Abstract
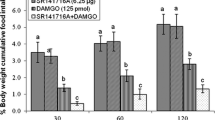
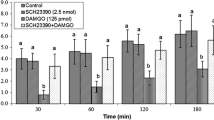
Central regulatory mechanisms for neurotransmitters of food intake vary among animals. Endocannabinoids have crucial role on central food intake regulation in mammals but its role has not been studied in layer-type chicken. Thus, in this study 6 experiments designed to evaluate effects of intracerebroventricular (ICV) administration of 2-AG (2-Arachidonoylglycerol, selective CB1 receptors agonist), SR141716A (selective CB1 receptors antagonist), JWH015 (selective CB2 receptors agonist), AM630 (selective CB2 receptors antagonist) on feeding behavior in 3 h food deprived neonatal layer-type chickens. In experiment 1, birds ICV injected with control solution and 2-AG (0.25, 0.5 and 1 μg). In experiment 2: control solution, SR141716A (6.25, 12.5 and 25 μg) were ICV injected to birds. In experiment 3 animals received: control solution, SR141716A (6.25 μg), 2-AG (1 μg) and co-injection of SR141716A+2-AG. In experiment 4, chickens received control solution and JWH015 (6.25, 12.5 and 25 μg). In experiment 5, control solution and AM630 (1.25, 2.5 and 5 μg) were injected. In experiment 6, the birds received control solution, AM630 (1.25 μg), JWH015 (25 μg) and co-administration of AM630+JWH015. Then, cumulative food intake was recorded until 120 min after injection. According to the results, 2-AG dose dependently increased cumulative food intake while SR141716A reduced appetite compared to control group (P < 0.05). Injection of 2-AG (1 μg) amplified food intake and its effect minimized by SR141716A (6.25 μg) (P < 0.05). Also, ICV injection of JWH015 (25 μg) dose dependently increased food intake and co-injection of JWH015+AM630 decreased JWH015-induced food intake (P < 0.05). These results suggest CB1 and CB2 receptors have an important role on ingestive behavior in FD3 neonatal layer-type chicken.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam AS, Wenger T, Csillag A (2008) The cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist rimonabant dose-dependently inhibits memory recall in the passive avoidance task in domestic chicks (Gallus domesticus). Brain Res Bull 76:272–274
Alimohammadi S, Zendehdel M, Babapour V (2015) Modulation of opioid-induced feeding behavior by endogenous nitric oxide in neonatal layer-type chicks. Vet Res Commun. doi:10.1007/s11259-015-9631-8
Bungo T, Kawamura K, Izumi T, Dodo K, Ueda H (2005) Effects of various lμ-, δ- and κ-opioid ligands on food intake in the meat type chick. Physiol Behav 85:519–523
Chen RZ, Frassetto A, Fong TM (2006) Effects of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor inverse agonist AM251 on food intake and body weight in mice lacking μ-opioid receptors. Brain Res 1108:176–178
D’Addario C, Micioni Di Bonaventura MV, Puccia M, Romano A, Gaetani S, Ciccocioppo R, Cifani C, Maccarrone M (2014) Endocannabinoid signaling and food addiction. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 47:203–224
Davis JL, Masuoka DT, Gerbrandt LK, Cherkin A (1979) Autoradiographic distribution of L-proline in chicks after intracerebral injection. Physiol Behav 22:693–695
Denbow DM (1994) Peripheral regulation of food intake in poultry. J Nutr 124:1349S–1354S
Di Marzo VGS, Wang L, Liu J, Batkai S, Jarai Z, Fezza F, Miura GI, Palmiter RD, Sugiura T, Kunos G (2001) Leptin regulated endocannabinoids are involved in maintaining food intake. Nature 410:822–825
Ehrhart J, Obregon D, Mori T, Hou H, Sun N, Bai Y, Klein T, Fernandez F, Tan J, Shytle RD (2005) Stimulation of cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2) suppresses microglial activation. J Neuroinflammation 2:29
Emadi L, Jonaidi H, Hosseini Amir Abad E (2011) The role of central CB2 cannabinoid receptors on food intake in neonatal chicks. J Comp Physiol A 197:1143–1147
