Abstract
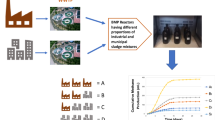
The anaerobic biodegradability of combined microwave-ultrasonic pretreated thickened excess activated sludge (PTEAS) mixed with raw primary sludge (PS) was investigated in this study. The pretreatment resulted in the enhancement of mesophilic anaerobic digester performance which in turn improved biogas production capacity and quality, total and volatile solid reduction, dewaterability, protein solubilisation and significant reduction of pathogens to produce class A biosolid. This study presented the results of two continuously stirred mesophilic anaerobic digesters charged with various proportions of a mixture of PTEAS and PS similar to the large-scale industrial practice. Digester 1 was charged with 75 % PTEAS and 25 % PS, while digester 2 was fed with 25 % PTEAS and 75 % PS. The methane production was 122 mL CH4/g total chemical oxygen demand for digester 2 after 20 days of anaerobic digestion. This amount further increased for both digesters with digestion time. The biogas quality in terms of methane to carbondioxide ratio (CH4/CO2) was significantly improved for digester 1 compared with digester 2 after 20 days of digestion. Volatile solid reduction of 76 and 57 % was achieved for digester 1 and digester 2 respectively after the same 20 days of digestion. The CH4/CO2 ratio reached 2.2:1 and 1.1:1 after 20 days of digestion for digester 1 and digester 2, respectively. Higher percentage of PTEAS increases the digestion kinetics, the methane production capacity and the biogas quality. Furthermore, total coliform reduction of 84 and 44 % was achieved for digester 1 and digester 2 respectively after 22 days of digestion. Hydrolysis rate and biochemical methane production were improved for both digesters based on the results of Gompertz kinetic model and the hydrolysis rate constants as determined by model fitting of the experimental data.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA, AWWA and WEF. (2000). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (21st ed.). Washington DC: American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association and Water Environment Federation.
Appels, L., Baeyens, J., Degreve, J., & Dewil, R. (2008). Principles and potential of the anaerobic digestion of waste-activated sludge. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 34(6), 755–781.
Apul, O. G., & Sanin, F. D. (2010). Ultrasonic pretreatment and subsequent anaerobic digestion under different operational conditions. Bioresource Technology, 101, 8984–8992.
Bougrier, C., Carrère, H., & Delgenès, J. P. (2005). Solubilisation of waste-activated sludge by ultrasonic treatment. Chemical Engineering Journal, 106(2), 163–169. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2004.11.013.
Carrère, H., Dumas, C., Battimelli, A., Batstone, D. J., Delgenès, J. P., Steyer, J. P., et al. (2010). Pretreatment methods to improve sludge anaerobic degradability: a review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 183(1–3), 1–15. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.06.129.
Chong, S., Sen, T. K., Kayaalp, A., & Ang, H. M. (2012). The performance enhancements of upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactors for domestic sludge treatment–a state-of-the-art review. Water Research, 46(11), 3434–3470. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2012.03.066.
Eskicioglu, C., Kennedy, K. J., & Droste, R. L. (2007a). Enhancement of batch waste activated sludge digestion by microwave pretreatment. Water Environment Research, 79(11), 2304–2317.
Eskicioglu, C., Terzian, N., Kennedy, K. J., Droste, R. L., & Hamoda, M. (2007b). Athermal microwave effects for enhancing digestibility of waste activated sludge. Water Research, 41(11), 2457–2466.
Farooq, R., Rehman, F., Baig, S., Sadique, M., Khan, S., & Farooq, U. (2009). The effect of ultrasonic irradiation on the anaerobic digestion of activated sludge. World Applied Sciences Journal, 6(2), 234–237.
Gadhamshetty, V., Arudchelvam, Y., Nirmalakhandan, N., & Johnson, D. C. (2010). Modeling dark fermentation for biohydrogen production: ADM1-based model vs. Gompertz model. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 35(2), 479–490. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.11.007.
Ghosh, S., Conrad, J., & Klass, D. (1975). Anaerobic acidogenesis of wastewater sludge. Journal Water Pollution Control Federation, 47(1), 30–45.
Grönroos, A., Kyllönen, H., Korpijärvi, K., Pirkonen, P., Paavola, T., & Jokela, J. (2005). Ultrasound assisted method to increase soluble chemical oxygen demand (SCOD) of sewage sludge for digestion. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 12(1–2), 115–120. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2004.05.012.
Haug, R., Stuckey, D., Gossett, J., & McCarty, P. (1978). Effect of thermal pretreatment on digestibility and dewaterability of organic sludges. Journal Water Pollution Control Federation, 50(1), 73–85.
Lafitte-Trouqué, S., & Forster, C. F. (2002). The use of ultrasound and γ-irradiation as pre-treatments for the anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge at mesophilic and thermophilic temperatures. Bioresource Technology, 84(2), 113–118. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(02)00038-X.
