Abstract
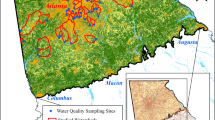
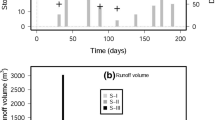
High levels of marine salt deposition present in coastal areas have a relevant effect on road runoff characteristics. This study assesses this effect with the purpose of identifying the relationships between monitored water quality parameters and intrinsic site variables. To achieve this objective, an extensive monitoring program was conducted on a Portuguese coastal highway. The study included 30 rainfall events, in different weather, traffic, and salt deposition conditions. The evaluations of various water quality parameters were carried out in over 200 samples. In addition, the meteorological, hydrological, and traffic parameters were continuously measured. The salt deposition rates were determined by means of a wet candle device, which is an innovative feature of the monitoring program. The relation between road runoff pollutants and independent variables associated with weather, traffic, and salt deposition conditions was assessed. Significant correlations among pollutants were observed. A high salinity concentration and its influence on the road runoff were confirmed. Furthermore, the concentrations of the most relevant pollutants seemed to be very dependent on some meteorological variables, particularly the duration of the antecedent dry period prior to each rainfall event and the average wind speed.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amini, B., & Tehrani, S. S. (2012). Simultaneous effects of salted water and water flow on asphalt concrete pavement deterioration under freeze-thaw cycles. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 155, 383–391.
Antunes, P., & Barbosa, A. (2005) Highway runoff characteristics in coastal areas—a case study in Aveiro, Portugal. Paper presented at the 10th International Conference on Urban Drainage, Copenhagen, Denmark.
APHA—American Public Health Association. (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). Washington DC, USA: American Water Works Association/American Public Works Association/Water Environment Federation.
ASTM—American Society for Testing and Materials. (2002). Standard test method for determining atmospheric chloride deposition rate by wet candle method. ASTM G140-02. West Conshohocken, PA, USA: ASTM International.
Bäckström, M., Karlsson, S., Bäckman, L., Folkeson, L., & Lind, B. (2004). Mobilization of heavy metals by deicing salts in a roadside environment. Water Research, 383, 720–732.
Barbosa, A. E., Henriques, M. J., & Fernandes, J. (2006). Quality of highway runoff in coastal areas: special cases? Paper presented at the 8th highway and urban environment symposium. Cyprus: Nicosia.
Barbosa, A. E., Almeida, L. V., Antunes, P. B., Baguinho, R., Fernandes, J. N., Jessica, C., Ramísio, P. J., Vieira, J., Whitehead, M., & Telhado, A. (2011). Directrizes para a gestão integrada das águas de escorrência de estradas em portugal (guidelines for integrated road runoff pollution management in portugal). laboratório nacional de engenharia civil. Portugal: Lisbon.
Bertrand-Krajewski, J. L., Chebbo, G., & Saget, A. (1998). Distribution of pollutant mass vs volume in stormwater discharges and the first flush phenomenon. Water Research, 328, 2341–2356.
Caltrans. (2003). Caltrans comprehensive protocols guidance manual. USA: California Department of Transportation.
Crabtree, B., Dempsey, P., Johnson, I., & Whitehead, M. (2008). The development of a risk-based approach to managing the ecological impact of pollutants in highway runoff. Water Science and Technology, 57(10), 1595–1600.
Dunkerley, D. (2008). Identifying individual rain events from pluviograph records: a review with analysis of data from an Australian dryland site. Hydrological Processes, 2226, 5024–5036.
FHWA—Federal Highway Administration. (1996). Evaluation and management of highway runoff water quality. Publication No. FHWA-PD-96-032. Washington DC, USA: U.S. Department of Transportation.
Fitzgerald, J. W. (1991). Marine aerosols: a review. Atmospheric Environment Part A General Topics, 253(4), 533–545.
Furumai, H., Balmer, H., & Boller, M. (2002). Dynamic behavior of suspended pollutants and particle size distribution in highway runoff. Water Science and Technology, 46(11–12), 413–418.
Gan, H., Zhuo, M., Li, D., & Zhou, Y. (2008) Quality characterization and impact assessment of highway runoff in urban and rural area of Guangzhou, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 140(1-3), 147–159.
Gupta, K., & Saul, A. J. (1996). Specific relationships for the first flush load in combined sewer flows. Water Research, 305, 1244–1252.
Hossain, K. M. A., & Easa, S. M. (2011). Spatial distribution of marine salts in coastal region using wet candle sensors. International Journal of Research and Reviews in Applied Sciences, 73, 228–232.
Hvitved-Jacobsen, T., & Vollertsen, J. (2005). Urban storm drainage. Pollution—concepts and engineering. Ph.D. course: process engineering of urban and highway runoff. Denmark: Aalborg University.
