Abstract
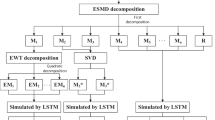
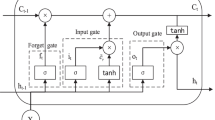
Accurate and consistent annual runoff prediction in a region is a hot topic in management, optimization, and monitoring of water resources. A novel prediction model (ESMD-SE-WPD-LSTM) is presented in this study. Firstly, extreme-point symmetric mode decomposition (ESMD) is used to produce several intrinsic mode functions (IMF) and a residual (Res) by decomposing the original runoff series. Secondly, sample entropy (SE) method is employed to measure the complexity of each IMF. Thirdly, wavelet packet decomposition (WPD) is adopted to further decompose the IMF with the maximum SE into several appropriate components. Then long short-term memory (LSTM) model, a deep learning algorithm based recurrent approach, is employed to predict all components. Finally, forecasting results of all components are aggregated to generate the final prediction. The proposed model, which is applied to seven annual series from different areas in China, is evaluated based on four evaluation indexes (R, MAE, MAPE and RMSE). Results indicate that ESMD-SE-WPD-LSTM outperforms other benchmark models in terms of four evaluation indexes. Hence the proposed model can provide higher accuracy and consistency for annual runoff prediction, rendering it an efficient instrument for scientific management and planning of water resources.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
All authors made sure that all data and materials support our published claims and comply with field standards.
References
Akbari Asanjan A, Yang T, Hsu K, Sorooshian S, Lin J, Peng Q (2018) Short-term precipitation forecast based on the PERSIANN system and LSTM recurrent neural networks. J Geophys Res Atmos 123:12543–12563. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JD028375
Al-Juboori AM (2021) A hybrid model to predict monthly streamflow using neighboring rivers. Annu Flows Water Resour Manag 35:729–743. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02757-4
Alcaraz R, Rieta JJ (2010) A review on sample entropy applications for the non-invasive analysis of atrial fibrillation electrocardiograms. Biomed Signal Process Control 5:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2009.11.001
Alickovic E, Kevric J, Subasi A (2018) Performance evaluation of empirical mode decomposition, discrete wavelet transform, and wavelet packed decomposition for automated epileptic seizure detection and prediction. Biomed Signal Process Control 39:94–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2017.07.022
Bai Y, Bezak N, Zeng B, Li C, Sapac K, Zhang J (2021) Daily runoff forecasting using a cascade long short-term memory model that considers different variables. Water Resour Manag 35:1167–1181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02759-2
Bojang PO, Yang TC, Pham QB, Yu PS (2020) Linking singular spectrum analysis and machine learning for monthly rainfall forecasting. Appl Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10093224
Chau KW, Wu CL, Li YS (2005) Comparison of several flood forecasting models in Yangtze River. J Hydrol Eng 10:485–491. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0699(2005)10:6(485)
Colominas MA, Schlotthauer G, Torres ME, Flandrin P (2012) Noise-assisted EMD methods in action. Adv Adapt Data Anal 04:1250025. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793536912500252
Dong Q, Sun Y, Li P (2017) A novel forecasting model based on a hybrid processing strategy and an optimized local linear fuzzy neural network to make wind power forecasting: a case study of wind farms in China. Renew Energy 102:241–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2016.10.030
Feng Z, Liu S, Niu W, Li S, Wu H, Wang J (2020a) Ecological operation of cascade hydropower reservoirs by elite-guide gravitational search algorithm with Lévy flight local search and mutation. J Hydrol 581:124425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124425
Feng Z, Niu W, Cheng X, Wang J, Wang S, Song Z (2020b) An effective three-stage hybrid optimization method for source-network-load power generation of cascade hydropower reservoirs serving multiple interconnected power grids. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119035
He XX, Luo JG, Li P, Zuo GG, Xie JC (2020) A hybrid model based on variational mode decomposition and gradient boosting regression tree for monthly runoff forecasting. Water Resour Manag 34:865–884. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02483-x
Kratzert F, Klotz D, Brenner C, Schulz K, Herrnegger M (2018) Rainfall-runoff modelling using Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 22:6005–6022. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-22-6005-2018
Liu H, Mi X, Li Y (2018) Smart multi-step deep learning model for wind speed forecasting based on variational mode decomposition, singular spectrum analysis, LSTM network and ELM. Energy Convers Manag 159:54–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.01.010
Meng ER et al (2021) A hybrid VMD-SVM model for practical streamflow prediction using an innovative input selection framework. Water Resour Manag 35:1321–1337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02786-7
Parisouj P, Mohebzadeh H, Lee T (2020) Employing machine learning algorithms for streamflow prediction: a case study of four river basins with different climatic zones in the United States. Water Resour Manag 34:4113–4131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02659-5
