Abstract
Background
In hemodialysis patients, the intradialytic rise in blood pressure (BP) is associated with increased mortality risk. However, the mechanisms of this adverse effect are not yet elucidated. This study examined whether intradialytic rise in BP is associated with increased arterial stiffness and wave reflections, which are powerful cardiovascular risk predictors in hemodialysis.
Methods
The pattern of intradialytic hemodynamic response was evaluated in 70 prevalent hemodialysis patients, by measuring seated brachial BP before and after the mid-week dialysis session. All patients had pre- and post-dialysis determination of aortic pulse wave velocity (PWV) and heart rate-adjusted augmentation index [AIx(75)], as measures of arterial stiffness and wave reflections, with the Sphygmocor device.
Results
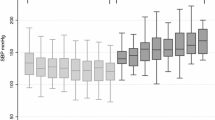
Intradialytic rise in brachial systolic BP (SBP) was evident in 17 patients, whereas intradialytic change in SBP (ΔSBP) of −10 to 0 mmHg was observed in 23 and ΔSBP greater than −10 mmHg in 30 patients. Participants with intradialytic SBP rise had significantly higher pre-dialysis aortic PWV (10.4 ± 1.6 vs 8.3 ± 1.9 vs 9.4 ± 2.4 m/s, P < 0.01) and AIx(75) (28.1 ± 7.3 vs 21.7 ± 8.6 vs 25.8 ± 8.2 %, P < 0.05) than those experiencing intradialytic ΔSBP of −10 to 0 and greater than −10 mmHg, respectively. Patients with rise in SBP during dialysis exhibited also lower intradialytic reduction in AIx(75) (−1.5 ± 4.9 vs −5.4 ± 5.9 vs −6.7 ± 5.3 %, P < 0.001).
Conclusions
This study shows that aortic stiffness and wave reflections are higher and not affected by dialysis procedure in patients with intradialytic SBP rise, suggesting that accelerated arteriosclerosis may be one possible explanation for the heightened cardiovascular risk associated with intradialytic hypertension.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY (2004) Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med 351:1296–1305
Tonelli M, Wiebe N, Culleton B, House A, Rabbat C, Fok M, McAlister F, Garg AX (2006) Chronic kidney disease and mortality risk: a systematic review. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:2034–2047
2013 USRDS annual data report—Atlas ESRD. http://www.usrds.org/atlas.aspx. Accessed 12 July 2014
Briet M, Boutouyrie P, Laurent S, London GM (2012) Arterial stiffness and pulse pressure in CKD and ESRD. Kidney Int 82:388–400
London GM, Safar ME, Pannier B (2015) Aortic aging in ESRD: structural, hemodynamic, and mortality implications. J Am Soc Nephrol. doi:10.1681/ASN.2015060617
Georgianos PI, Sarafidis PA, Haidich AB, Karpetas A, Stamatiadis D, Nikolaidis P, Lasaridis AN (2013) Diverse effects of interdialytic intervals on central wave augmentation in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 28:2160–2169
Hung SC, Kuo KL, Peng CH, Wu CH, Lien YC, Wang YC, Tarng DC (2014) Volume overload correlates with cardiovascular risk factors in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 85:703–709
Koutroumbas G, Georgianos PI, Sarafidis PA, Protogerou A, Karpetas A, Vakianis P, Raptis V, Liakopoulos V, Panagoutsos S, Syrganis C, Passadakis P (2015) Ambulatory aortic blood pressure, wave reflections and pulse wave velocity are elevated during the third in comparison to the second interdialytic day of the long interval in chronic haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 30:2046–2053
Georgianos PI, Sarafidis PA, Lasaridis AN (2015) Arterial stiffness: a novel cardiovascular risk factor in kidney disease patients. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 13:229–238
Vlachopoulos C, Aznaouridis K, Stefanadis C (2010) Prediction of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality with arterial stiffness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 55:1318–1327
Blacher J, Guerin AP, Pannier B, Marchais SJ, Safar ME, London GM (1999) Impact of aortic stiffness on survival in end-stage renal disease. Circulation 99:2434–2439
