Abstract
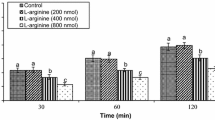
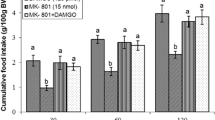
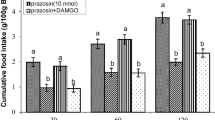
The current study was designed to evaluate the effects of central administration of L-arginine (The precursor of nitric oxide), NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME), a nitric oxide (NO) synthase inhibitor, selective opioid receptor agonists and involvement of central nitrergic/opioidergic systems on feeding behavior in neonatal layer-type chicks. The results of this study showed that the intracerebroventricular (ICV) injection of L-arginine (400 and 800 nmol) significantly decreased food intake (P < 0.001) but the injection of 200 nmol L-arginine had no effect on cumulative food intake in FD3 chickens (P > 0.05). The ICV injection of L-NAME (200 and 400 nmol) increased food intake (P < 0.001) but 100 nmol of L-NAME had no significant effect (P > 0.05). On the other hand, the co-injection of 100 nmol L-NAME significantly attenuated the anorexigenic effect of 800 nmol L-arginine (P < 0.001). Moreover, the food intake of chicks was significantly decreased by ICV injection of DAMGO (μ-opioid receptor agonist, 125 pmol) (P < 0.001) while both DPDPE (δ-opioid receptor agonist, 40 pmol) and U-50488H (κ-opioid receptor agonist, 30 nmol) significantly stimulated food intake (P < 0.001). In addition, the hypophagic effect of DAMGO was significantly amplified by administration of L-arginine (P < 0.001) while the administration of L-NAME attenuated the hypophagic effect of DAMGO (P < 0.001). In contrast, co-injection of L-arginine or L-NAME with DPDPE had no effect on the hyperphagia induced by DPDPE as well as the hyperphagic effect of U-50488H on food intake was not affected by concurrent injection of L-arginine or L-NAME (P > 0.05). These results suggest that nitrergic and opioidergic systems have an important role on feeding behavior in the CNS of neonatal layer-type chicks and it seems that interaction between them is mediated by μ-opioid receptor.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amarante LH, Duarte ID (2002) The kappa-opioid agonist (+/−)-bremazocine elicits peripheral antinociception by activation of the L-arginine/nitric oxide/cyclic GMP pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 454(1):19–23
Anand R, Gulati K, Ray A (2012) Pharmacological evidence for the role of nitric oxide in the modulation of stress-induced anxiety by morphine in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 676:71–74
Barjavel MJ, Bhargava HN (1994) Effect of opioid receptor agonists on nitric oxide synthase activity in rat cerebral cortex homogenate. Neurosci Lett 181(1–2):27–30
Benamar K, Geller EB, Adler MW (2002) Role of the nitric oxide pathway in κ-opioid-induced hypothermia in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 303(1):375–378
Boswell T (2005) Regulation of energy balance in birds by the neuroendocrine hypothalamus. J Poult Sci 42(3):161–181
Bredt DS, Snyder SH (1992) Nitric oxide, a novel neuronal messenger. Neuron 8(1):3–11
Bungo T, Izumi T, Kawamura K, Takagi T, Ueda H, Furuse M (2003) Intracerebroventricular injection of muscimol, baclofen or nipecotic acid stimulates food intake in layer-type, but not meat-type, chicks. Brain Res 993(1–2):235–238
Bungo T, Kawamura K, Izumi T, Dodo K-I, Ueda H (2004) Feeding responses to μ, δ and κ-opioid receptor agonists in the meat-type chick. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 78(4):707–710
Bungo T, Dodo K-I, Kawamura K, Izumi T, Ueda H (2005) Effects of various μ- and δ-opioid ligands on food intake in the meat-type chick. Physiol Behav 85(5):519–523
Bungo T, Dodo K-I, Izumi T (2007) Central injection of endomorphin-2, but not endomorphin-1, increases food intake in chicks via μ1-opioid receptors. J Poult Sci 44(2):205–208
Choi YH, Furuse M, Okumura J, Denbow DM (1994) Nitric oxide controls feeding behavior in the chicken. Brain Res 654:163–166
Choi YH, Furuse M, Okumura J, Denbow DM (1995) The interaction of clonidine and nitric oxide on feeding behavior in the chicken. Brain Res 699:161–164
Cuellar B, Fernandez AP, Lizasoain I, Moro MA, Lorenzo P, Bentura ML, Rodrigo J, Leza JC (2000) Up-regulation of neuronal NO synthase immunoreactivity in opiate dependence and withdrawal. Psychopharmacology 148:66–73
Czech DA, Kazel MR, Harris J (2003) A nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, N(G)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester, attenuates lipoprivic feeding in mice. Physiol Behav 80(1):75–79
Davis JL, Masuoka DT, Gerbrandt LK, Cherkin A (1979) Autoradiographic distribution of L-proline in chicks after intracerebral injection. Physiol Behav 22:693–695
