Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the role of urinary neutrophil gelatinase-induced lipocalin (uNGAL) measurement in the early diagnosis of acute kidney injury that may occur after intraoperative ischemia in patients undergoing partial nephrectomy (PN).
Methods
This prospective study included 86 patients who underwent open laparoscopic or robotic partial nephrectomy between May 2017 and May 2019. During the surgery, whether the patients had ischemia or not, type of vascular clamping and the ischemia time were noted. The definition of acute kidney injury (AKI) was classified according to Acute Kidney Injury Network (AKIN) criteria. Urine samples were collected preoperatively and 3 h after renal pedicle clamp removal and uNGAL was measured.
Results
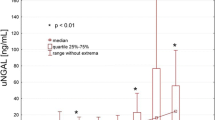
AKI was recorded in 34 (39.5%) of 86 patients after PN. Of the 34 patients, 26 (76.4%) had level 1 and 8 (23.6%) had level 2 AKI. uNGAL levels increased significantly as an early reflection of AKI in patients who underwent intraoperative total or renal artery clamping (p = 0.024). There was no significant postoperative increase in uNGAL in the non-ischemic group (p = 0.163). uNGAL expression was detected well before serum creatinine increase. Patients with AKI after PN had higher uNGAL expression (p = 0.008) However, there was no correlation between the level of AKI and uNGAL expression (r = 0.201, p = 0.066).
Conclusion
Ischemic acute kidney injury after nephron-sparing surgery can be detected early by uNGAL measurement. In future studies comparing outcomes of different surgical techniques on renal functions after PN, uNGAL levels may be used.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gill IS, Kamoi K, Aron M, Desai MM (2010) 800 Laparoscopic partial nephrectomies: a single surgeon series. J Urol 183(1):34–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2009.08.114
Lane BR, Russo P, Uzzo RG, Hernandez AV, Boorjian SA, Thompson RH, Fergany AF, Love TE, Campbell SC (2011) Comparison of cold and warm ischemia during partial nephrectomy in 660 solitary kidneys reveals predominant role of nonmodifiable factors in determining ultimate renal function. J Urol 185(2):421–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2010.09.131
Parekh DJ, Weinberg JM, Ercole B, Torkko KC, Hilton W, Bennett M, Devarajan P, Venkatachalam MA (2013) Tolerance of the human kidney to isolated controlled ischemia. J Am Soc Nephrol 24(3):506–517. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.2012080786
Zhang Z, Zhao J, Dong W, Remer E, Li J, Demirjian S, Zabell J, Campbell SC (2016) Acute kidney injury after partial nephrectomy: role of parenchymal mass reduction and ischemia and impact on subsequent functional recovery. Eur Urol 69(4):745–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2015.10.023
Weight CJ, Larson BT, Fergany AF, Gao T, Lane BR, Campbell SC, Kaouk JH, Klein EA, Novick AC (2010) Nephrectomy induced chronic renal insufficiency is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular death and death from any cause in patients with localized cT1b renal masses. J Urol 183(4):1317–1323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2009.12.030
Clerico A, Galli C, Fortunato A, Ronco C (2012) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as biomarker of acute kidney injury: a review of the laboratory characteristics and clinical evidences. Clin Chem Lab Med 50(9):1505–1517. https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm-2011-0814
Nguyen MT, Devarajan P (2008) Biomarkers for the early detection of acute kidney injury. Pediatr Nephrol 23(12):2151–2157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-007-0470-x
Cruz DN, Goh CY, Palazzuoli A, Slavin L, Calabro A, Ronco C, Maisel A (2011) Laboratory parameters of cardiac and kidney dysfunction in cardio-renal syndromes. Heart Fail Rev 16(6):545–551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-011-9231-9
Mishra J, Dent C, Tarabishi R, Mitsnefes MM, Ma Q, Kelly C, Ruff SM, Zahedi K, Shao M, Bean J, Mori K, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2005) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery. Lancet 365(9466):1231–1238. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(05)74811-x
Haase M, Bellomo R, Devarajan P, Schlattmann P, Haase-Fielitz A (2009) Accuracy of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in diagnosis and prognosis in acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis 54(6):1012–1024. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2009.07.020
Abassi Z, Shalabi A, Sohotnik R, Nativ O, Awad H, Bishara B, Frajewicki V, Sukhotnik I, Abbasi A, Nativ O (2013) Urinary NGAL and KIM-1: biomarkers for assessment of acute ischemic kidney injury following nephron sparing surgery. J Urol 189(4):1559–1566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2012.10.029
Shalabi A, Nativ O, Sumri M, Bishara B, Khoury W, Awad H (2017) Impact of pneumoperitoneum on the post-operative renal function and level of acute kidney injury markers: comparison between laparoscopic and open nephrectomy. Clin Surg 2017(2):1493
Koo KC, Hong JH, Lee HS, Jeh SU, Choi YD, Rha KH, Ham WS (2015) Accuracy of urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in quantifying acute kidney ınjury after partial nephrectomy in patients with normal contralateral kidney. PLoS ONE 10(7):e0133675. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0133675
Sprenkle PC, Wren J, Maschino AC, Feifer A, Power N, Ghoneim T, Sternberg I, Fleisher M, Russo P (2013) Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a marker of acute kidney injury after kidney surgery. J Urol 190(1):159–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2013.01.101
