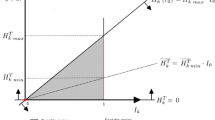
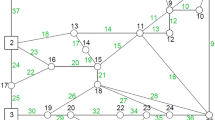
Abstract
Conduit hydropower systems improve the efficiency of water supply networks (WSNs) by utilizing excess network pressure for providing renewable energy while significantly reducing leakage. A major problem in using conduit hydropower is finding the optimum location for installing power generation devices like in-line turbines or pumps operating as turbines (PATs). This paper suggests an optimization model to find the optimum location for placing in-line turbines in WSNs using a non-parametric Rao algorithm for optimal daily power generation. The methodology is tested on a hypothetical 5-Node network and later applied to a benchmark 25-Node network. Installing turbines at optimum locations reduced network leakage by 76332.00 and 380473.87 L, representing approximately 2.57% & 2.94% of the total water demand of 5-Node and 25-Node networks, respectively, and generated 184.12 & 547.48 kWh/day of hydropower.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data, codes, and models used are available upon request.
Abbreviations
- Chw :
-
Hazen Williams roughness coefficient
- Ck :
-
Leakage coefficient for pipe k
- DM:
-
Demand Multiplier
- g:
-
Acceleration due to gravity (m/s2)
- Hex :
-
Excess pressure head at any point (m)
- Hi :
-
Available pressure head at node i
- Hj :
-
Available pressure head at node j
- Hj,min :
-
Minimum required pressure head at node j
- Hk :
-
Pressure head at pipe k (m)
- km :
-
Minor head loss coefficient
- Lk :
-
Length of pipe k (m)
- LRRmax :
-
Maximum leakage reduction ratio
- N:
-
Node number
- n:
-
Size of population
- Pi :
-
Power generation of ith turbine (kW).
- Pmax :
-
Maximum available power (kW)
- Pnet :
-
Power generation of the network (kW)
- Qj :
-
Discharge at node j (m3/s or L/s)
- QL0 :
-
Initial leakage discharge (m3/s)
- QL1 :
-
Final leakage discharge (m3/s)
- Qlk :
-
Leakage discharge at pipe k (m3/s)
- R:
-
Random number between 0 and 1
- V:
-
Velocity of flow (m/s)
- W:
-
Weightage
- Z:
-
Objective function
- Δt:
-
Time step (h)
- α:
-
Leakage exponent
- ρ:
-
Density of water (kg/m3)
References
Arun Raskar M, Gawande S (2015) A Compressive Study of Water Loss in Urban Water distribution system. Int J Eng Res Gen Sci 3(4):1001–1007 www.ijergs.org
Bonthuys GJ, van Dijk M, Cavazzini G (2020) Energy Recovery and Leakage-Reduction Optimization of Water Distribution Systems Using Hydro Turbines. J Water Resour Plan Manag 146(5):04020026. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)wr.1943-5452.0001203
Corcoran L, McNabola A, Coughlan P (2016) Optimization of Water Distribution Networks for Combined Hydropower Energy Recovery and Leakage Reduction. J Water Resour Plan Manag 142(2):04015045. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)wr.1943-5452.0000566
Corcoran L, McNabola A, Coughlan P (2017) Predicting and quantifying the effect of variations in long-term water demand on micro-hydropower energy recovery in water supply networks. Urban Water J 14(7):676–684. https://doi.org/10.1080/1573062X.2016.1236136
e Souza DES, Mesquita ALA, Blanco CJC (2023) Pressure regulation in a water distribution network using pumps as turbines at variable speed for Energy Recovery. Water Resour Manage 37(3):1183–1206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03421-9
Ebrahimi S, Riasi A, Kandi A (2021) Selection optimization of variable speed pump as turbine (PAT) for energy recovery and pressure management. Energy Conv Manag 227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2020.113586
Germanopoulos G (1985) A technical note on the inclusion of pressure dependent demand and leakage terms in water supply network models. Civil Eng Syst 2(3):171–179. https://doi.org/10.1080/02630258508970401
Gupta A, Bokde N, Marathe D, Kulat K (2017) Leakage reduction in water distribution systems with efficient Placement and Control of pressure reducing valves using Soft Computing techniques. Eng Technol Appl Sci Res 7(2):1528–1534
Heysel CS, Filion YR (2014) Estimating the payback period of in-line micro turbines with analytical probabilistic models. Procedia Eng 70:815–822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2014.02.089
Jafari-Asl J, Kashkooli S, B., Bahrami M (2020) Using particle swarm optimization algorithm to optimally locating and controlling of pressure reducing valves for leakage minimization in water distribution systems. Sustainable Water Resour Manage 6(4). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-020-00426-3
