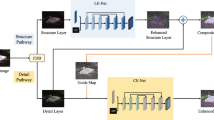
Abstract
Light adaptation or brightness correction is a key step in improving the contrast and visual appeal of an image. There are multiple light-related tasks (for example, low-light enhancement and exposure correction) and previous studies have mainly investigated these tasks individually. It is interesting to consider whether the common light adaptation sub-problem in these light-related tasks can be executed by a unified model, especially considering that our visual system adapts to external light in such way. In this study, we propose a biologically inspired method to handle light-related image enhancement tasks with a unified network (called LA-Net). First, we proposed a new goal-oriented task decomposition perspective to solve general image enhancement problems, and specifically decouple light adaptation from multiple light-related tasks with frequency-based decomposition. Then, a unified module is built inspired by biological visual adaptation to achieve light adaptation in the low-frequency pathway. Combined with the proper noise suppression and detail enhancement along the high-frequency pathway, the proposed network performs unified light adaptation across various scenes. Extensive experiments on three tasks—low-light enhancement, exposure correction, and tone mapping—demonstrate that the proposed method obtains reasonable performance simultaneously for all of these three tasks compared with recent methods designed for these individual tasks. Our code is made publicly available at https://github.com/kaifuyang/LA-Net.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
13 February 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-023-01764-3
References
Afifi, M., Derpanis, K. G., & Ommer, B., et al. (2021). Learning multi-scale photo exposure correction. In CVPR (pp. 9157–9167).
Aujol, J. F., Gilboa, G., Chan, T., et al. (2006). Structure-texture image decomposition-modeling, algorithms, and parameter selection. International Journal of Computer Vision, 67(1), 111–136.
Blau, Y., Mechrez, R., & Timofte, R., et al. (2018). The 2018 pirm challenge on perceptual image super-resolution. In ECCV workshops.
Cao, X., Lai, K., & Yanushkevich, S. N., et al. (2020). Adversarial and adaptive tone mapping operator for high dynamic range images. In 2020 IEEE symposium series on computational intelligence (pp. 1814–1821). IEEE.
Chen, Y. S., Wang, Y. C., & Kao. M. H., et al. (2018). Deep photo enhancer: Unpaired learning for image enhancement from photographs with gans. In CVPR (pp. 6306–6314).
Durand, F., & Dorsey, J. (2002). Fast bilateral filtering for the display of high-dynamic-range images. In ACM transactions on graphics (pp. 257–266). ACM.
Eilertsen, G., Kronander, J., Denes, G., et al. (2017). Hdr image reconstruction from a single exposure using deep cnns. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 36(6), 1–15.
Fairchild, M. D. (2007). The hdr photographic survey. In Color and imaging conference, society for imaging science and technology (pp. 233–238).
Fattal, R., Lischinski, D., & Werman, M. (2002). Gradient domain high dynamic range compression. In ACM transactions on graphics (pp. 249–256). ACM.
Fu, X., Huang, J., & Zeng, D., et al. (2017). Removing rain from single images via a deep detail network. In CVPR (pp. 3855–3863).
Fu, X., Zeng, D., & Huang, Y., et al. (2016). A weighted variational model for simultaneous reflectance and illumination estimation. In CVPR (pp. 2782–2790).
Gao, S. B., Zhang, M., Zhao, Q., et al. (2019). Underwater image enhancement using adaptive retinal mechanisms. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 28(11), 5580–5595.
Guo, C., Li, C., & Guo, J., et al. (2020). Zero-reference deep curve estimation for low-light image enhancement. In CVPR (pp. 1780–1789).
Guo, X., Li, Y., & Ling, H. (2016). Lime: Low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 26(2), 982–993.
Gu, K., Wang, S., Zhai, G., et al. (2016). Blind quality assessment of tone-mapped images via analysis of information, naturalness, and structure. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 18(3), 432–443.
He, K., Sun, J., & Tang, X. (2012). Guided image filtering. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 35(6), 1397–1409.
Ignatov, A., Kobyshev, N., & Timofte, R., et al. (2017). Dslr-quality photos on mobile devices with deep convolutional networks. In ICCV, (pp. 3277–3285).
Jiang, Y., Gong, X., Liu, D., et al. (2021). Enlightengan: Deep light enhancement without paired supervision. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 30, 2340–2349.
Jobson, D. J., Rahman, Zu., & Woodell, G. A. (1997). A multiscale retinex for bridging the gap between color images and the human observation of scenes. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 6(7), 965–976.
Jobson, D. J., Rahman, Zu., & Woodell, G. A. (1997). Properties and performance of a center/surround retinex. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 6(3), 451–462.
