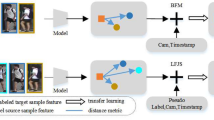
Abstract
Person re-identification (ReID) has made great strides thanks to the data-driven deep learning techniques. However, the existing benchmark datasets lack diversity, and models trained on these data cannot generalize well to dynamic wild scenarios. To meet the goal of improving the explicit generalization of ReID models, we develop a new Open-World, Diverse, Cross-Spatial-Temporal dataset named OWD with several distinct features. (1) Diverse collection scenes: multiple independent open-world and highly dynamic collecting scenes, including streets, intersections, shopping malls, etc. (2) Diverse lighting variations: long time spans from daytime to nighttime with abundant illumination changes. (3) Diverse person status: multiple camera networks in all seasons with normal/adverse weather conditions and diverse pedestrian appearances (e.g., clothes, personal belongings, poses, etc.). (4) Protected privacy: invisible faces for privacy critical applications. To improve the implicit generalization of ReID, we further propose a Latent Domain Expansion (LDE) method to develop the potential of source data, which decouples discriminative identity-relevant and trustworthy domain-relevant features and implicitly enforces domain-randomized identity feature space expansion with richer domain diversity to facilitate domain-invariant representations. Our comprehensive evaluations with most benchmark datasets in the community are crucial for progress, although this work is far from the grand goal toward open-world and dynamic wild applications. The project page is https://github.com/fxw13/OWD.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
An open-world dataset, i.e., OWD, is developed, which is available from the corresponding author upon acceptance and reasonable request. This paper also uses other 11 public datasets for person re-identification (Li et al., 2014; Zheng et al., 2015, 2017b; Wei et al., 2018; Shu et al., 2021a; Barbosa et al., 2018; Bak et al., 2018; Sun and Zheng, 2019; Wang et al., 2020b; Zhang et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2022).
References
Bai, Y. , Jiao, J. , Ce, W. , Liu, J. , Lou, Y. , Feng, X. , & Duan, L.-Y. (2021). Person30k: A dual-meta generalization network for person re-identification. In Cvpr (pp. 2123–2132).
Bak, S. , Carr, P. , & Lalonde, J.-F. (2018). Domain adaptation through synthesis for unsupervised person re-identification. In Eccv (pp. 189–205).
Baltieri, D. , Vezzani, R. , & Cucchiara, R. (2011). 3dpes: 3d people dataset for surveillance and forensics. In ACM workshop on human gesture and behavior understanding (pp. 59–64).
Barbosa, I. B., Cristani, M., Caputo, B., Rognhaugen, A., & Theoharis, T. (2018). Looking beyond appearances: Synthetic training data for deep CNNs in re-identification. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 167, 50–62.
Blanchard, G., Lee, G., & Scott, C. (2011). Generalizing from several related classification tasks to a new unlabeled sample. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 24, 2178–2186.
Chen, P. , Dai, P. , Liu, J. , Zheng, F. , Tian, Q. , & Ji, R. (2020). Dual distribution alignment network for generalizable person re-identification. 7, 8. arXiv preprint arXiv:2007.13249
Chen, P. , Dai, P. , Liu, J. , Zheng, F. , Xu, M. , Tian, Q. , & Ji, R. (2021). Dual distribution alignment network for generalizable person re-identification. In AAAI (Vol. 35, pp. 1054–1062).
Chen, X. , Fu, C. , Zhao, Y. , Zheng, F. , Song, J. , Ji, R. , & Yang, Y. (2020). Salience-guided cascaded suppression network for person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 3300–3310).
Cheng, D. S. , Cristani, M. , Stoppa, M. , Bazzani, L. , & Murino, V. (2011). Custom pictorial structures for re-identification. In BMVC (Vol. 1, p. 6).
Choi, S. , Kim, T. , Jeong, M. , Park, H. , & Kim, C. (2021). Meta batch-instance normalization for generalizable person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 3425–3435).
Dai, Y. , Li, X. , Liu, J. , Tong, Z. , & Duan, L.-Y. (2021). Generalizable person re-identification with relevance-aware mixture of experts. In CVPR (pp. 16145–16154).
Fu, D., Chen, D., Bao, J., Yang, H., Yuan, L., Zhang, L., Li, H., & Chen, D. (2021). Unsupervised pre-training for person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 14750–14759).