Fowler CJ, Nilsson O, Andersson M, Disney G, Jacobsson SO, Tiger G (2001) Pharmacological properties of cannabinoid receptors in the avian brain: similarity of rat and chicken cannabinoid1 receptor recognition sites and expression of cannabinoid2 receptor-like immunoreactivity in the embryonic chick brain. Pharmacol Toxicol 88:213–222
Furuse M, Matsumoto M, Saito N, Sugahara K, Hasegawa S (1997) The central corticotropin-releasing factor and glucagon-like peptide-1 in food intake of the neonatal chick. Eur J Pharmacol 339:211–214
Galiegue S, Mary S, Marchand J, Dussossoy D, Carriere D, Carayon P, Bouaboula M, Shire D, Le Fur G, Casellas P (1995) Expression of central and peripheral cannabinoid receptors in human immune tissues and leukocyte subpopulations. Eur J Biochem 232:54–61
Gamber KM, Macarthur H, Westfall TC (2005) Cannabinoids augment therelease of neuropeptide Y in the rat hypothalamus. Neuropharmacology 49:646–652
Hentges ST, Low MJ, Williams JT (2005) Differential regulation of synaptic inputsby constitutively released endocannabinoids and exogenous cannabinoids. J Neurosci 25:9746–9751
Irwin N, Hunter K, Frizzell N, Flatt PR (2008) Antidiabetic effects of sub-chronic administration of the cannabinoid receptor (CB1) antagonist, AM251, in obese diabetic (ob/ob) mice. Eur J Pharmacol 581:226–233
Kaiya H, Miyazato M, Kangawa K (2011) Recent advances in the phylogenetic study of ghrelin. Peptides 32:2155–2174
Kaneko K, Yoshikawa M, Ohinata K (2012) Novel orexigenic pathway prostaglandin D2-NPY system-Involvement in orally active orexigenic δ opioid peptide. Neuropeptides 46:353–357
Le Merrer J, Becker JAJ, Befort K, Kieffer BL (2009) Reward processing by the opioid system in the brain. Physiol Rev 89:1379–1412
Levine AS (2006) The animal model in food intake regulation: examples from the opioid literature. Physiol Behav 89:92–96
Lim CT, Kola B, Korbonits M (2010) AMPK as a mediator of hormonal signaling. J Mol Endocrinol 44:87–97
López HH (2010) Cannabinoid–hormone interactions in the regulation of motivational processes. Horm Behav 58:100–110
Nicoll RA, Alger BE (2004) The brain’s own marijuana. Sci Am 291:68–75
Novoseletsky N, Nussinovitch A, Friedman-Einat M (2011) Attenuation of food intake in chicks by an inverse agonist of cannabinoid receptor 1 administered by either injection or ingestion in hydrocolloid carriers. Gen Comp Endocrinol 170:522–527
Olanrewaju HA, Thaxton JP, Dozier WA, Purswell J, Roush WB, Branton SL (2006) A review of lighting programs for broiler production. Int J Poult Sci 5(4):301–308
Onaivi ES, Carpio O, Ishiguro H, Schanz N, Uhl GR, Benno R (2008) Behavioral effects of CB2 cannabinoid receptor activation and its influence on food and alcohol consumption. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1139:426–433
Onaivi ES, Ishiguro H, Gu S, Liu QR (2012) CNS effects of CB2 cannabinoid receptors: beyond neuro-immuno-cannabinoid activity. J Psychopharmacol 26:92–103
Parker KE, Johns HW, Floros TG, Will MJ (2014) Central amygdala opioid transmission is necessary for increased high-fat intake following 24-h food deprivation, but not following intra-accumbens opioid administration. Behav Brain Res 260:131–138
Pertwee RG (2005) Pharmacological actions of cannabinoids. Handb Exp Pharmacol 168:1–51
Pingwen X, Siegel PB, Denbow DM (2011) Genetic selection for body weight in chickens has altered responses of the brain’s AMPK system to food intake regulation effect of ghrelin, but not obestatin. Behav Brain Res 221:216–226
Richards MP (2003) Genetic regulation of feed intake and energy balance in poultry. Poult Sci 82:907–916
Saito ES, Kaiya H, Tachibana T, Tomonaga S, Denbow DM, Kangawa K, Furuse M (2005) Inhibitory effect of ghrelin on food intake is mediated by the corticotropin-releasing factor system in neonatal chicks. Regul Pept 125:201–208
