Abstract
Background
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is associated with increased cardiovascular (CVD) morbidity and mortality. Hence, this study was carried out to assess the biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction and inflammation as predictors of CVD risk in Indian patients with CKD.
Methods
In this case control study, we recruited 43 patients with CKD and 43 healthy control volunteers. Circulating levels of endothelial dysfunction markers [asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA), angiopoietin-like protein-2 (ANGPTL2), matrix metallopeptidase 9 (MMP-9)] and systemic inflammation [high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP)] were assessed in the study population. All study participants underwent brachial artery flow mediated dilation (FMD) to estimate endothelial dysfunction. Disease severity (e-GFR) was assessed by a nephrologist.
Results
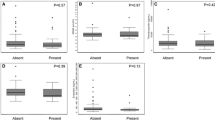
CKD patients showed markedly elevated levels of ADMA, ANGPTL2, MMP-9, and hs-CRP. FMD and eGFR were significantly decreased in cases, as compared to the controls. ADMA, ANGPTL2, MMP-9 and hs-CRP showed significant positive correlation with one another and significant negative correlation with FMD and disease severity. We also observed a significant negative correlation of FMD with disease severity and duration of CKD. In the multiple linear regression model, ADMA and ANGPTL2 were found to be independent predictors of FMD.
Conclusion
In CKD patients, there is significantly increased endothelial dysfunction and systemic inflammation, which showed a positive correlation with disease severity. Thus, the markers of endothelial dysfunction such as ADMA and ANGPTL2 can be used as predictors of CVD risk in CKD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Di Marco GS, Reuter S, Hillebrand U, Amler S, König M, Larger E, Oberleithner H, Brand E, Pavenstädt H, Brand M (2009) The soluble VEGF receptor sFlt1 contributes to endothelial dysfunction in CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol 20(10):2235–2245
Sharma J, Kapoor A, Muthu R, Prasad N, Sinha A, Khanna R, Kumar S, Garg N, Tewari S, Sharma RK, Goel P (2014) Assessment of endothelial dysfunction in Asian Indian patients with chronic kidney disease and changes following renal transplantation. Clin Transpl 28(8):889–896
Gluba-Brzozka A, Michalska-Kasiczak M, Franczyk-Skora B, Nocun M, Banach M, Rysz J (2014) Markers of increased cardiovascular risk in patients with chronic kidney disease. Lipids Health Dis 13(1):135
Currie G, Delles C (2014) Proteinuria and its relation to cardiovascular disease. Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis 7:13
Cianfrone P, Simeoni M, Comi N, Piraina V, Talarico R, Cerantonio A, Gentile I, Fabiano FF, Lucisano G, Foti D, Gulletta E (2017) How to improve duration and efficiency of the antiproteinuric response to Ramipril: RamiPROT—a prospective cohort study. J Nephrol 30(1):95–102
Lishmanov A, Dorairajan S, Pak Y, Chaudhary K, Chockalingam A (2012) Elevated serum parathyroid hormone is a cardiovascular risk factor in moderate chronic kidney disease. Int Urol Nephrol 44(2):541–547
Simeoni M, Perna AF, Fuiano G (2020) Secondary hyperparathyroidism and hypertension: an intriguing couple. J Clin Med 9(3):629
Zbroch E, Malyszko J, Koc-Zorawska E, Mysliwiec M (2012) Renalase, kidney function, and markers of endothelial dysfunction in renal transplant recipients. Pol Arch Med Wewn 122(1–2):40–44
Jablonski KL, Decker E, Perrenoud L, Kendrick J, Chonchol M, Seals DR, Jalal D (2014) Assessment of vascular function in patients with chronic kidney disease. J Vis Exp 88:e51478
Muntner P, He J, Hamm L, Loria C, Whelton PK (2002) Renal insufficiency and subsequent death resulting from cardiovascular disease in the United States. J Am Soc Nephrol 13(3):745–753
Packard RR, Libby P (2008) Inflammation in atherosclerosis: from vascular biology to biomarker discovery and risk prediction. Clin Chem 54(1):24–38
Lambert J, Janssen MJ, Donker AJ, Stehouwer CD (1997) Endothelium-dependent vasodilatation and distensibility of large arteries in chronic haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transpl 12:14–18
Hogas SM, Voroneanu L, Serban DN, Segall L, Hogas MM, Serban IL, Covic A (2010) Methods and potential biomarkers for the evaluation of endothelial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease: a critical approach. J Am Soc Hypertens 4(3):116–127
Sarnak MJ, Coronado BE, Greene T, Wang SR, Kusek JW, Beck GJ, Levey AS (2002) Cardiovascular disease risk factors in chronic renal insufficiency. Clin Nephrol 57(5):327–335
Pant S, Deshmukh A, Gurumurthy GS, Pothineni NV, Watts TE, Romeo F et al (2014) Inflammation and atherosclerosis—revisited. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther 19:170–178
Wanner C, Krane V, März W, Olschewski M, Mann JF, Ruf G, Ritz E (2005) Atorvastatin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus undergoing hemodialysis. N Engl J Med 353(3):238–248
Fellstrom BC, Jardine AG, Schmieder RE, Holdaas H, Bannister K, Beutler J, Chae DW, Chevaile A, Cobbe SM, Gronhagen-Riska C, De Lima JJ (2009) Rosuvastatin and cardiovascular events in patients undergoing hemodialysis. N Engl J Med 360(14):1395–1407