Gray, D., & Tao, H. (2008). Viewpoint invariant pedestrian recognition with an ensemble of localized features. In ECCV.
He, L., Liao, X., Liu, W., Liu, X., Cheng, P., & Mei, T. (2020). Fastreid: A pytorch toolbox for real-world person re-identification. 1(6). arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.02631.
He, K., Zhang, X., & Ren, S., Sun, J. (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. In CVPR (pp. 770–778).
Hermans, A., Beyer, L., & Leibe, B. (2017). In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.07737.
Hirzer, M., Beleznai, C., Roth, P. M., & Bischof, H. (2011). Person re-identification by descriptive and discriminative classification. In Scandinavian conference on image analysis (pp. 91–102).
Hu, J., Shen, L., & Sun, G. (2018). Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In CVPR.
Huang, Y., Wu, Q., Xu, J., & Zhong, Y. (2019). Celebrities-reid: A benchmark for clothes variation in long-term person re-identification. In IJCNN (pp. 1–8).
Huang, Q., Xiong, Y., & Lin, D. (2018). Unifying identification and context learning for person recognition. In CVPR (pp. 2217–2225).
Huang, Y., Fu, X., Li, L., & Zha, Z.-J. (2022). Learning degradation-invariant representation for robust real-world person re-identification. International Journal of Computer Vision, 130(11), 2770–2796.
Huang, Y., Xu, J., Wu, Q., Zhong, Y., Zhang, P., & Zhang, Z. (2019). Beyond scalar neuron: Adopting vector-neuron capsules for long-term person re-identification. IEEE TCSVT, 30(10), 3459–3471.
Jia, J., Ruan, Q., & Hospedales, T. M. (2019). Frustratingly easy person re-identification: Generalizing person re-id in practice. arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.03422.
Jin, X., Lan, C., Zeng, W., Chen, Z., & Zhang, L. (2020a). Style normalization and restitution for generalizable person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 3140–3149).
Jin, X., Lan, C., Zeng, W., Chen, Z., & Zhang, L. (2020b). Style normalization and restitution for generalizable person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 3143–3152).
Li, W., & Wang, X. (2013). Locally aligned feature transforms across views. In CVPR (pp. 3594–3601).
Li, P., Li, D., Li, W., Gong, S., Fu, Y., & Hospedales, T.M. (2021). A simple feature augmentation for domain generalization. In ICCV (pp. 8886–8895).
Li, Y., Song, J., Ni, H., & Shen, H. T. (2023). Style-controllable generalized person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM international conference on multimedia. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:264492134.
Li, D., Yang, Y., Song, Y.-Z., & Hospedales, T. M. (2018). Learning to generalize: Meta-learning for domain generalization. In AAAI.
Li, W., Zhao, R., & Wang, X. (2012). Human reidentification with transferred metric learning. In ACCV (pp. 31–44).
Li, W., Zhao, R., Xiao, T., & Wang, X. (2014). Deepreid: Deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 152–159).
Liao, S., & Shao, L. (2020). Interpretable and generalizable person re-identification with query-adaptive convolution and temporal lifting. In ECCV (pp. 456–474).
Liao, S., & Shao, L. (2022). Graph sampling based deep metric learning for generalizable person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 7359–7368).
Li, W., Zhu, X., & Gong, S. (2020). Scalable person re-identification by harmonious attention. International Journal of Computer Vision, 128(6), 1635–1653.
Loy, C. C., Liu, C., & Gong, S. (2013). Person re-identification by manifold ranking. In ICIP (pp. 3567–3571).
Luo, H., Gu, Y., Liao, X., Lai, S., & Jiang, W. (2019). Bag of tricks and a strong baseline for deep person re-identification. In CVPRW.
Luo, P., Zhang, R., Ren, J., Peng, Z., & Li, J. (2019). Switchable normalization for learning-to-normalize deep representation. IEEE TPAMI, 43(2), 712–728.
Ma, L., Liu, H., Hu, L., Wang, C., & Sun, Q. (2016). Orientation driven bag of appearances for person re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1605.02464.
Martinel, N., & Micheloni, C. (2012). Re-identify people in wide area camera network. In CVPRW (pp. 31–36).
