Abstract
Purpose
In this paper, we aimed to prove that resveratrol can inhibit inflammation in the detrusor smooth muscle of diabetic rats, which may provide a new direction for diabetic cystopathy (DCP) treatment.
Methods
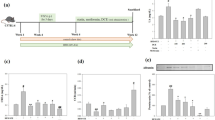
We induced a Sprague–Dawley (SD) rat model of type 1 diabetes by intraperitoneal injections of streptozotocin (STZ). Then, we separated the SD rats into four groups: (1) an excipient-treated control group; (2) a resveratrol-treated control group; (3) an excipient-treated streptozotocin (STZ)-injected group; and (4) a resveratrol-treated STZ-injected group. We administered the resveratrol or excipient by intragastric administration. After 12 weeks of diabetes induction, we measured the blood–sugar concentrations and bladder weights, and we took the bladder tissues of each group of rats for hematoxylin–eosin staining to observe the histological changes. We used real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) and Western blotting to analyze the expression levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-1β.
Results
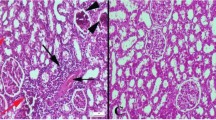
The bodyweights of the diabetic rats were appreciably reduced, while the bladder weights and blood–glucose concentrations were substantially increased. Oral resveratrol could not improve the changes in the bodyweights and blood–glucose concentrations, but it had a certain effect on the bladder weights. In a macroscopic evaluation, the bladder walls of the STZ-induced diabetes rats were thickened, and, from the H&E staining, we could see that the bladder tissues of the diabetic rats had inflammatory cell infiltration, edema, and the capillary congestion of the mucosa and lamina propria. After resveratrol treatment, the bladder-wall thickening was reduced, and the tissue damage and inflammation were significantly ameliorated. We could associate all these changes with markedly heightened expressions of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and NF-κB in the detrusor smooth muscle (DSM) tissues of the diabetic rats. Oral treatment with resveratrol alleviated the expressivity of the inflammatory cytokines in the DSM tissues.
Conclusions
Resveratrol treatment ameliorated the histological changes in the bladder and inhibited the expressions of DSM–tissue inflammatory factors in diabetes rats. Resveratrol may provide a new direction of research for the treatment of diabetic cystopathy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Forbes JM, Cooper ME (2013) Mechanisms of diabetic complications. Physiol Rev 93(1):137–188. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00045.2011
Arrellano-Valdez F, Urrutia-Osorio M, Arroyo C, Soto-Vega E (2014) A comprehensive review of urologic complications in patients with diabetes. Springerplus 3:549. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-3-549
Daneshgari F, Liu G, Birder L, Hanna-Mitchell AT, Chacko S (2009) Diabetic bladder dysfunction: current translational knowledge. J Urol 182(6 Suppl):S18-26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2009.08.070
Daneshgari F, Liu G, Imrey PB (2006) Time dependent changes in diabetic cystopathy in rats include compensated and decompensated bladder function. J Urol 176(1):380–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-5347(06)00582-9
Moller CF, Olesen KP (1976) Diabetic cystopathy. IV: micturition cystourethrography compared with urodynamic investigation. Danish Med Bull 23(6):291–294
Moller CF (1976) Diabetic cystopathy. III: urinary bladder dysfunction in relation to bacteriuria. Danish Med Bull 23(6):287–291
Fayyad AM, Hill SR, Jones G (2009) Prevalence and risk factors for bothersome lower urinary tract symptoms in women with diabetes mellitus from hospital-based diabetes clinic. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 20(11):1339–1344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-009-0949-z
Yoshimura N, Chancellor MB, Andersson KE, Christ GJ (2005) Recent advances in understanding the biology of diabetes-associated bladder complications and novel therapy. BJU Int 95(6):733–738. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2005.05392.x
Wang CC, Nagatomi J, Toosi KK, Yoshimura N, Hsieh JH, Chancellor MB, Sacks MS (2009) Diabetes-induced alternations in biomechanical properties of urinary bladder wall in rats. Urology 73(4):911–915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2008.11.026
Navarro JF, Mora C (2005) Role of inflammation in diabetic complications. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20(12):2601–2604. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfi155
Wang-Fischer Y, Garyantes T (2018) Improving the reliability and utility of streptozotocin-induced rat diabetic model. J Diabetes Res 2018:8054073. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8054073
Akash MS, Rehman K, Chen S (2013) Role of inflammatory mechanisms in pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Cell Biochem 114(3):525–531. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.24402