Jain P, Khare R (2021) Application of Parameter-less Rao Algorithm in Optimization of Water Distribution Networks through Pressure-Driven Analysis. Water Resour Manage 35(12). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02931-2
Jain P, Khare R (2022) Multi-objective Rao algorithm in resilience-based optimal design of water distribution networks. Water Supply 22(4):4346–4360. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2022.054
Jowitt PW, Xu C (1990) Optimal valve control in water-distribution networks. J Water Resour Plan Manag 116(4):455–472
Klise KA, Murray R, Haxton T (2018) An Overview of the Water Network Tool for Resilience (WNTR). https://github.com/USEPA/WNTR
Leão AS, Sipert SA, Medeiros DL, Cohim EB (2022) Water footprint of drinking water: the consumptive and degradative use. J Clean Prod 355:131731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131731
Letting L, Hamam Y, Abu-Mahfouz A (2017) Estimation of Water demand in water distribution systems using particle swarm optimization. Water 9(8):593. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080593
Majidi M, Etezadi-Amoli M (2018) Recapturing wasted energy in water pressure reducing valves via in-conduit hydropower generators. Measurement: J Int Meas Confederation 123:62–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2018.03.061
Morani MC, Carravetta A, D’Ambrosio C, Fecarotta O (2021) A new mixed integer non-linear programming model for optimal PAT and PRV location in water distributionnetworks. Urban Water J 18(6):394–409. https://doi.org/10.1080/1573062X.2021.1893359
Mutikanga HE (2012) Water loss management: tools and methods for developing countries. CRC Press/Balkema
Patelis M, Kanakoudis V, Gonelas K (2017) Combining pressure management and energy recovery benefits in a water distribution system installing PATs. J Water Supply: Res Technol - AQUA 66(7):520–527. https://doi.org/10.2166/aqua.2017.018
Puust R, Kapelan Z, Savic DA, Koppel T (2010) A review of methods for leakage management in pipe networks. Urban Water J 7(1):25–45. https://doi.org/10.1080/15730621003610878
Rao RV (2020) Rao algorithms: three metaphor-less simple algorithms for solving optimization problems. Int J Ind Eng Comput 107–130. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.ijiec.2019.6.002
Rao RV, Pawar RB (2020) Constrained design optimization of selected mechanical system components using Rao algorithms. Appl Soft Comput 89:106141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106141
Rodríguez-Pérez ÁM, Pérez-Calañas C, Pulido-Calvo I (2021) Energy Recovery in pressurized hydraulic networks. Water Resour Manage 35(6):1977–1990. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02824-4
Rossman LA (2000) EPANET 2 users manual. Water Supply and Water Resources Division, National Risk Management Research Laboratory, Cincinnati, OH
Samora I, Manso P, Franca MJ, Schleiss AJ, Ramos HM (2016) Energy recovery using micro-hydropower technology in water supply systems: the case study of the city of Fribourg. Water (Switzerland) 8(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080344
Shekofteh M, Jalili Ghazizadeh M, Yazdi J (2020) A methodology for leak detection in water distribution networks using graph theory and artificial neural network. Urban Water J 17(6):525–533. https://doi.org/10.1080/1573062X.2020.1797832
Stefanizzi M, Capurso T, Balacco G, Binetti M, Torresi M, Camporeale SM (2019) Pump as turbine for throttling energy recovery in water distribution networks. AIP Conf Proc 2191. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5138875
Süme V, Daneshfaraz R, Kerim A, Abbaszadeh H, Abraham J (2024) Investigation of Clean Energy Production in drinking Water networks. Water Resour Manage. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-024-03752-9
Tocados-Franco E, Martínez-Dalmau J, Espinosa-Tasón J, Montilla-López NM (2024) Trends in Water-Energy Nexus and Carbon emissions Balance in Axarquia Region, Spain, in the period 1990–2030. Environ Processes 11(1):11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-024-00689-4
Funding
No funding was received to support the manuscript preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Priyanshu Jain wrote the paper, designed optimization model and did statistical analysis. Ruchi Khare monitored and enhanced the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare relevant to this article’s content.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jain, P., Khare, R. Strategic Placement of In-line Turbines for Optimum Power Generation and Leakage Reduction in Water Supply Networks. Water Resour Manage (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-024-03831-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-024-03831-x