Poul AK, Shourian M, Ebrahimi H (2019) A comparative study of MLR, KNN, ANN and ANFIS models with Wavelet transform in monthly stream flow prediction. Water Resour Manag 33:2907–2923. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02273-0
Reddy BSN, Pramada SK, Roshni T (2021) Monthly surface runoff prediction using artificial intelligence: a study from a tropical climate river basin. J Earth Syst Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-020-01508-8
Saeed A, Li C, Danish M, Rubaiee S, Tang G, Gan Z, Ahmed A (2020) Hybrid bidirectional LSTM model for short-term wind speed interval prediction. IEEE Access 8:182283–182294. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.3027977
Sahoo BB, Jha R, Singh A, Kumar D (2019) Long short-term memory (LSTM) recurrent neural network for low-flow hydrological time series forecasting. Acta Geophys 67:1471–1481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-019-00330-1
Seo Y, Kim S, Kisi O, Singh VP, Parasuraman K (2016) River stage forecasting using wavelet packet decomposition and machine learning models. Water Resour Manag 30:4011–4035. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1409-4
Sun D, Zhang H, Guo Z (2018) Complexity Analysis of precipitation and runoff series based on approximate entropy and extreme-point symmetric mode. Decomposition 10:1388
Sun SZ, Fu JQ, Zhu F, Du DJ (2020) A hybrid structure of an extreme learning machine combined with feature selection, signal decomposition and parameter optimization for short-term wind speed forecasting. Trans Inst Meas Control 42:3–21. https://doi.org/10.1177/0142331218771141
Sun W, Huang C (2020) A hybrid air pollutant concentration prediction model combining secondary decomposition and sequence reconstruction. Environ Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115216
Tao YM, Gao XG, Ihler A, Sorooshian S, Hsu KL (2017) Precipitation identification with bispectral satellite information using deep learning approaches. J Hydrometeorol 18:1271–1283. https://doi.org/10.1175/jhm-d-16-0176.1
Tayyab M, Zhou JZ, Dong XH, Ahmad I, Sun N (2019) Rainfall-runoff modeling at Jinsha River basin by integrated neural network with discrete wavelet transform. Meteorol Atmos Phys 131:115–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-017-0546-5
Wang J-L, Li Z-J (2013) Extreme-point symmetric mode decomposition method for data analysis. Adv Adapt Data Anal 05:1350015. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793536913500155
Xiang ZR, Yan J, Demir I (2020) A rainfall-runoff model with LSTM-based sequence-to-sequence learning. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019wr025326
Yen MH, Liu DW, Hsin YC, Lin CE, Chen CC (2019) Application of the deep learning for the prediction of rainfall in Southern Taiwan. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-49242-6
Yin Y, Bai Y, Ge F, Yu H, Liu Y (2019) Long-term robust identification potential of a wavelet packet decomposition based recursive drift correction of E-nose data for Chinese spirits. Measurement 139:284–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2019.03.011
Yuan RF et al (2021) Daily runoff forecasting using ensemble empirical mode decomposition and long short-term memory. Front Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2021.621780
Yuan XH, Chen C, Lei XH, Yuan YB, Adnan RM (2018) Monthly runoff forecasting based on LSTM-ALO model. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 32:2199–2212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-018-1560-y
Zhang JF, Zhu Y, Zhang XP, Ye M, Yang JZ (2018) Developing a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) based model for predicting water table depth in agricultural areas. J Hydrol 561:918–929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.04.065
Zhou J, Xu X, Huo X, Li Y (2019) Forecasting Models for wind power using extreme-point symmetric mode decomposition and artificial neural networks. Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11030650
Zuo G, Luo J, Wang N, Lian Y, He X (2020) Decomposition ensemble model based on variational mode decomposition and long short-term memory for streamflow forecasting. J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124776
Funding
Project of key science and technology of the Henan province (No: 202102310259; No: 202102310588), Henan province university scientific and technological innovation team (No: 18IRTSTHN009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WW: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing-original draft. YD: Methodology, data curation, Writing—original draft preparation. KC: Writing and editing-original draft. DX: Formal analysis and data collection. CL: Formal analysis. QM: Investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
All authors kept the ‘Ethical Responsibilities of Authors’.
Consent to Participate
All authors gave explicit consent to participate in this work.
Consent to Publish
All authors gave explicit consent to publish this manuscript.
Competing of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Wc., Du, Yj., Chau, Kw. et al. An Ensemble Hybrid Forecasting Model for Annual Runoff Based on Sample Entropy, Secondary Decomposition, and Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network. Water Resour Manage 35, 4695–4726 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02920-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02920-5