Johnson, J., Alahi, A., & Fei-Fei, L. (2016). Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In ECCV (pp. 694–711). Springer.
Kim, S. Y., Oh, J., & Kim, M. (2019). Deep sr-itm: Joint learning of super-resolution and inverse tone-mapping for 4k uhd hdr applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (pp. 3116–3125).
Land, E. H. (1977). The retinex theory of color vision. Scientific American, 237(6), 108–129.
Lee, C., Lee, C., & Kim, C. S. (2012). Contrast enhancement based on layered difference representation. In ICIP (pp. 965–968). IEEE.
Liang, Z., Xu, J., & Zhang, D., et al. (2018). A hybrid l1-l0 layer decomposition model for tone mapping. In CVPR (pp. 4758–4766).
Li, C., Guo, C., Han, L. H., et al. (2021). Low-light image and video enhancement using deep learning: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 01, 1–1.
Li, M., Liu, J., Yang, W., et al. (2018). Structure-revealing low-light image enhancement via robust retinex model. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 27(6), 2828–2841.
Liu, Y.L., Lai, W.S., & Chen, Y.S., et al. (2020). Single-image hdr reconstruction by learning to reverse the camera pipeline. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 1651–1660).
Liu, R., Ma, L., & Zhang, J., et al. (2021). Retinex-inspired unrolling with cooperative prior architecture search for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 10,561–10,570).
Lore, K. G., Akintayo, A., & Sarkar, S. (2017). Llnet: A deep autoencoder approach to natural low-light image enhancement. Pattern Recognition, 61, 650–662.
Ma, C., Yang, C. Y., Yang, X., et al. (2017). Learning a no-reference quality metric for single-image super-resolution. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 158, 1–16.
Mertens, T., Kautz, J., & Van Reeth, F. (2009). Exposure fusion: A simple and practical alternative to high dynamic range photography. In Computer graphics forum (pp. 161–171) Wiley Online Library.
Meylan, L., Alleysson, D., & Süsstrunk, S. (2007). Model of retinal local adaptation for the tone mapping of color filter array images. Journal of the Optical Society of America A: Optics, Image Science & Vision, 24(9), 2807–2816.
Meylan, L., & Susstrunk, S. (2006). High dynamic range image rendering with a retinex-based adaptive filter. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 15(9), 2820–2830.
Mittal, A., Soundararajan, R., & Bovik, A. C. (2012). Making a completely blind image quality analyzer. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 20(3), 209–212.
Montulet, R., Briassouli, A., & Maastricht, N. (2019). Deep learning for robust end-to-end tone mapping. In BMVC (p. 194).
Moran, S., Marza, P., & McDonagh, S., et al. (2020). Deeplpf: Deep local parametric filters for image enhancement. In CVPR, (pp. 12,826–12,835).
Naka, K., & Rushton, W. (1966). S-potentials from colour units in the retina of fish (cyprinidae). The Journal of Physiology, 185(3), 536–555.
Panetta, K., Kezebou, L., Oludare, V., et al. (2021). Tmo-net: A parameter-free tone mapping operator using generative adversarial network, and performance benchmarking on large scale hdr dataset. IEEE Access, 9, 39500–39517.
Pisano, E. D., Zong, S., Hemminger, B. M., et al. (1998). Contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization image processing to improve the detection of simulated spiculations in dense mammograms. Journal of Digital Imaging, 11(4), 193–200.
Pizer, S. M., Amburn, E. P., Austin, J. D., et al. (1987). Adaptive histogram equalization and its variations. Computer Vision, Graphics, and Image Processing, 39(3), 355–368.
Rana, A., Singh, P., Valenzise, G., et al. (2019). Deep tone mapping operator for high dynamic range images. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 29, 1285–1298.
Reinhard, E., Heidrich, W., Debevec, & P., et al. (2010). High dynamic range imaging: acquisition, display, and image-based lighting. Morgan Kaufmann.
Rieke, F., & Rudd, M. E. (2009). The challenges natural images pose for visual adaptation. Neuron, 64(5), 605–616.
Schiller, P. H. (2010). Parallel information processing channels created in the retina. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 107(40), 17087–17094.
Shapley, R., & Enroth-Cugell, C. (1984). Visual adaptation and retinal gain controls. Progress in Retinal Research, 3, 263–346.
Shibata, T., Tanaka, M., & Okutomi, M. (2016). Gradient-domain image reconstruction framework with intensity-range and base-structure constraints. In CVPR (pp. 2745–2753).
Su, C. C., Wang, R., Lin, H. J., et al. (2021). Explorable tone mapping operators. In ICPR (pp. 10320–10326). IEEE.
