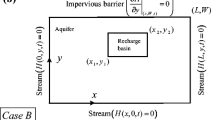
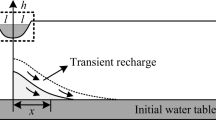
Abstract
Prediction of water table fluctuations in response to proposed schemes of recharging and pumping is important to make judicious selection of an appropriate scheme out of many schemes to achieve the preset objective of sustainable management of groundwater resources without compromising the regional water balance. This is achieved by solving groundwater flow equation with suitable initial and boundary conditions, aquifer parameters, and recharge/pumping parameters. Earlier, analytical solutions were developed to predict water table fluctuations in aquifer due to time varying recharge rate from multiple basins considering spatially uniform recharge rate for the entire basin area. However, the recharge rate may vary spatially within a single basin due to many factors such as variation in the height of water column above the base of the basin, degree of siltation of the base of the basin etc. In the present work, we develop an analytical solution for modeling of water table fluctuations in an anisotropic aquifer due to intermittently applied spatio-temporally varying rate of recharge from multiple basins and pumping from multiple wells arbitrarily distributed within the model domain. In the present solution, wells are treated as point sources, which helps in reducing numerical artifacts. Some earlier obtained analytical solutions are the special cases of the present solution.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bansal RK, Das SK (2011) Response of an unconfined sloping aquifer to constant recharge and seepage from the stream of varying water level. Water Resour Manag 25:893–911
Bear J (1979) Hydraulics of Groundwater. McGraw-Hill, New York
Bouwer H (1999) Artificial recharge of groundwater: system, design and management. In: Mays LW (ed) Hydraulik design hand book. The McGraw-Hill Companies Inc, Chapter-24.
Bouwer H (2002) Artificial recharge of groundwater: hydrogeology and engineering. Hydrogeol J 10:121–142
Bouwer H, Rice RC (1989) Effect of water depth in groundwater recharge basin on infiltration rate. J Irrig Drain E-ASCE 115:556–568
Dagan G (1964) Linearized solution of unsteady deep flow towards an array of horizontal drains. J Geophys Res 69:3361–3369
Detay M (1995) Rational groundwater reservoir management, the role of artificial recharge. In: Johnson AI, Pyne RDG (eds) Artificial Recharge of Groundwater II. ACSE, New York, pp 231–240
Dickenson JM, Bachman SB (1995) The optimization of spreading ground operations. In: Johnson AI, Pyne RDG (eds) Artificial Recharge of Groundwater II. ACSE, New York, pp 630–639
Glover RE (1960) Mathematical derivations as pertain to groundwater recharge. Agric. Res. Serv., USDA, Fort Collins, Collins, Colorado, U.S.A
Hantush MS (1967) Growth and decay of ground water mounds in response to uniform percolation. Water Resour Res 3:227–234
Hunt BW (1971) Vertical recharge of unconfined aquifer. J Hydraul Div-ASCE96(HY7), pp.1017–1030.
Mahdavi A, Seyyedian H (2013) Transient-State Analytical Solution for Groundwater Recharge in Triangular-Shaped Aquifers Using the Concept of Expanded Domain. Water Resour Manag 27:2785–2806
Manglik A, Rai SN (1998) Two-dimensional modelling of water table fluctuations due to time varying recharge from rectangular basin. Water Resour Manag 12:467–478
Manglik A, Rai SN (2000) Modeling of water table fluctuations in response to time varying recharge and withdrawal. Water Resour Manag 14:339–347
Manglik A, Rai SN, Singh RN (1997) Response of an unconfined aquifer induced by time varying recharge from a rectangular basin. Water Resour Manag 11:185–196
Manglik A, Rai SN, Singh VS (2004) Modelling of aquifer response to time varying recharge and pumping from multiple basins and wells. J Hydrol 292:23–29
Manglik A, Rai SN, Singh VS (2013) A generalized predictive model of water table fluctuations in anisotropic aquifer due to intermittently applied time varying recharge from multiple basins. Water Resour Manag 27:25–36
Marino MA (1967) Hele-Shaw model study of the growth and decay of groundwater ridges. J Geophys Res 72:1195–1205
Marino MA (1974) Rise and decline of water table induced by vertical recharge. J Hydrol 23:289–298
Mousavi SF, Rezai V (1999) Evaluation of scraping treatments to restore initial infiltration capacity of three artificial recharge projects in central Iran. Hydrogeol J 7:490–500
Racz AJ, Fisher AT, Schmidt CM, Lockwood BS, Huertos ML (2012) Spatial and Temporal Infiltration Dynamics During Managed Aquifer Recharge. Groundw 50:562–570. doi:10.1111/j.1745-6584.2011.00875.x
Rai SN, Manglik A (2012) An analytical solution of Boussinesq equation to predict water table fluctuations due to time varying recharge and withdrawal from multiple basins, wells and leakage sites. Water Resour Manag 26:243–252
Rai SN, Manglik A, Singh RN (1994) Water table fluctuation in response to transient recharge from a rectangular basin. Water Resour Manag 8:1–10
Rai SN, Manglik A, Singh VS (2006) Water table fluctuation owing to time varying recharge, pumping and leakage. J Hydrol 324:350–358
Rao NH, Sarma PBS (1981) Groundwater recharge from rectangular areas. Groundw 19:271–274
Teloglou IS, Zisis TS, Panagopoulos AC (2008) Water table fluctuation in aquifers overlying a semi-impervious layer due to transient recharge from a circular basin. J Hydrol 348:215–223
Yue-zan T, Mei Y, Bing-feng Z (2007) Solution and its application of transient stream/groundwater model subjected to time-dependent vertical seepage. Appl Math Mech 28:1173–1180
Zomorodi K (1991) Evaluation of the response of a water table to a variable recharge. Hydrolg Sci J 36:67–78
Acknowledgment
Authors are grateful to the Director, CSIR-National Geophysical Research Institute for according permission for publication of this paper. The work was supported under the project PSC0204 (INDEX).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manglik, A., Rai, S.N. Modeling Water Table Fluctuations in Anisotropic Unconfined Aquifer Due to Time Varying Recharge from Multiple Heterogeneous Basins and Pumping from Multiple Wells. Water Resour Manage 29, 1019–1030 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0857-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0857-y