kuschk, P., Kappelmeyer, U., Kästner, M., Bederski, O., Müller, R. A., & Moormann, H. (2003). Effects of plants and microorganisms in constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment. Biotechnology Advances, 22, 93–117.
Vymazal, J. (2013). The use of hybrid constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment with special attention to nitrogen removal: a review of a recent development. Water Res, 47, 4795–4811.
Wang, C., Zhang, S. H., Wang, P. F., Hou, J., Li, W., & Zhang, W. J. (2008). Metabolic adaptations to ammonia-induced oxidative stress in leaves of the submerged macrophyte Vallisneria natans (Lour.) Hara. Aquatic Toxicology, 87, 88–98.
Wang, C., Zhang, S. H., Wang, P. F., Li, W., & Lu, J. (2010). Effects of ammonium on the antioxidative response in Hydrilla verticillata (Lf) Royle plants. Ecotox Environ Safe, 73, 189–195.
Wang, Y., Wang, J., Zhao, X., Song, X., & Gong, J. (2016). The inhibition and adaptability of four wetland plant species to high concentration of ammonia wastewater and nitrogen removal efficiency in constructed wetlands. Bioresource Technol, 202, 198–205.
Winston, G. W., & Di Giulio, R. T. (1991). Prooxidant and antioxidant mechanisms in aquatic organisms. Aquatic Toxicology, 19, 137–161.
Wolfe, N., & Hoehamer, C. (2003). Enzymes used by plants and microorganisms to detoxify organic compounds. In S. C. McCutcheon & J. L. Schnoor (Eds.), Phytoremediation: Transformation and control of contaminants (pp. 159–187). Hoboken: Wiley.
Xu, J., Zhang, J., Xie, H., Li, C., Bao, N., Zhang, C., & Shi, Q. (2010a). Physiological responses of Phragmites australis to wastewater with different chemical oxygen demands. Ecol Eng, 36, 1341–1347.
Xu, Q., Hu, J., Xie, K., Yang, H., Du, K., & Shi, G. (2010b). Accumulation and acute toxicity of silver in Potamogeton crispus L. J Hazard Mater, 173, 186–193.
Xu, Y., Shi, G., Ding, C., & Xu, X. (2011). Polyamine metabolism and physiological responses of Potamogeton crispus leaves under lead stress. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology, 58, 460–466.
Xu, Q., Min, H., Cai, S., Fu, Y., Sha, S., Xie, K., & Du, K. (2012). Subcellular distribution and toxicity of cadmium in Potamogeton crispus L. Chemosphere, 89, 114–120.
Ye, X. & Guo, X. (2011). Testing of winter vegetation construction and water purification effect of a cascaded wetland model of Jialu river Water Resource and Environmental Protection (ISWREP), 2011 International Symposium on, 658-661.
Yordanova, R., Alexieva, V., & Popova, L. (2003). Influence of root oxygen deficiency on photosynthesis and antioxidant status in Barley plants1. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology, 50, 163–167.
Zhang, M., Cao, T., Ni, L., Xie, P., & Li, Z. (2010). Carbon, nitrogen and antioxidant enzyme responses of Potamogeton crispus to both low light and high nutrient stresses. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 68, 44–50.
Zhu, Z, Yuan, H, Wei, Y, Li, P, Zhang, P, & Xie, D (2015). Effects of ammonia nitrogen and sediment nutrient on growth of the submerged plant Vallisneria natans. CLEAN – Soil, Air, Water, 43(12), 1653–1659.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21307076, No. 51578321 and No. 21507072) and the Fundamental Research Funds of Shandong University (No. 2014TB003 and No. 2015JC056).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, X., Zhang, J., Guo, Y. et al. Physiological Responses of Potamogeton crispus to Different Levels of Ammonia Nitrogen in Constructed Wetland. Water Air Soil Pollut 227, 65 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2763-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2763-9