Vinker, Y., Huberman-Spiegelglas, I., & Fattal, R. (2021). Unpaired learning for high dynamic range image tone mapping. In ICCV (pp. 14,657–14,666).
Vonikakis, V. (2021). Busting image enhancement and tone-mapping algorithms. https://sites.google.com/site/vonikakis/datasets.
Wang, W., Wei, C., & Yang, W., et al. (2018). Gladnet: Low-light enhancement network with global awareness. In IEEE international conference on automatic face & gesture recognition (pp. 751–755). IEEE.
Wang, R., Zhang, Q., & Fu, C. W., et al. (2019). Underexposed photo enhancement using deep illumination estimation. In CVPR (pp. 6849–6857).
Wang, Z., Bovik, A. C., Sheikh, H. R., et al. (2004). Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 13(4), 600–612.
Wang, S., Zheng, J., Hu, H. M., et al. (2013). Naturalness preserved enhancement algorithm for non-uniform illumination images. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 22(9), 3538–3548.
Wei, C., Wang, W., & Yang, W., et al. (2018). Deep retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement. In BMVC.
Xu, K., Yang, X., & Yin, B., et al. (2020). Learning to restore low-light images via decomposition-and-enhancement. In CVPR (pp. 2281–2290).
Yan, W., Tan, R. T., & Dai, D. (2020). Nighttime defogging using high-low frequency decomposition and grayscale-color networks. In ECCV (pp. 473–488). Springer.
Yang, W., Wang, S., & Fang, Y., et al. (2020b). From fidelity to perceptual quality: A semi-supervised approach for low-light image enhancement. In CVPR (pp. 3063–3072).
Yang, K. F., Li, H., Kuang, H., et al. (2019). An adaptive method for image dynamic range adjustment. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 29(3), 640–652.
Yang, K. F., Zhang, X. S., & Li, Y. J. (2020). A biological vision inspired framework for image enhancement in poor visibility conditions. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 29, 1493–1506.
Yeganeh, H., & Wang, Z. (2012). Objective quality assessment of tone-mapped images. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 22(2), 657–667.
Yu, R., Liu, W., & Zhang, Y., et al. (2018). Deepexposure: Learning to expose photos with asynchronously reinforced adversarial learning. In NeurIPS (pp. 2153–2163).
Yuan, L., & Sun, J. (2012). Automatic exposure correction of consumer photographs. In ECCV (pp. 771–785). Springer.
Zamir, S. W., Arora, A., & Khan, S., et al. (2020). Learning enriched features for real image restoration and enhancement. In European conference on computer vision (pp. 492–511). Springer.
Zhang, Q., Nie, Y., & Zheng, W. S. (2019). Dual illumination estimation for robust exposure correction. In Computer graphics forum (pp. 243–252). Wiley Online Library.
Zhang, Y., Tian, Y., & Kong, Y., et al. (2018). Residual dense network for image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 2472–2481).
Zhang, Y., Zhang, J., & Guo, X. (2019b). Kindling the darkness: A practical low-light image enhancer. In ACM MM (pp. 1632–1640).
Zhang, Y., Guo, X., Ma, J., et al. (2021). Beyond brightening low-light images. International Journal of Computer Vision, 129(4), 1013–1037.
Zhang, X. S., Kf, Yang, Zhou, J., et al. (2020). Retina inspired tone mapping method for high dynamic range images. Optics Express, 28(5), 5953–5964.
Zhang, X. S., Yu, Y. B., Yang, K. F., et al. (2022). A fish retina-inspired single image dehazing method. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 32(4), 1875–1888.
Zhang, K., Zuo, W., Chen, Y., et al. (2017). Beyond a gaussian denoiser: Residual learning of deep cnn for image denoising. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 26(7), 3142–3155.
Zhao, L., Lu, S. P., & Chen, T., et al. (2021). Deep symmetric network for underexposed image enhancement with recurrent attentional learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (pp. 12,075–12,084).
Zheng, Z., Ren, W., & Cao, X., et al. (2021b). Ultra-high-definition image hdr reconstruction via collaborative bilateral learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (pp. 4449–4458).
Zheng, C., Shi, D., & Shi, W. (2021a). Adaptive unfolding total variation network for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (pp. 4439–4448).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by STI2030-Major Projects (2022ZD0204600) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62076055). This work was also partly supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (ZYGX2019J114).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by Boxin Shi.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, KF., Cheng, C., Zhao, SX. et al. Learning to Adapt to Light. Int J Comput Vis 131, 1022–1041 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-022-01745-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-022-01745-y