London GM, Blacher J, Pannier B, Guerin AP, Marchais SJ, Safar ME (2001) Arterial wave reflections and survival in end-stage renal failure. Hypertension 38:434–438
Agarwal R, Flynn J, Pogue V, Rahman M, Reisin E, Weir MR (2014) Assessment and management of hypertension in patients on dialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 25:1630–1646
Van Buren PN, Kim C, Toto RD, Inrig JK (2012) The prevalence of persistent intradialytic hypertension in a hemodialysis population with extended follow-up. Int J Artif Organs 35:1031–1038
Georgianos PI, Sarafidis PA, Zoccali C (2015) Intradialysis hypertension in end-stage renal disease patients: clinical epidemiology, pathogenesis and treatment. Hypertension 66:456–463
Inrig JK, Patel UD, Toto RD, Reddan DN, Himmelfarb J, Lindsay RM, Stivelman J, Winchester JF, Szczech LA (2009) Decreased pulse pressure during hemodialysis is associated with improved 6-month outcomes. Kidney Int 76:1098–1107
Inrig JK, Patel UD, Toto RD, Szczech LA (2009) Association of blood pressure increases during hemodialysis with 2-year mortality in incident hemodialysis patients: a secondary analysis of the Dialysis Morbidity and Mortality Wave 2 Study. Am J Kidney Dis 54:881–890
Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, Redon J, Zanchetti A, Bohm M, Christiaens T, Cifkova R, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Galderisi M, Grobbee DE, Jaarsma T, Kirchhof P, Kjeldsen SE, Laurent S, Manolis AJ, Nilsson PM, Ruilope LM, Schmieder RE, Sirnes PA, Sleight P, Viigimaa M, Waeber B, Zannad F (2013) 2013 ESH/ESC Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens 31:1281–1357
DeLoach SS, Townsend RR (2008) Vascular stiffness: its measurement and significance for epidemiologic and outcome studies. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3:184–192
Laurent S, Cockcroft J, Van Bortel L, Boutouyrie P, Giannattasio C, Hayoz D, Pannier B, Vlachopoulos C, Wilkinson I, Struijker-Boudier H (2006) Expert consensus document on arterial stiffness: methodological issues and clinical applications. Eur Heart J 27:2588–2605
Hoffman JI, Buckberg GD (1978) The myocardial supply: demand ratio—a critical review. Am J Cardiol 41:327–332
Mourad A, Khoshdel A, Carney S, Gillies A, Jones B, Nanra R, Trevillian P (2005) Haemodialysis-unresponsive blood pressure: cardiovascular mortality predictor? Nephrology (Carlton) 10:438–441
El-Shafey EM, El-Nagar GF, Selim MF, El-Sorogy HA, Sabry AA (2008) Is there a role for endothelin-1 in the hemodynamic changes during hemodialysis? Clin Exp Nephrol 12:370–375
Gutierrez-Adrianzen OA, Moraes ME, Almeida AP, Lima JW, Marinho MF, Marques AL, Madeiro JP, Nepomuceno L, da Silva JM, Silva GB, Daher EF, Rodrigues Sobrinho CR (2015) Pathophysiological, cardiovascular and neuroendocrine changes in hypertensive patients during the hemodialysis session. J Hum Hypertens 29:366–372
Park J, Rhee CM, Sim JJ, Kim YL, Ricks J, Streja E, Vashistha T, Tolouian R, Kovesdy CP, Kalantar-Zadeh K (2013) A comparative effectiveness research study of the change in blood pressure during hemodialysis treatment and survival. Kidney Int 84:795–802
Agarwal R, Peixoto AJ, Santos SF, Zoccali C (2006) Pre- and postdialysis blood pressures are imprecise estimates of interdialytic ambulatory blood pressure. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 1:389–398
Sinha AD, Agarwal R (2009) Peridialytic, intradialytic, and interdialytic blood pressure measurement in hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 54:788–791
Funding
This study was not supported by any source and represents an original effort of our part.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Georgianos, P.I., Mpoutsiouki, F., Sabani, E. et al. Hemodialysis patients with intradialytic rise in blood pressure display higher baseline aortic stiffness and negligible drop in augmentation index with dialysis. Int Urol Nephrol 48, 601–608 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-015-1205-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-015-1205-8