Wang Z, Cheng Z, Cristofaro V, Li J, Xiao X, Gomez P, Ge R, Gong E, Strle K, Sullivan MP, Adam RM, White MF, Olumi AF (2012) Inhibition of TNF-α improves the bladder dysfunction that is associated with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 61(8):2134–2145. https://doi.org/10.2337/db11-1763
Ding H, Zhang P, Li N, Liu Y, Wang P (2019) The phosphodiesterase type 4 inhibitor roflumilast suppresses inflammation to improve diabetic bladder dysfunction rats. Int Urol Nephrol 51(2):253–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-018-2038-z
Schöppner A, Kindl H (1984) Purification and properties of a stilbene synthase from induced cell suspension cultures of peanut. J Biol Chem 259(11):6806–6811. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9258(17)39799-5
Zhong M, Cheng GF, Wang WJ, Guo Y, Zhu XY, Zhang JT (1999) Inhibitory effect of resveratrol on interleukin 6 release by stimulated peritoneal macrophages of mice. Phytomedicine 6(2):79–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0944-7113(99)80039-7
Birrell MA, McCluskie K, Wong S, Donnelly LE, Barnes PJ, Belvisi MG (2005) Resveratrol, an extract of red wine, inhibits lipopolysaccharide induced airway neutrophilia and inflammatory mediators through an NF-kappaB-independent mechanism. FASEB J 19(7):840–841. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.04-2691fje
Wang XL, Li T, Li JH, Miao SY, Xiao XZ (2017) The effects of resveratrol on inflammation and oxidative stress in a rat model of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22091529
Gocmez SS, Sahin TD, Yazir Y, Duruksu G, Eraldemir FC, Polat S, Utkan T (2019) Resveratrol prevents cognitive deficits by attenuating oxidative damage and inflammation in rat model of streptozotocin diabetes induced vascular dementia. Physiol Behav 201:198–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2018.12.012
Yin L, Chen X, Li N, Jia W, Wang N, Hou B, Yang H, Zhang L, Qiang G, Yang X, Du G (2021) Puerarin ameliorates skeletal muscle wasting and fiber type transformation in STZ-induced type 1 diabetic rats. Biomed Pharmacother 133:110977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110977
Ma KL, Liu L, Zhang Y, Wang GH, Hu ZB, Chen PP, Lu J, Lu CC, Gong TK, Gong YX, Liu BC (2019) Aspirin attenuates podocyte injury in diabetic rats through overriding cyclooxygenase-2-mediated dysregulation of LDL receptor pathway. Int Urol Nephrol 51(3):551–558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-018-2059-7
Daneshgari F, Huang X, Liu G, Bena J, Saffore L, Powell CT (2006) Temporal differences in bladder dysfunction caused by diabetes, diuresis, and treated diabetes in mice. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 290(6):R1728-1735. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00654.2005
Zhang J, Zhang Y, Yang X, Wang J, Xu Y, Wang R, Tan B, Huang P, Cao H (2020) Diabetic bladder dysfunction in T2D KK-Ay mice and its changes in the level of relevant gene expression. Biomed Pharmacother 131:110706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110706
Chen R, Ji L, Chen L, Chen L, Cai D, Feng B, Kuang H, Li H, Li Y, Liu J, Shan Z, Sun Z, Tian H, Xu Z, Xu Y, Yang Y, Yang L, Yu X, Zhu D, Zou D (2015) Glycemic control rate of T2DM outpatients in China: a multi-center survey. Med Sci Monit 21:1440–1446. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.892246
Daneshgari F, Moore C (2006) Diabetic uropathy. Semin Nephrol 26(2):182–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semnephrol.2005.09.009
Yuan Z, Tang Z, He C, Tang W (2015) Diabetic cystopathy: a review. J Diabetes 7(4):442–447. https://doi.org/10.1111/1753-0407.12272
Golbidi S, Laher I (2010) Bladder dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Front Pharmacol 1:136. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2010.00136
Gomez CS, Kanagarajah P, Gousse AE (2011) Bladder dysfunction in patients with diabetes. Curr Urol Rep 12(6):419–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-011-0214-0
Beshay E, Carrier S (2004) Oxidative stress plays a role in diabetes-induced bladder dysfunction in a rat model. Urology 64(5):1062–1067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2004.06.021
Liu G, Daneshgari F (2014) Diabetic bladder dysfunction. Chin Med J 127(7):1357–1364
Luc K, Schramm-Luc A, Guzik TJ, Mikolajczyk TP (2019) Oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in prediabetes and diabetes. J Physiol Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.26402/jpp.2019.6.01
Ola MS, Aleisa AM, Al-Rejaie SS, Abuohashish HM, Parmar MY, Alhomida AS, Ahmed MM (2014) Flavonoid, morin inhibits oxidative stress, inflammation and enhances neurotrophic support in the brain of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Neurol Sci 35(7):1003–1008. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-014-1628-5
Cai Z, Zhao Y, Yao S, Bin Zhao B (2011) Increases in β-amyloid protein in the hippocampus caused by diabetic metabolic disorder are blocked by minocycline through inhibition of NF-κB pathway activation. Pharmacol Rep 63(2):381–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1734-1140(11)70504-7
Prabhakar O (2013) Cerebroprotective effect of resveratrol through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in diabetic rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 386(8):705–710. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-013-0871-2
