Abstract
Purpose
To prove that phosphodiesterase type-4 inhibitors could potentially treat obesity-associated overactive bladder through modulation of the systemic inflammatory response.
Methods
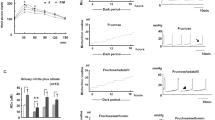
In this 12-week study, 90 female Sprague–Dawley rats were divided into three groups: (1) vehicle-treated normal diet (ND)-fed rats; (2) vehicle-treated high-fat diet (HFD)-fed rats; and (3) roflumilast-treated HFD-fed rats. Oral roflumilast (5 mg/kg/day) was administered during the last 4 weeks of HFD feeding in the test group. At 12 weeks, a urodynamic study was performed in ten rats of each group. Bladder tissue was extracted, the bladder mucosa was separated under microscopy, and bladder detrusor smooth muscle (DSM) expression of TNF-α, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1β, and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) were analyzed using Western blotting and quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR).
Results
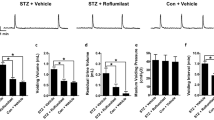
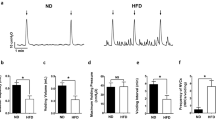
Bodyweights of the HFD-fed rats significantly increased and were not ameliorated by roflumilast treatment. Cystometry evidenced augmented frequency and non-void contractions in obese rats that were also prevented by roflumilast. These alterations were accompanied by a markedly increased expression of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and NF-κB in DSM of obese rats. Furthermore, roflumilast decreased expression of inflammatory factors in DSM.
Conclusions
Oral treatment with roflumilast in rats fed an HFD restores normal bladder function and downregulates expression of inflammatory factors in the bladder.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Drake MJ (2014) Do we need a new definition of the overactive bladder syndrome? ICI-RS 2013. Neurourol Urodyn 33(5):622–624
Gulur DM, Drake MJ (2004) Management of overactive bladder. Dis Manage Health Outcomes 350(2):786–799
Wen JG, Li JS, Wang ZM, Huang CX, Shang XP, Su ZQ, Lu YT, Suo ZH, Wang Y, Qin GJ (2014) The prevalence and risk factors of OAB in middle-aged and old people in China. Neurourol Urodyn 33(4):387–391
Laven BA, Orsini N, Andersson SO, Johansson JE, Gerber GS, Wolk A (2008) Birth weight, abdominal obesity and the risk of lower urinary tract symptoms in a population based study of Swedish men. J Urol 179(5):1895–1896
Wellen KE, Gs H (2003) Obesity-induced inflammatory changes in adipose tissue. J Clin Investig 112(12):1785–1788
Haldar S, Dru C, Choudhury D, Mishra R, Fernandez A, Biondi S, Liu Z, Shimada K, Arditi M, Bhowmick NA (2015) Inflammation and pyroptosis mediate muscle expansion in an interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta)-dependent manner. J Biol Chem 290(10):6574–6583. doi:10.1074/jbc.M114.617886
Bouchelouche K, Alvarez S, Horn T, Nordling J, Bouchelouche P (2006) Human detrusor smooth muscle cells release interleukin-6, interleukin-8, and RANTES in response to proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α. Urology 67(1):214–219
Rohrmann S, Smit E, Giovannucci E, Platz EA (2005) Association between markers of the metabolic syndrome and lower urinary tract symptoms in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III). Prostate 67(15):1693–1698
Rahman NU, Phonsombat S, Bochinski D, Carrion RE, Nunes L, Lue TF (2007) An animal model to study lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction: the hyperlipidaemic rat. BJU Int 100(3):658–663
Leiria LO, Sollon C, Calixto MC, Lintomen L, Mónica FZ, Anhê GF, De NG, Zanesco A, Grant AD, Antunes E (2012) Role of PKC and CaV1.2 in detrusor overactivity in a model of obesity associated with insulin resistance in mice. PLoS ONE 7(11):e48507–e48507
Staskin DR, Robinson D (2009) Oxybutynin chloride topical gel: a new formulation of an established antimuscarinic therapy for overactive bladder. Expert Opin Pharmacother 10(18):3103–3111
Schafer PH, Truzzi F, Parton A, Wu L, Kosek J, Zhang LH, Horan G, Saltari A, Quadri M, Lotti R, Marconi A, Pincelli C (2016) Phosphodiesterase 4 in inflammatory diseases: effects of apremilast in psoriatic blood and in dermal myofibroblasts through the PDE4/CD271 complex. Cell Signal 28(7):753–763. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2016.01.007
Sturton G, Fitzgerald M (2002) Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors for the treatment of COPD. Chest 121(5 Suppl):192S–196S
Oger S, Behr-Roussel D, Gorny D, Denys P, Lebret T, Alexandre L, Giuliano F (2007) Relaxation of phasic contractile activity of human detrusor strips by cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase type 4 inhibition. Eur Urol 51(3):772–780; discussion 780–781