McCullough PA, Agrawal V, Danielewicz E, Abela GS (2008) Accelerated atherosclerotic calcification and Mönckeberg's sclerosis: a continuum of advanced vascular pathology in chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3(6):1585–1598
Foley RN (2010) Clinical epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease. J Ren Care 36(Suppl 1):4–8
Eiselt J, Rajdl D, Racek J, Vostrý M, Rulcová K, Wirth J (2014) Asymmetric dimethylarginine and progression of chronic kidney disease-a one-year follow-up study. Kidney Blood Press Res 39(1):50–57
Ueda S, Yamagishi SI, Kaida Y, Okuda S (2007) Asymmetric dimethylarginine may be a missing link between cardiovascular disease and chronic kidney disease. Nephrology 12(6):582–590
Ueda S, Yamagishi SI, Matsumoto Y, Fukami K, Okuda S (2007) Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) is a novel emerging risk factor for cardiovascular disease and the development of renal injury in chronic kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol 11(2):115–121
Usui T, Ninomiya T, Nagata M, Takahashi O, Doi Y, Hata J, Fukuhara M, Kitazono T, Oike Y, Kiyohara Y (2013) Angiopoietin-like protein 2 is associated with chronic kidney disease in a general Japanese population. Circ J. 77(9):2311–2317
Horio E, Kadomatsu T, Miyata K, Arai Y, Hosokawa K, Doi Y, Ninomiya T, Horiguchi H, Endo M, Tabata M, Tazume H (2014) Role of endothelial cell-derived Angptl2 in vascular inflammation leading to endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis progression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 34(4):790–800
Morinaga J, Kadomatsu T, Miyata K, Endo M, Terada K, Tian Z, Sugizaki T, Tanigawa H, Zhao J, Zhu S, Sato M (2016) Angiopoietin-like protein 2 increases renal fibrosis by accelerating transforming growth factor-β signaling in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 89(2):327–341
Musiał K, Zwolińska D (2011) Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-2, 9) and their tissue inhibitors (TIMP-1, 2) as novel markers of stress response and atherogenesis in children with chronic kidney disease (CKD) on conservative treatment. Cell Stress Chaperones 16(1):97–103
Tan TK, Zheng G, Hsu TT, Wang Y, Lee VW, Tian X, Wang Y, Cao Q, Wang Y, Harris DC (2010) Macrophage matrix metalloproteinase-9 mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vitro in murine renal tubular cells. Am J Pathol 176(3):1256–1270
Tschesche H, Zölzer V, Triebel S, Bartsch S (2001) The human neutrophil lipocalin supports the allosteric activation of matrix metalloproteinases. Eur J Biochem 268(7):1918–1928
Newby AC (2005) Dual role of matrix metalloproteinases (matrixins) in intimal thickening and atherosclerotic plaque rupture. Physiol Rev 85(1):1–31
Pawlak K, Mysliwiec M, Pawlak D (2011) Peripheral blood level alterations of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in patients with chronic kidney disease on conservative treatment and on hemodialysis. Clin Biochem 44(10–11):838–843
Halade GV, Jin YF, Lindsey ML (2013) Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9: a proximal biomarker for cardiac remodeling and a distal biomarker for inflammation. Pharmacol Ther 139(1):32–40
Fox ER, Benjamin EJ, Sarpong DF, Nagarajarao H, Taylor JK, Steffes MW, Salahudeen AK, Flessner MF, Akylbekova EL, Fox CS, Garrison RJ (2010) The relation of C-reactive protein to chronic kidney disease in African Americans: the Jackson Heart Study. BMC Nephrol 11(1):1
Trachtman H, Futterweit S, Arzberger C, Bod J, Goldschmiedt J, Gorman H, Reddy K, Franki N, Singhal PC (2006) Nitric oxide and superoxide in rat mesangial cells: modulation by C-reactive protein. Pediatr Nephrol 21(5):619–626
Sesso HD, Wang L, Buring JE, Ridker PM, Gaziano JM (2007) Comparison of interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein for the risk of developing hypertension in women. Hypertension 49(2):304–310
Karkar AM, Smith J, Pusey CD (2001) Prevention and treatment of experimental crescentic glomerulonephritis by blocking tumour necrosis factor-α. Nephrol Dial Transpl 16(3):518–524
Nakahara C, Kanemoto K, Saito N, Oyake Y, Kamoda T, Nagata M, Matsui A (2001) C-reactive protein frequently localizes in the kidney in glomerular diseases. Clin Nephrol 55(5):365–370
Shukla V, Dey R, Chandra A, Karoli R, Khanduri S (2015) Endothelial dysfunction by flow-mediated vasodilatation in chronic kidney disease. J Assoc Physicians India 63:30–33
Ghiadoni L, Cupisti A, Huang Y, Mattei P, Cardinal H, Favilla S, Rindi P, Barsotti G, Taddei S, Salvetti A (2004) Endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress in chronic renal failure. J Nephrol 17(4):512–519
Yu M, Kim YJ, Kang DH (2011) Indoxyl sulfate-induced endothelial dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease via an induction of oxidative stress. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6(1):30–39
Funding
The present study was funded by the JIPMER Intramural Research Grant. Funding from JIPMER, Puducherry, India in the name of the corresponding author (Medha Rajappa) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashokachakkaravarthy, K., Rajappa, M., Parameswaran, S. et al. Asymmetric dimethylarginine and angiopoietin-like protein-2 are independent predictors of cardiovascular risk in pre-dialysis non-diabetic chronic kidney disease patients. Int Urol Nephrol 52, 1321–1328 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02484-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02484-0