Abstract
Purpose
There are few studies on the establishment of diagnostic models for diabetic nephropathy (DN) in in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients based on biomarkers. This study was to establish a model for diagnosing DN in T2DM.
Methods
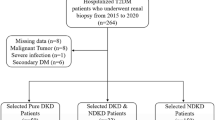
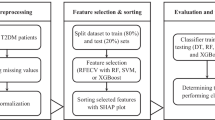
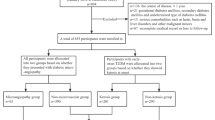
In this cross-sectional study, data were collected from the Second Hospital of Shijiazhuang between August 2018 to March 2021. Totally, 359 eligible participants were included. Clinical characteristics and laboratory data were collected. LASSO regression analysis was used to screen out diagnostic factors, and the selected factors were input into the decision tree for fivefold cross validation; then a diagnostic model was established. The performances of the diagnosis model were evaluated by the area under the receiver operator characteristic curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and accuracy. The diagnostic performance of the model was also validated through risk stratifications.
Results
Totally, 199 patients (55.43%) were diagnosed with DN. Age, diastolic blood pressure (DBP), fasting blood glucose, insulin treatment, mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC), platelet distribution width (PDW), uric acid (UA), serum creatinine (SCR), fibrinogen (FIB), international normalized ratio (INR), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) were the diagnostic factors for DN in T2DM. The diagnostic model presented good performances, with the sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, AUC, and accuracy being 0.849, 0.969, 0.971, 0.838, 0.965, and 0.903, respectively. The diagnostic model based on the stratifications also showed excellent diagnostic performance for diagnosing DN in T2DM patients.
Conclusion
Our diagnostic model with simple and accessible factors provides a noninvasive method for the diagnosis of DN.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Magliano DJ, Chen L, Islam RM, Carstensen B, Gregg EW, Pavkov ME, Andes LJ, Balicer R, Baviera M, Boersma-van Dam E, Booth GL, Chan JCN, Chua YX, Fosse-Edorh S, Fuentes S, Gulseth HL, Gurevicius R, Ha KH, Hird TR, Jermendy G, Khalangot MD, Kim DJ, Kiss Z, Kravchenko VI, Leventer-Roberts M, Lin CY, Luk AOY, Mata-Cases M, Mauricio D, Nichols GA, Nielen MM, Pang D, Paul SK, Pelletier C, Pildava S, Porath A, Read SH, Roncaglioni MC, Lopez-Doriga Ruiz P, Shestakova M, Vikulova O, Wang KL, Wild SH, Yekutiel N, Shaw JE (2021) Trends in the incidence of diagnosed diabetes: a multicountry analysis of aggregate data from 22 million diagnoses in high-income and middle-income settings. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 9(4):203–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-8587(20)30402-2
Magliano DJ, Islam RM, Barr ELM, Gregg EW, Pavkov ME, Harding JL, Tabesh M, Koye DN, Shaw JE (2019) Trends in incidence of total or type 2 diabetes: systematic review. BMJ (Clinical research ed) 366:l5003. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l5003
Cosentino F, Grant PJ, Aboyans V, Bailey CJ, Ceriello A, Delgado V, Federici M, Filippatos G, Grobbee DE, Hansen TB, Huikuri HV, Johansson I, Jüni P, Lettino M, Marx N, Mellbin LG, Östgren CJ, Rocca B, Roffi M, Sattar N, Seferović PM, Sousa-Uva M, Valensi P, Wheeler DC (2020) 2019 ESC guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD. Eur Heart J 41(2):255–323. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehz486
Quan KY, Yap CG, Jahan NK, Pillai N (2021) Review of early circulating biomolecules associated with diabetes nephropathy—ideal candidates for early biomarker array test for DN. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 182:109122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109122
Gong P, Wang P, Pi S, Guo Y, Pei S, Yang W, Chang X, Wang L, Chen F (2021) Proanthocyanidins protect against cadmium-induced diabetic nephropathy through p38 MAPK and KEAP1/Nrf2 signaling pathways. Front Pharmacol 12:801048. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.801048
Bülow RD, Boor P (2019) Extracellular matrix in kidney fibrosis: more than just a Scaffold. J Histochem Cytochem 67(9):643–661. https://doi.org/10.1369/0022155419849388
Stehouwer CDA (2018) Microvascular dysfunction and hyperglycemia: a vicious cycle with widespread consequences. Diabetes 67(9):1729–1741. https://doi.org/10.2337/dbi17-0044
Wang G, Ouyang J, Li S, Wang H, Lian B, Liu Z, Xie L (2019) The analysis of risk factors for diabetic nephropathy progression and the construction of a prognostic database for chronic kidney diseases. J Transl Med 17(1):264. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-019-2016-y
Ruiz-Ortega M, Rodrigues-Diez RR, Lavoz C, Rayego-Mateos S (2020) Special issue “Diabetic nephropathy: diagnosis, prevention and treatment.” J Clin Med 9(3):813. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030813
Bermejo S, Pascual J, Soler MJ (2018) The current role of renal biopsy in diabetic patients. Minerva Med 109(2):116–125. https://doi.org/10.23736/s0026-4806.17.05446-5
Hogan JJ, Mocanu M, Berns JS (2016) The native kidney biopsy: update and evidence for best practice. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol CJASN 11(2):354–362. https://doi.org/10.2215/cjn.05750515
Zhang D, Ye S, Pan T (2019) The role of serum and urinary biomarkers in the diagnosis of early diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. PeerJ 7:e7079. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.7079
Thipsawat S (2021) Early detection of diabetic nephropathy in patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a review of the literature. Diab Vasc Dis Res 18(6):14791641211058856. https://doi.org/10.1177/14791641211058856
Yu D, Shang J, Cai Y, Wang Z, Zhao B, Zhao Z, Simmons D (2020) A low-cost laboratory-based method for predicting newly diagnosed biopsy-proven diabetic nephropathy in people with type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med 37(10):1728–1736. https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.14195