Lee, I.-S., Parameswaran, P., & Rittmann, B. E. (2011). Effects of solids retention time on methanogenesis in anaerobic digestion of thickened mixed sludge. Bioresource Technology, 102(22), 10266–10272. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2011.08.079.
Lin, C.-Y., & Lee, Y.-S. (2002). Effect of thermal and chemical pretreatments on anaerobic ammonium removal in treating septage using the UASB system. Bioresource Technology, 83(3), 259–261. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(01)00223-1.
Müller, J. (2001). Prospects and problems of sludge pre-treatment processes. Water Science and Technology: a Journal of the International Association on Water Pollution Research, 44(10), 121.
Navaratnam (2007). Anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge with ultrasonic pretreatment. Master of engineering in environmental engineering and management, Asian Institute of Technology, Thailand.
Park, W. J. (2011). Effects of microwave pretreatment on mesophilic anaerobic digestion for mixture of primary and secondary sludges compared with thermal pretreatment. Environmental Engineering Research, 16(2), 103–109.
Park, W. J., & Ahn, J.-H. (2011). Effects of microwave pretreatment on mesophilic anaerobic digestion for mixture of primary and secondary sludges compared with thermal pretreatment. Environmental Engineering Research (EER), 16(2), 103–109.
Penaud, V., Delgenes, J., & Moletta, R. (2000). Influence of thermo-chemical pre-treatment conditions on solubilization and anaerobic biodegradability of a microbial biomass. Environmental Technology, 21, 87–96.
Portenlanger, G. (1999). Mechanical and radical effects of ultrasound. Ultrasound in Environmental Engineering, TU Hamburg-Harburg Reports on Sanitary Engineering, 25, 139–151.
Rolfe, R. D., Hentges, D. J., Campbell, B. J., & Barrett, J. T. (1978). Factors related to the oxygen tolerance of anaerobic bacteria. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 36(2), 306–313.
Saha, M., Eskicioglu, C., & Marin, J. (2011). Microwave, ultrasonic and chemo-mechanical pretreatments for enhancing methane potential of pulp mill wastewater treatment sludge. Bioresource Technology, 102(17), 7815–7826. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2011.06.053.
Saifuddin, N., & Fazlili, S. A. (2009). Effect of microwave and ultrasonic pretreatments on biogas production from anaerobic digestion of palm oil mill effluent. American Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, 2, 139–146.
Shao, L., Wang, T., Li, T., Lü, F., & He, P. (2013). Comparison of sludge digestion under aerobic and anaerobic conditions with a focus on the degradation of proteins at mesophilic temperature. Bioresource Technology, 140, 131–137. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2013.04.081.
Stuckey, D., & McCarty, P. (1978). Thermo-chemical pre-treatment of nitrogeneous to increase methane yield. Biotech Eng, 8, 219–233.
Tanaka, S., & Kamiyama, K. (2002). Thermo-chemical pre-treatment in the anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Water Science and Technology, 46, 173–179.
Tiehm, A., Nickel, K., & Neis, U. (1997). The use of ultrasound to accelerate the anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Water Science and technology, 36(11), 121–128.
Tiehm, A., Nickel, K., Zellhorn, M., & Neis, U. (2001). Ultrasonic waste activated sludge disintegration for improving anaerobic stabilization. Water Research, 35(8), 2003–2009.
Toreci, I., Kennedy, K. J., & Droste, R. L. (2010). Effect of high-temperature microwave irradiation on municipal thickened waste activated sludge solubilization. Heat Transfer Engineering, 31(9), 766–773.
Weiland, P. (2010). Biogas production: current state and perspectives. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 85(4), 849–860.
Yeneneh, A. M., Chong, S., Sen, T. K., Ang, H. M., & Kayaalp, A. (2013a). Effect of ultrasonic, microwave and combined microwave–ultrasonic pretreatment of municipal sludge on anaerobic digester performance. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 224(5), 1–9.
Yeneneh, A. M., Sen, T. K., Chong, S., Ang, H. M., & Kayaalp, A. (2013b). Effect of combined microwave-ultrasonic pretreatment on anaerobic biodegradability of primary, excess activated and mixed sludge. Computational water, Energy and Envrionmental Engineering, 2(Number 3B), 7–11. doi:10.4236/cweee.2013.23B002.
Yeom, I. T., Lee, K. R., Lee, Y. H., Ahn, K. H., & Lee, S. H. (2002). Effects of ozone treatment on the biodegradability of sludge from municipal wastewater treatment plants. Water Science and Technology, 46(4–5), 421–425.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Water Corporation, Perth WA and Chemical Engineering department of Curtin University, Perth for proving funding and laboratory space for this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeneneh, A.M., Kayaalp, A., Sen, T.K. et al. Effect of Combined Microwave-Ultrasonic Pretreatment of Real Mixed Sludge on the Enhancement of Anaerobic Digester Performance. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 314 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2586-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2586-0