Hvitved-Jacobsen, T., & Yousef, Y. A. (1991). Highway runoff quality, environmental impacts and control. In R. S. Hamilton & R. M. Harrison (Eds.), Highway pollution studies in environmental science (pp. 165–208). Amsterdam, Holland: Elsevier.
Kayhanian, M. (2012). Trend and concentrations of legacy lead Pb in highway runoff. Environmental Pollution, 1601, 169–177.
Kayhanian, M., Suverkropp, C., Ruby, A., & Tsay, K. (2007). Characterization and prediction of highway runoff constituent event mean concentration. Journal of Environmental Management, 852, 279–295.
Kayhanian, M., Fruchtman, B. D., Gulliver, J. S., Montanaro, C., Ranieri, E., & Wuertz, S. (2012). Review of highway runoff characteristics: comparative analysis and universal implications. Water Research, 4620, 6609–6624.
Kim, L. H., Kayhanian, M., Zoh, K. D., & Stenstrom, M. K. (2005). Modeling of highway stormwater runoff. Science of the Total Environment, 3481–3, 1–18.
Luker, M., & Montague, K. (1994). Control of pollution from highway drainage discharges. Construction Industry Research & Information Association, London, England: CIRIA Report.
Merrikhpour, H., & Jalali, M. (2013). The effects of road salt application on the accumulation and speciation of cations and anions in an urban environment. Water and Environment Journal, 274, 524–534.
Mesoplano, Ecossistema and Naturibérica. (1994). IP5 En. 109–7 Pirâmides-Barra, Estudo de Impacte Ambiental. Mesoplano, Ecossistema. Lisbon, Portugal: Naturibérica.
Morcillo, M., Chico, B., Mariaca, L., & Otero, E. (2000). Salinity in marine atmospheric corrosion: its dependence on the wind regime existing in the site. Corrosion Science, 421, 91–104.
Opher, T., & Friedler, E. (2010). Fators affecting highway runoff quality. Urban Water Journal, 73, 155–172.
Opher, T., Ostfeld, A., & Friedler, E. (2009). Modeling highway runoff pollutant levels using a data driven model. Water Science and Technology, 60(1), 19–28.
Pio, C. A., Castro, L. M., Cerqueira, M. A., Santos, I. M., Belchior, F., & Salgueiro, M. L. (1996). Source assessment of particulate air pollutants measured at the southwest European coast. Atmospheric Environment, 3019, 3309–3320.
Ramísio, P. (2007). Retenção de metais pesados de escorrências rodoviárias por filtração reactiva (Unpublished Ph.D. thesis). Braga, Portugal: University of Minho.
Ramísio, P. J., & Vieira, J. M. P. (2011). Characterization of road runoff: a case study on the A3 Portuguese highway. In S. Rauch & G. M. Morrison (Eds.), In proceedings of the 10th urban environment symposium (pp. 285–295). Netherlands: Springer. Dordrecht.
Sansalone, J. J., & Buchberger, S. G. (1997). Partitioning and first flush of metals in urban roadway storm water. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 1232, 134–143.
Shumway, R. H., Azari, R. S., & Kayhanian, M. (2002). Statistical approaches to estimating mean water quality concentrations with detection limits. Environmental Science & Technology, 3615, 3345–3353.
Smullen, J. T., Shallcross, A. L., & Cave, K. A. (1999). Updating the U.S. nationwide urban runoff quality data base. Water Science and Technology, 39(12), 9–16.
Stotz, G., & Krauth, K. (1994). The pollution of effluents from pervious pavements of an experimental highway section: first results. Science of the Total Environment, 146(147), 465–470.
Thomson, N. R., McBean, E. A., Snodgrass, W., & Mostrenko, I. B. (1997). Highway stormwater runoff quality: development of surrogate parameter relationships. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 94(3–4), 307–347.
TMUA—Torre Meteorológica da Universidade de Aveiro (Weather Station of Aveiro University) (2014) Weather in Aveiro http://torre.fis.ua.pt/Aveiroclimate.asp (accessed in 12 March 2014).
Woodbridge, M. S., Obika, B., Freer-Hewish, R., & Newill, D. (1994) Salt damage to bituminous surfacings: results from road trials in Botswana. In Proceedings of the 6th Conference on Asphalt Pavements for Southern Africa Vol. 1. (pp. 149–162). Cape Town, South Africa.
Acknowledgments
Part of this study was developed within a project financed by the Portuguese National Foundation for Science and Technology (PTDC/AMB/64953/2006).
Antunes P. thanks the Portuguese National Foundation for Science and Technology for the Ph.D. grant (SFRH-BD-43638-2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antunes, P., Ramísio, P.J. Assessment of Distinctive Road Runoff Quality in Coastal Areas, Based on a Monitoring Case Study. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 399 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2657-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2657-2