Rai RC, Bagul PK, Banerjee SK (2020) NLRP3 inflammasome drives inflammation in high fructose fed diabetic rat liver: effect of resveratrol and metformin. Life Sci 253:117727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117727
Riba A, Deres L, Sumegi B, Toth K, Szabados E, Halmosi R (2017) Cardioprotective effect of resveratrol in a postinfarction heart failure model. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017:6819281. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6819281
Cai TT, Ye XL, Li RR, Chen H, Wang YY, Yong HJ, Pan ML, Lu W, Tang Y, Miao H, Snijders AM, Mao JH, Liu XY, Lu YB, Ding DF (2020) Resveratrol modulates the gut microbiota and inflammation to protect against diabetic nephropathy in mice. Front Pharmacol 11:1249. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.01249
Rehman K, Akash MSH (2017) Mechanism of generation of oxidative stress and pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus: how are they interlinked? J Cell Biochem 118(11):3577–3585. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26097
King GL (2008) The role of inflammatory cytokines in diabetes and its complications. J Periodontol 79(8 Suppl):1527–1534. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2008.080246
Olefsky JM, Glass CK (2010) Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol 72:219–246. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physiol-021909-135846
Yoon J, Ryoo S (2013) Arginase inhibition reduces interleukin-1beta-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by increasing nitric oxide synthase-dependent nitric oxide production. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 435(3):428–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.05.002
Rotondo S, Rajtar G, Manarini S, Celardo A, Rotillo D, de Gaetano G, Evangelista V, Cerletti C (1998) Effect of trans-resveratrol, a natural polyphenolic compound, on human polymorphonuclear leukocyte function. Br J Pharmacol 123(8):1691–1699. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0701784
Martinez J, Moreno JJ (2000) Effect of resveratrol, a natural polyphenolic compound, on reactive oxygen species and prostaglandin production. Biochem Pharmacol 59(7):865–870. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-2952(99)00380-9
Feng YH, Zou JP, Li XY (2002) Effects of resveratrol and ethanol on production of pro-inflammatory factors from endotoxin activated murine macrophages. Acta Pharmacol Sin 23(11):1002–1006
Cianciulli A, Calvello R, Cavallo P, Dragone T, Carofiglio V, Panaro MA (2012) Modulation of NF-κB activation by resveratrol in LPS treated human intestinal cells results in downregulation of PGE2 production and COX-2 expression. Toxicol In Vitro 26(7):1122–1128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2012.06.015
Lee HY, Kim IK, Yoon HK, Kwon SS, Rhee CK, Lee SY (2017) Inhibitory effects of resveratrol on airway remodeling by transforming growth factor-beta/smad signaling pathway in chronic asthma model. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res 9(1):25–34. https://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2017.9.1.25
Xu D, Li Y, Zhang B, Wang Y, Liu Y, Luo Y, Niu W, Dong M, Liu M, Dong H, Zhao P, Li Z (2016) Resveratrol alleviate hypoxic pulmonary hypertension via anti-inflammation and anti-oxidant pathways in rats. Int J Med Sci 13(12):942–954. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.16810
He Y, Zeng H, Yu Y, Zhang J, Duan X, Liu Q, Yang B (2017) Resveratrol improves smooth muscle carcinogenesis in the progression of chronic prostatitis via the downregulation of c-kit/SCF by activating Sirt1. Biomed Pharmacother 95:161–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.08.064
Huang DD, Shi G, Jiang Y, Yao C, Zhu C (2020) A review on the potential of Resveratrol in prevention and therapy of diabetes and diabetic complications. Biomed Pharmacother 125:109767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109767
Wen D, Huang X, Zhang M, Zhang L, Chen J, Gu Y, Hao CM (2013) Resveratrol attenuates diabetic nephropathy via modulating angiogenesis. PLoS ONE 8(12):e82336. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0082336
Aktas HS, Ozel Y, Ahmad S, Pence HH, Ayaz-Adakul B, Kudas I, Tetik S, Sekerler T, Canbey-Goret C, Kabasakal L, Elcioglu HK (2019) Protective effects of resveratrol on hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Mol Cell Biochem 460(1–2):217–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-019-03582-z
Acknowledgements
Supported by the educational department of Liaoning Province No. QN2019018 grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable International, National, and Institutional Guidelines on the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, F., Du, H., Hou, J. et al. Anti-inflammation properties of resveratrol in the detrusor smooth muscle of the diabetic rat. Int Urol Nephrol 54, 2833–2843 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-022-03334-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-022-03334-x