Chung JO, Cho DH, Chung DJ, Chung MY (2012) Associations between hemoglobin concentrations and the clinical characteristics of patients with type 2 diabetes. Korean J Intern Med 27(3):285–292. https://doi.org/10.3904/kjim.2012.27.3.285
Al-Rubeaan K, Siddiqui K, Alghonaim M, Youssef AM, AlNaqeb D (2018) The Saudi diabetic kidney disease study (Saudi-DKD): clinical characteristics and biochemical parameters. Ann Saudi Med 38(1):46–56. https://doi.org/10.5144/0256-4947.2018.03.01.1010
Liu J, Liu X, Li Y, Quan J, Wei S, An S, Yang R, Liu J (2018) The association of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, mean platelet volume, and platelet distribution width with diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy: a meta-analysis. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/bsr20180172
American Diabetes Association (2010) Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 33(Suppl 1):S62-69. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc10-S062
AlSahow A, AlHelal B, Alyousef A, AlQallaf A, Marzouq A, Nawar H, Fanous G, Abdelaty M, Bahbahani Y, AlRajab H, AlTerkait A, Ali H (2020) Renal data from the Arab world dialysis in Kuwait: 2013–2019. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 31(4):826–830. https://doi.org/10.4103/1319-2442.292317
Zhang W, Liu X, Dong Z, Wang Q, Pei Z, Chen Y, Zheng Y, Wang Y, Chen P, Feng Z, Sun X, Cai G, Chen X (2022) New diagnostic model for the differentiation of diabetic nephropathy from non-diabetic nephropathy in Chinese patients. Front Endocrinol 13:913021. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.913021
Li H, Shen Y, Yu Z, Huang Y, He T, Xiao T, Li Y, Xiong J, Zhao J (2021) Potential role of the renal arterial resistance index in the differential diagnosis of diabetic kidney disease. Front Endocrinol 12:731187. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2021.731187
Liu MY, Chen XM, Sun XF, Zhou JH, Zhang XG, Zhu HY, Chen YZ, Liu SW, Wei RB, Tang L, Cai GY, Zhang L, Bai XY (2014) Validation of a differential diagnostic model of diabetic nephropathy and non-diabetic renal diseases and the establishment of a new diagnostic model. J Diabetes 6(6):519–526. https://doi.org/10.1111/1753-0407.12150
Miao DD, Pan EC, Zhang Q, Sun ZM, Qin Y, Wu M (2017) Development and validation of a model for predicting diabetic nephropathy in Chinese people. Biomed Environ Sci BES 30(2):106–112. https://doi.org/10.3967/bes2017.014
Li L, Yang Y, Zhu X, Xiong X, Zeng L, Xiong S, Jiang N, Li C, Yuan S, Xu H, Liu F, Sun L (2020) Design and validation of a scoring model for differential diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy and nondiabetic renal diseases in type 2 diabetic patients. J Diabetes 12(3):237–246. https://doi.org/10.1111/1753-0407.12994
Kamijo-Ikemori A, Sugaya T, Yasuda T, Kawata T, Ota A, Tatsunami S, Kaise R, Ishimitsu T, Tanaka Y, Kimura K (2011) Clinical significance of urinary liver-type fatty acid-binding protein in diabetic nephropathy of type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 34(3):691–696. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc10-1392
Zhou XW, Jiang J, Ren W, Fei YY, Peng L, Jiang JL, Lan L, Ye SD (2018) Related factors of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 98(30):2403–2406. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2018.30.007
Cai W, Li J, Xu JX, Liu Y, Zhang W, Xiao JR, Zhu LY, Liu JY (2015) Association of 2184AG polymorphism in the RAGE gene with diabetic nephropathy in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Res 2015:310237. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/310237
Martin CL, Albers JW, Pop-Busui R (2014) Neuropathy and related findings in the diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study. Diabetes Care 37(1):31–38. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc13-2114
Lachin JM, White NH, Hainsworth DP, Sun W, Cleary PA, Nathan DM (2015) Effect of intensive diabetes therapy on the progression of diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 1 diabetes: 18 years of follow-up in the DCCT/EDIC. Diabetes 64(2):631–642. https://doi.org/10.2337/db14-0930
de Kort H, de Koning EJ, Rabelink TJ, Bruijn JA, Bajema IM (2011) Islet transplantation in type 1 diabetes. BMJ (Clin Res Ed) 342:d217. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.d217
Mi AE, Abdallah N, Eldars W (2021) Mean platelet volume and platelet distribution width correlate with microvascular complications in Egyptian People with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Diabetes Rev 17(8):e080621193947. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573399817666210608121024
Tessari P, Kiwanuka E, Barazzoni R, Vettore M, Zanetti M (2006) Diabetic nephropathy is associated with increased albumin and fibrinogen production in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 49(8):1955–1961. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-006-0288-2
Matuszewski W, Stefanowicz-Rutkowska MM, Szychlińska M, Bandurska-Stankiewicz E (2020) Differences in risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in North-East Poland. Medicina (Kaunas) 56(4):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56040177
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YX designed the study and wrote the manuscript. XC, KL and GC collected, analyzed, and interpreted the data. YX critically reviewed, edited, and approved the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the ethics committee of the Second Hospital of Shijiazhuang (No. Sey2021005).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, Y., Chai, X., Liu, K. et al. Establishment and validation of a diagnostic model for diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int Urol Nephrol 56, 1439–1448 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-023-03815-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-023-03815-7