Saneyasu T, Honda K, Kamisoyama H, Ikura A, Nakayama Y, Hasegawa S (2011) Neuropeptide Y effect on food intake in broiler and layer chicks. Comp Biochem Physiol A Physiol 159:422–426
Sanudo-Pena MC, Romero J, Seale GE, Fernandez-Ruiz JJ, Walker JM (2000) Activational role of cannabinoids on movement. Eur J Pharmacol 391:269–274
Sharkey KA, Darmani NA, Parker LA (2014) Regulation of nausea and vomiting by cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system. Eur J Pharmacol 722:134–146
Shiraishi J, Yanagita K, Fukumori R, Sugino T, Fujita M, Kawakami S, McMurtry JP, Bungo T (2011) Comparisons of insulin related parameters in commercial-type chicks: evidence for insulin resistance in broiler chicks. Physiol Behav 103:233–239
Soria-Gomez E, Matias I, Rueda-Orozco PE, Cisneros M, Petrosino S, Navarro L, Di Marzo V, Prospero-Garcia O (2007) Pharmacological enhancement of the endocannabinoid system in the nucleus accumbens shell stimulates food intake and increases c-Fos expression in the hypothalamus. Br J Pharmacol 151:1109–1116
Tedesco L, Valerio A, Cervino C, Cardile A, Pagano C, Vettor R, Pasquali R, Carruba MO, Marsicano G, Lutz B, Pagotto U, Nisoli E (2008) Cannabinoid type 1 receptor blockade promotes mitochondrial biogenesis through endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression in white adipocytes. Diabetes 57:2028–2036
Van Sickle MD, Duncan M, Kingsley PJ, Mouihate A, Urbani P, Mackie K, Stella N, Makriyannis A, Piomelli D, Davison JS, Marnett LJ, Di Marzo V, Pittman QJ, Patel KD, Sharkey KA (2005) Identification and functional characterization of brainstem cannabinoid CB2 receptors. Science 310:329–332
Van Tienhoven A, Juhasz LP (1962) The chicken telencephalon, diencephalon and mesencephalon in sterotaxic coordinates. J Comp Neurol 118:185–197
Verty ANA, McFarlane JR, McGregor IS, Mallet PE (2004) Evidence for an interaction between CB1 cannabinoid and melanocortin MCR-4 receptors in regulating food intake. Endocrinology 145(7):3224–3231
Wiley JL, Marusich JA, Zhang Y, Fulp A, Maitra R, Thomas BF, Mahadevan A (2012) Structural analogs of pyrazole and sulfonamide cannabinoids: effects on acute food intake in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 695:62–70
Williams CM, Kirkham TC (2002) Reversal of ∆9-THC hyperphagia by SR141716 and naloxone but not dexfenfluramine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:333–340
Wren AM, Small CJ, Ward HL, Murphy KG, Dakin CL, Taheri S et al (2000) The novel hypothalamic peptide ghrelin stimulates food intake and growth hormone secretion. Endocrinology 141:4325–4328
Zendehdel M, Hassanpour S (2014) Ghrelin-induced hypophagia is mediated by the β2 adrenergic receptor in chicken. J Physiol Sci 64:383–391
Zendehdel M, Mokhtarpouriani K, Hamidi F, Montazeri R (2013) Intracerebroventricular injection of ghrelin produces hypophagia through central serotonergic mechanisms in chicken. Vet Res Commun 37:37–41
Zendehdel M, Hamidi F, Hassanpour S (2015) The effect of histaminergic system on nociceptin/orphanin FQ induced food intake in chicken. Int J Pept Res Ther. doi:10.1007/s10989-014-9445-5
Conflict of interest
Abbas Alizadeh, Morteza Zendehdel, Vahab Babapour, Saeed Charkhkar and Shahin Hassanpour declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
This manuscript does not contain any studies with human subjects performed by any of the authors.
Human and animal rights
All experiments executed according to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and approved by the institutional animal ethics committee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alizadeh, A., Zendehdel, M., Babapour, V. et al. Role of cannabinoidergic system on food intake in neonatal layer-type chicken. Vet Res Commun 39, 151–157 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-015-9636-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-015-9636-3