Earley A, Miskulin D, Lamb EJ, Levey AS, Uhlig K (2012) Estimating equations for glomerular filtration rate in the era of creatinine standardization: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med 156(11):785–795. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-156-6-201203200-00391(w-270, w-271, w-272, w-273, w-274, w-275, w-276, w-277, w-278)
Kutikov A, Uzzo RG (2009) The R.E.N.A.L. nephrometry score: a comprehensive standardized system for quantitating renal tumor size, location and depth. J Urol 182(3):844–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2009.05.035
Mehta RL, Kellum JA, Shah SV, Molitoris BA, Ronco C, Warnock DG, Levin A (2007) Acute Kidney Injury Network: report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit Care 11(2):R31. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc5713
Lane BR, Babineau DC, Poggio ED, Weight CJ, Larson BT, Gill IS, Novick AC (2008) Factors predicting renal functional outcome after partial nephrectomy. J Urol 180(6):2363–2368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2008.08.036(discussion 2368–2369)
Thomas AA, Demirjian S, Lane BR, Simmons MN, Goldfarb DA, Subramanian VS, Campbell SC (2011) Acute kidney injury: novel biomarkers and potential utility for patient care in urology. Urology 77(1):5–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2010.05.004
Schrier RW, Wang W, Poole B, Mitra A (2004) Acute renal failure: definitions, diagnosis, pathogenesis, and therapy. J Clin Invest 114(1):5–14. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci22353
Mir MC, Pavan N, Parekh DJ (2016) Current paradigm for ıschemia in kidney surgery. J Urol 195(6):1655–1663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2015.09.099
Devarajan P (2010) Review: neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: a troponin-like biomarker for human acute kidney injury. Nephrology (Carlton) 15(4):419–428. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1797.2010.01317.x
Wagener G, Jan M, Kim M, Mori K, Barasch JM, Sladen RN, Lee HT (2006) Association between increases in urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and acute renal dysfunction after adult cardiac surgery. Anesthesiology 105(3):485–491. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-200609000-00011
Lahoud Y, Hussein O, Shalabi A, Nativ O, Awad H, Khamaisi M, Matar I, Nativ O, Abassi Z (2015) Effects of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor on ischemic kidney injury during nephron sparing surgery: quantitative assessment by NGAL and KIM-1. World J Urol 33(12):2053–2062. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-015-1579-3
Takagi T, Kondo T, Iizuka J, Tomita E, Kobayashi H, Hashimoto Y, Tanabe K (2012) Predictors for postoperative renal function after open partial nephrectomy: including postoperative biomarkers. Int J Urol 19(9):823–828. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-2042.2012.03037.x
Marconi L, Desai MM, Ficarra V, Porpiglia F, Van Poppel H (2016) Renal preservation and partial nephrectomy: patient and surgical factors. Eur Urol Focus 2(6):589–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euf.2017.02.012
Simhan J, Smaldone MC, Tsai KJ, Canter DJ, Li T, Kutikov A, Viterbo R, Chen DY, Greenberg RE, Uzzo RG (2011) Objective measures of renal mass anatomic complexity predict rates of major complications following partial nephrectomy. Eur Urol 60(4):724–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2011.05.030
Klatte T, Ficarra V, Gratzke C, Kaouk J, Kutikov A, Macchi V, Mottrie A, Porpiglia F, Porter J, Rogers CG, Russo P, Thompson RH, Uzzo RG, Wood CG, Gill IS (2015) A literature review of renal surgical anatomy and surgical strategies for partial nephrectomy. Eur Urol 68(6):980–992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2015.04.010
Kawamura N, Yokoyama M, Tanaka H, Nakayama T, Yasuda Y, Kijima T, Yoshida S, Ishioka J, Matsuoka Y, Saito K, Kihara K, Fujii Y (2019) Acute kidney injury and intermediate-term renal function after clampless partial nephrectomy. Int J Urol 26(1):113–118. https://doi.org/10.1111/iju.13799
Veccia A, Antonelli A, Uzzo RG, Novara G, Kutikov A, Ficarra V, Simeone C, Mirone V, Hampton LJ, Derweesh I, Porpiglia F, Autorino R (2020) Predictive value of nephrometry scores in nephron-sparing surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Urol Focus 6(3):490–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euf.2019.11.004
Liu S, Che M, Xue S, Xie B, Zhu M, Lu R, Zhang W, Qian J, Yan Y (2013) Urinary L-FABP and its combination with urinary NGAL in early diagnosis of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery in adult patients. Biomarkers 18(1):95–101. https://doi.org/10.3109/1354750x.2012.740687
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CA: data collection, data analysis, and manuscript writing; OD: data collection and data analysis; EK: data collection; MIG, ES and OG: project development and manuscript writing; SB: project development, manuscript editing and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee at which the studies were conducted (approval number; 08-412-17) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
All participants have given informed consent before inclusion in the present study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akpinar, C., Dogan, O., Kubilay, E. et al. The evaluation of acute kidney injury due to ischemia by urinary neutrophil gelatinase-induced lipocalin (uNGAL) measurement in patients who underwent partial nephrectomy. Int Urol Nephrol 53, 393–400 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02660-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02660-2