De Luca B, Monda M, Sullo A (1995) Changes in eating behavior and thermogenic activity following inhibition of nitric oxide formation. Am J Physiol 268:1533–1538
Dodo K-I, Izumi T, Ueda H, Bungo T (2005) Response of neuropeptide Y-induced feeding to μ-δ- and κ-opioid receptor antagonists in the neonatal chick. Neurosci Lett 373:85–88
Dortch-Carnes J, Russell K (2007) Morphine-stimulated nitric oxide release in rabbit aqueous humor. Exp Eye Res 84(1):185–190
Feng Y, He X, Yang Y, Chao D, Lazarus LH, Xia Y (2012) Current research on opioid receptor function. Curr Drug Targets 13(2):230–246
Filizola M, Devi LA (2013) Grand opening of structure-guided design for novel opioids. Trends Pharmacol Sci 34(1):6–12
Furuse M (2002) Central regulation of food intake in the neonatal chick. Anim Sci J 73(2):83–94
Furuse M, Matsumoto M, Saito N, Sugahara K, Hasegawa S (1997) The central corticotropin-releasing factor and glucagon-like peptide-1 in food intake of the neonatal chick. Eur J Pharmacol 339:211–214
Gray AC, Coupar IM, White PJ (2006) Comparison of opioid receptor distributions in the rat central nervous system. Life Sci 79(7):674–685
Guix FX, Uribesalgo I, Coma M, Muñoz FJ (2005) The physiology and pathophysiology of nitric oxide in the brain. Prog Neurobiol 76(2):126–152
Han C, Zhao Q, Lu B (2013) The role of nitric oxide signaling in food intake; insights from the inner mitochondrial membrane peptidase 2 mutant mice. Redox Biol 1(1):498–507
Herráez-Baranda LA, Carretero J, González-Sarmiento R, Laorden ML, Milanés MV, Rodríguez RE (2005) Evidence of involvement of the nNOS and the kappa-opioid receptor in the same intracellular network of the rat periaqueductal gray that controls morphine tolerance and dependence. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 137(1–2):166–173
Hervera A, Negrete R, Leánez S, Martín-Campos JM, Pol O (2011) Peripheral effects of morphine and expression of μ-opioid receptors in the dorsal root ganglia during neuropathic pain: nitric oxide signaling. Mol Pain. doi:10.1186/1744-8069-7-25
Homayoun H, Khavandgar S, Namiranian K, Gaskari SA, Dehpour AR (2002) The role of nitric oxide in anticonvulsant and proconvulsant effects of morphine in mice. Epilepsy Res 48:33–41
Jonaidi H, Noori Z (2012) Neuropeptide Y-induced feeding is dependent on GABAA receptors in neonatal chicks. J Comp Physiol A 198:827–832
Kamerman P, Mitchell D, Laburn H (2002) Circadian variation in the effects of nitric oxide synthase inhibitors on body temperature, feeding and activity in rats. Eur J Physiol 443:609–616
Kaneko K, Yoshikawa M, Ohinata K (2012) Novel orexigenic pathway prostaglandin D2-NPY system-Involvement in orally active orexigenic δ opioid peptide. Neuropeptides 46:353–357
Khan MSI, Dodo K-I, Yahata K, Nishimoto S, Ueda H, Taneike T, Kitazawa T, Hosaka Y, Bungo T (2006) Intracerebroventricular administration of growth hormone releasing peptide-6 (GHRP-6) inhibits food intake, but not food retention of crop and stomach in neonatal chicks. J Poult Sci 43(1):35–40
Khan MSI, Tachibana T, Hasebe Y, Masuda N, Ueda H (2007) Peripheral or central administration of nitric oxide synthase inhibitor affects feeding behavior in chicks. Comp Biochem Physiol A 148:458–462
Khan MSI, Nakano Y, Tachibana T, Ueda H (2008) Nitric oxide synthase inhibitor attenuates the anorexigenic effect of corticotropin-releasing hormone in neonatal chicks. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 149(3):325–329
Khan MSI, Ohkubo T, Masuda N, Tachibana T, Ueda H (2009) Central administration of metastin increases food intake through opioid neurons in chicks. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 153(2):209–212
Kiss JP, Vizi ES (2001) Nitric oxide: a novel link between synaptic and nonsynaptic transmission. Trends Neurosci 24(4):211–215
Koch JE, Pasternak GW, Arjune D, Bodnar RJ (1992) Naloxone benzoylhydrazone, a κ3 opioid agonist, stimulates food intake in rats. Brain Res 581(2):311–314
Le Merrer J, Becker JA, Befort K, Kieffer BL (2009) Reward processing by the opioid system in the brain. Physiol Rev 89(4):1379–1412
Llorente J, Santamarta MT, Henderson G, Pineda J (2012) Enhancement of μ-opioid receptor desensitization by nitric oxide in rat locus coeruleus neurons: involvement of reactive oxygen species. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 342(2):552–560
McCormack JF, Denbow DM (1988) Feeding, drinking and temperature responses to intracerebroventricular beta-endorphin in the domestic fowl. Peptides 9(4):709–715
McCormack JF, Denbow DM (1989) Ingestive responses to mu and delta opioid receptor agonists in the domestic fowl. Br Poult Sci 30(2):327–340