Ni, H., Song, J., Luo, X., Zheng, F., Li, W., & Shen, H. T. (2022). Meta distribution alignment for generalizable person re-identification. In 2022 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 2477–2486).
Nichol, A., Achiam, J., & Schulman, J. (2018). On first-order meta-learning algorithms. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.02999.
Pan, X., Luo, P., Shi, J., & Tang, X. (2018). Two at once: Enhancing learning and generalization capacities via ibn-net. In ECCV.
Qian, X., Wang, W., Zhang, L., Zhu, F., Fu, Y., Xiang, T., Jiang, Y. G., & Xue, X. (2020). Long-term cloth-changing person re-identification. In ACCV.
Qiao, S., Liu, C., Shen, W., & Yuille, A. L. (2018). Few-shot image recognition by predicting parameters from activations. In CVPR (pp. 7229–7238).
Rao, Y., Lu, J., & Zhou, J. (2019). Learning discriminative aggregation network for video-based face recognition and person re-identification. International Journal of Computer Vision, 127, 701–718.
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H., Krause, J., Satheesh, S., Ma, S., Huang, Z., Karpathy, A., Khosla, A., Bernstein, M., & Berg, A. C. (2015). Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. International journal of computer vision, 115(3), 211–252.
Selvaraju, R. R., Cogswell, M., Das, A., Vedantam, R., Parikh, D., & Batra, D. (2017). Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In ICCV (pp. 618–626).
Shankar, S., Piratla, V., Chakrabarti, S., Chaudhuri, S., Jyothi, P., & Sarawagi, S. (2018). Generalizing across domains via cross-gradient training. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.10745.
Shu, Y., Cao, Z., Wang, C., Wang, J., & Long, M. (2021). Open domain generalization with domain-augmented meta-learning. In CVPR (pp. 9624–9633).
Shu, X., Wang, X., Zang, X., Zhang, S., Chen, Y., Li, G., & Tian, Q. (2021). Large-scale spatio-temporal person re-identification: Algorithms and benchmark. In IEEE TCSVT.
Song, J., Yang, Y., Song, Y.-Z., Xiang, T., & Hospedales, T. M. (2019). Generalizable person re-identification by domain-invariant mapping network. In CVPR (pp. 719–728).
Sun, X., & Zheng, L. (2019). Dissecting person re-identification from the viewpoint of viewpoint. In CVPR (pp. 608–617).
Sun, Y., Zheng, L., Yang, Y., Tian, Q., & Wang, S. (2018). Beyond part models: Person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline). In ECCV (pp. 480–496).
Tamura, M., & Murakami, T. (2019). Augmented hard example mining for generalizable person re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.05280.
Van der Maaten, L., & Hinton, G. (2008). Visualizing data using t-SNE. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 9(11).
Wang, Y., Liang, X., & Liao, S. (2022). Cloning outfits from real-world images to 3d characters for generalizable person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 4900–4909).
Wang, Y., Liao, S., & Shao, L. (2020). Surpassing real-world source training data: Random 3d characters for generalizable person re-identification. In ACMMM (pp. 3422–3430).
Wang, Y., Pan, X., Song, S., Zhang, H., Huang, G., & Wu, C. (2019). Implicit semantic data augmentation for deep networks. In NeurIPS (pp. 12635–12644).
Wang, G., Yuan, Y., Chen, X., Li, J., & Zhou, X. (2018). Learning discriminative features with multiple granularities for person re-identification. In ACMMM (pp. 274–282).
Wang, G., Wang, G., Zhang, X., Lai, J., Yu, Z., & Lin, L. (2020). Weakly supervised person re-id: Differentiable graphical learning and a new benchmark. IEEE TNNLS, 32(5), 2142–2156.
Wei, L., Zhang, S., Gao, W., & Tian, Q. (2018). Person transfer gan to bridge domain gap for person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 79–88).
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J. Y., & Kweon, I. S. (2018). Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In ECCV.
Xiao, T., Li, S., Wang, B., Lin, L., & Wang, X. (2017). Joint detection and identification feature learning for person search. In CVPR (pp. 3415–3424).
Xu, P., & Zhu, X. (2023). Deepchange: A long-term person re-identification benchmark with clothes change. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV).
Yang, Q., Wu, A., & Zheng, W.-S. (2019). Person re-identification by contour sketch under moderate clothing change. IEEE TPAMI, 43(6), 2029–2046.