Longhurst PA, Briscoe JA, Rosenberg DJ, Leggett RE (1997) The role of cyclic nucleotides in guinea-pig bladder contractility. Br J Pharmacol 121(8):1665–1672
Xin W, Li N, Cheng Q, Petkov GV (2014) BK channel-mediated relaxation of urinary bladder smooth muscle: a novel paradigm for phosphodiesterase type 4 regulation of bladder function. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 349(1):56
Hansen MJ, Jovanovska V, Morris MJ (2004) Adaptive responses in hypothalamic neuropeptide Y in the face of prolonged high-fat feeding in the rat. J Neurochem 88(4):909–916
Fan EW, Chen LJ, Cheng JT, Tong YC (2014) Changes of urinary bladder contractility in high-fat diet-fed mice: the role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Int J Urol 21(8):831–835. doi:10.1111/iju.12428
Li N, He X, Li Z, Liu Y, Wang P (2016) Partial bladder outlet obstruction is associated with decreased expression and function of the small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel in guinea pig detrusor smooth muscle. Int Urol Nephrol 49(1):17–26. doi:10.1007/s11255-016-1455-0
Li N, Ding H, He X, Li Z, Liu Y (2017) Expression and function of the small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel is decreased in urinary bladder smooth muscle cells from female guinea pig with partial bladder outlet obstruction. Int Urol Nephrol. doi:10.1007/s11255-017-1592-0
Bulló M, García-Lorda P, Megias I, Ph.D. JS-SMD (2003) Systemic inflammation, adipose tissue tumor necrosis factor, and leptin expression. Obes Res 11(4):525–531
Conti M, Richter W, Mehats C, Livera G, Park JY, Jin C (2003) Cyclic AMP-specific PDE4 phosphodiesterases as critical components of cyclic AMP signaling. J Biol Chem 278(8):5493–5496. doi:10.1074/jbc.R200029200
Essayan DM (1999) Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitors and immunomodulation. Biochem Pharmacol 57(9):965–973
de Heredia FP, Gómezmartínez S, Marcos A (2012) Obesity, inflammation and the immune system. Proc Nutr Soc 71(71):332–338
Lee MK, Yvan-Charvet L, Masters SL, Murphy AJ (2016) The modern interleukin-1 superfamily: divergent roles in obesity. Semin Immunol. doi:10.1016/j.smim.2016.10.001
Fry CH, Sahai A, Vahabi B, Kanai AJ, Birder LA (2014) What is the role for biomarkers for lower urinary tract disorders? ICI-RS 2013. Neurourol Urodyn 33(5):602–605. doi:10.1002/nau.22558
Schäfer W, Abrams P, Liao L, Mattiasson A, Pesce F, Spangberg A, Sterling AM, Zinner NR, Kerrebroeck PV (2002) Good urodynamic practices: uroflowmetry, filling cystometry, and pressure-flow studies. Neurourol Urodyn 21(3):261–274
Seki S, Sasaki K, Fraser MO, Igawa Y, Nishizawa O, Chancellor MB, de Groat WC, Yoshimura N (2002) Immunoneutralization of nerve growth factor in lumbosacral spinal cord reduces bladder hyperreflexia in spinal cord injured rats. J Urol 168(168):2269–2274
Yoon J, Ryoo S (2013) Arginase inhibition reduces interleukin-1beta-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by increasing nitric oxide synthase-dependent nitric oxide production. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 435(3):428–433. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.05.002
Abrams P, Andersson KE (2007) Muscarinic receptor antagonists for overactive bladder. BJU Int 100(5):987–1006. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2007.07205.x
Andersson KE (2016) Potential future pharmacological treatment of bladder dysfunction. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 119(3 Suppl):75–85
Truss MC, Uckert S, Stief CG, Forssmann WG, Jonas U (1996) Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE) isoenzymes in the human detrusor smooth muscle. I. Effect of various PDE inhibitors on smooth muscle tone and cyclic nucleotide levels in vitro. Urolithiasis 24(3):123–128
Calverley PM, Rabe KF, Goehring UM, Kristiansen S, Fabbri LM, Martinez FJ (2009) Roflumilast in symptomatic chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: two randomised clinical trials. Lancet 374(9691):685–694
Houslay MD, Schafer P, Zhang KY (2005) Phosphodiesterase-4 as a therapeutic target. Drug Discov Today 10(22):1503–1519
Oba Y, Lone NA (2012) Efficacy and safety of roflumilast in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther Adv Respir Dis 7(1):13–24
Funding
This study was funded by a grant from LNCCC of LNCCC-D16-2015 to Ning Li.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interests with regard to the work reported in this manuscript.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, H., Li, N., He, X. et al. Treatment of obesity-associated overactive bladder by the phosphodiesterase type-4 inhibitor roflumilast. Int Urol Nephrol 49, 1723–1730 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-017-1671-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-017-1671-2