Morley JE, Flood JF (1991) Evidence that nitric oxide modulates food intake in mice. Life Sci 49(10):707–711
Morley JE, Farr SA, Sell RL, Hileman SM, Banks WA (2011) Nitric oxide is a central component in neuropeptide regulation of appetite. Peptides 32:776–780
Olszewski PK, Levine AS (2004) Minireview: characterization of influence of central nociceptin/orphanin FQ on consummatory behavior. Endocrinology 145(6):2627–2632
Ortiz MI, Castro-Olguin J, Pena-Samaniego N, Castaneda-Hernandez G (2005) Probable activation of the opioid receptor-nitric oxide-cyclic GMP-K+ channels pathway by codeine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 82(4):695–703
Pacheco DF, Reis GML, Francischi JN, Castro MSA, Perez AC, Duarte IDG (2005) Opioid receptor agonist SNC80 elicits peripheral antinociception via δ1 and δ2 receptors and activation of the L-arginine/nitric oxide/cyclic GMP pathway. Life Sci 78:54–60
Parker KE, Johns HW, Floros TG, Will MJ (2014) Central amygdala opioid transmission is necessary for increased high-fat intake following 24-h food deprivation, but not following intra-accumbens opioid administration. Behav Brain Res 260:131–138
Pu S, Horvath TL, Diano S, Naftolin F, Kalra PS, Kalra SP (1997) Evidence showing that β-endorphin regulates cyclic guanosine 3′,5′-monophosphate (cGMP) efflux: anatomical and functional support for an interaction between opiates and nitric oxide. Endocrinology 138:1537–1543
Sahraei H, Poorheidari G, Foadaddini M, Khoshbaten A, Asgari A, Noroozzadeh A, Ghoshooni H, Firoozabadi SH, Zarrindast MR (2004) Effects of nitric oxide on morphine self-administration in rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 77:111–116
Saito ES, Kaiya H, Tachibana T, Tomonaga S, Denbow DM, Kangawa K, Furuse M (2005) Inhibitory effect of ghrelin on food intake is mediated by the corticotropin-releasing factor system in neonatal chicks. Regul Pept 125:201–208
Savory CJ, Gentle MJ, Yeomans MR (1989) Opioid modulation of feeding and drinking in fowls. Br Poult Sci 30:379–392
Schneider GM, Lysle DT (1998) Role of central μ-opioid receptors in the modulation of nitric oxide production by splenocytes. J Neuroimmunol 89:150–159
Smart D, Lambert DG (1996) The stimulatory effects of opioids and their possible role in the development of tolerance. Trends Pharmacol Sci 17(7):264–269
Southam E, East SJ, Garthwaite J (1991) Excitatory amino acid receptors coupled to the nitric oxide/cyclic GMP pathway in rat cerebellum during development. J Neurochem 56:2072–2081
Toda N, Kishioka S, Hatano Y, Toda H (2009) Anesthesiology 110(1):166–181
Van Tienhoven A, Juhasz LP (1962) The chicken telencephalon, diencephalon and mesencephalon in sterotaxic coordinates. J Comp Neurol 118:185–197
Wang C, Hou SS, Huang W, Xu TS, Rong GH, Xie M (2014) Arginine affects appetite via nitric oxide in ducks. Poult Sci 93(8):2048–2053
Yanagita K, Shiraishi J, Fujita M, Bungo T (2008) Effects of N-terminal fragments of β-endorphin on feeding in chicks. Neurosci Lett 442(2):140–142
Yang SJ, Denbow DM (2007) Interaction of leptin and nitric oxide on food intake in broilers and Leghorns. Physiol Behav 92(4):651–657
Yoo JH, Cho JH, Lee SY, Lee S, Loh HH, Ho IK, Jang CG (2006) Differential effects of morphine and cocaine-induced nNOS immunoreactivity in the dentate gyrus of hippocampus of mice lacking μ-opioid receptors. Neurosci Lett 395:98–102
Zendehdel M, Baghbanzadeh A, Babapour V, Cheraghi J (2009) The effects of bicuculline and muscimol on glutamate-induced feeding behaviour in broiler cockerels. J Comp Physiol A 195:715–720
Zendehdel M, Mokhtarpouriani K, Hamidi F, Montazeri R (2012) Intracerebroventricular injection of ghrelin produces hypophagia through central serotonergic mechanisms in chicken. Vet Res Commun 37(1):37–41
Zheng H, Patterson LM, Berthoud HR (2007) Orexin signaling in the ventral tegmental area is required for high-fat appetite induced by opioid stimulation of the nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci 27(41):11075–11082
Zhu W, Ma Y, Bell A, Esch T, Guarna M, Bilfinger TV, Bianchi E, Stefano GB (2004) Presence of morphine in rat amygdala: evidence for the mu3 opiate receptor subtype via nitric oxide release in limbic structures. Med Sci Monit 10(12):433–439
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from the Research Council of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Tehran, Iran.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alimohammadi, S., Zendehdel, M. & Babapour, V. Modulation of opioid-induced feeding behavior by endogenous nitric oxide in neonatal layer-type chicks. Vet Res Commun 39, 105–113 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-015-9631-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-015-9631-8