Ye, M., Shen, J., Lin, G., Xiang, T., Shao, L., & Hoi, S. C. H. (2020). Deep learning for person re-identification: A survey and outlook. arXiv preprint arXiv:2001.04193.
Yin, J., Wu, A., & Zheng, W.-S. (2020). Fine-grained person re-identification. International Journal of Computer Vision, 128, 1654–1672.
Zhai, Y., Peng, P., Jia, M., Li, S., Chen, W., Gao, X., & Tian, Y. (2023). Population-based evolutionary gaming for unsupervised person re-identification. International Journal of Computer Vision, 131(1), 1–25.
Zhang, L., Deng, Z., Kawaguchi, K., Ghorbani, A., & Zou, J. (2020). How does mixup help with robustness and generalization? arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.04819.
Zhang, Z., Lan, C., Zeng, W., Jin, X., & Chen, Z. (2020). Relation-aware global attention for person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 3186–3195).
Zhang, X., Luo, H., Fan, X., Xiang, W., Sun, Y., Xiao, Q., & Sun, J. (2017). Alignedreid: Surpassing human-level performance in person re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.08184.
Zhang, N., Paluri, M., Taigman, Y., Fergus, R., & Bourdev, L. (2015). Beyond frontal faces: Improving person recognition using multiple cues. In CVPR (pp. 4804–4813).
Zhang, T., Xie, L., Wei, L., Zhuang, Z., Zhang, Y., Li, B., & Tian, Q. (2021). Unrealperson: An adaptive pipeline towards costless person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 11506–11515).
Zhang, J., Yuan, Y., & Wang, Q. (2019). Night person re-identification and a benchmark. IEEE Access, 99, 1.
Zhao, J., Zhao, Y., Chen, X., & Li, J. (2022). Revisiting stochastic learning for generalizable person re-identification. In ACMMM (pp. 1758–1768).
Zhao, Y., Zhong, Z., Yang, F., Luo, Z., Lin, Y., Li, S., & Nicu, S. (2021). Learning to generalize unseen domains via memory-based multi-source meta-learning for person re-identification. In CVPR.
Zheng, W.-S., Gong, S., & Xiang, T. (2009). Associating groups of people. In BMVC (Vol. 2, pp. 1–11).
Zheng, M., Karanam, S., & Radke, R. J. (2018). Rpifield: A new dataset for temporally evaluating person re-identification. In CVPRW (pp. 1893–1895).
Zheng, L., Shen, L., Tian, L., Wang, S., Wang, J., & Tian, Q. (2015). Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark. In ICCV (pp. 1116–1124).
Zheng, L., Zhang, H., Sun, S., Chandraker, M., Yang, Y., & Tian, Q. (2017). Person re-identification in the wild. In CVPR (pp. 1367–1376).
Zheng, Z., Zheng, L., & Yang, Y. (2017). Unlabeled samples generated by gan improve the person re-identification baseline in vitro. In ICCV (pp. 3754–3762).
Zhou, K., Yang, Y., Cavallaro, A., & Xiang, T. (2021). Learning generalisable omni-scale representations for person re-identification. In IEEE TPAMI.
Zhou, K., Yang, Y., Qiao, Y., & Xiang, T. (2021). Domain generalization with mixstyle. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.02008.
Zhu, X., Zhu, X., Li, M., Murino, V., & Gong, S. (2019). Intra-camera supervised person re-identification: A new benchmark. In ICCVW.
Zhuang, Z., Wei, L., Xie, L., Zhang, T., Zhang, H., Wu, H., Ai, H., & Tian, Q. (2020). Rethinking the distribution gap of person re-identification with camera-based batch normalization. In ECCV (pp. 140–157).
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by National Key R &D Program of China (2021YFB3100800), National Natural Science Fund of China (62271090), Chongqing Natural Science Fund (cstc2021jcyj-jqX0023). This work is also supported by Huawei computational power of Chongqing Artificial Intelligence Innovation Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Bumsub Ham.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Fu, X., Huang, F. et al. An Open-World, Diverse, Cross-Spatial-Temporal Benchmark for Dynamic Wild Person Re-Identification. Int J Comput Vis (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-024-02057-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-024-02057-z