Abstract
Aim
The incidence of atrial fibrillation is increased during hemodialysis (HD); however, the effects of hemodiafiltration (HDF) on atrial arrhythmias have not been evaluated. The prolongation of the P wave and P dispersion (Pd) can predict atrial arrhythmias.
Methods
Data from 30 patients receiving HDF over a period of 3 months were collected; the same group of patients was then evaluated during treatment with conventional HD for at least another 3 months. Electrolyte values were obtained, and surface electrocardiograms (ECG), echocardiography, and Holter ECGs were performed.
Results
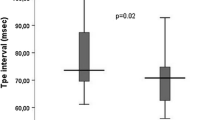
The duration of the P wave and Pd increased significantly during HD. The left atrial diameter decreased significantly only during HDF. During HDF, the left atrial cross diameter measured at the beginning of the session was positively correlated with the incidence of supraventricular premature beats (p = 0.011, r = 0.4556). The decrease in left atrial diameter during HDF was negatively correlated with the incidence of supraventricular premature beats (p = 0.016, r = −0.43). During HDF, the changes in sodium and Pd were significantly positively correlated (p < 0.05, r = 0.478). During HD, the changes in ionized calcium levels and Pd were positively correlated (p < 0.05, r = 0.377).
Conclusion
Our results suggest that HDF has a more beneficial effect on P wave duration and Pd than HD. The alterations in the ECG markers may be the result of the simultaneous occurrence of certain electrolyte imbalances and renal replacement methods.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
McCullough PA, Steigerwalt S, Tolia K et al (2011) Cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease: data from the Kidney Early Evaluation Program (KEEP). Curr Diab Rep 11(1):47–55
Meier P, Vogt P, Blanc E (2001) Ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death in end-stage renal disease patients on chronic hemodialysis. Nephron 87(3):199–214
Abe S, Yoshizawa M, Nakanishi N et al (1996) Electrocardiographic abnormalities in patients receiving hemodialysis. Am Heart J 131(6):1137–1144
Dittrich HC, Pearce LA, Asinger RW et al (1999) Left atrial diameter in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: an echocardiographic study. Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Investigators. Am Heart J 137(3):494–499
Shapira OM, Bar-Khayim Y (1992) ECG changes and cardiac arrhythmias in chronic renal failure patients on hemodialysis. J Electrocardiol 25(4):273–279
Genovesi S, Vincenti A, Rossi E et al (2008) Atrial fibrillation and morbidity and mortality in a cohort of long-term hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 51(2):255–262
Vanholder R, Meert N, Schepers E et al (2008) From uremic toxin retention to removal by convection: do we know enough? Contrib Nephrol 161:125–131
Locatelli F, Marcelli D, Conte F et al (1999) Comparison of mortality in ESRD patients on convective and diffusive extracorporeal treatments. The Registro Lombardo Dialisi E Trapianto. Kidney Int 55(1):286–293
Shimada K, Tomita T, Kamijo Y et al (2012) Hemodialysis-induced P-wave signal-averaged electrocardiogram alterations are indicative of vulnerability to atrial arrhythmias. Circ J 76(3):612–617
Andrikopoulos GK, Dilaveris PE, Richter DJ et al (2000) Increased variance of P wave duration on the electrocardiogram distinguishes patients with idiopathic paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 23(7):1127–1132
Aytemir K, Ozer N, Atalar E et al (2000) P wave dispersion on 12-lead electrocardiography in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 23(7):1109–1112
Dilaveris PE, Gialafos EJ, Sideris SK et al (1998) Simple electrocardiographic markers for the prediction of paroxysmal idiopathic atrial fibrillation. Am Heart J 135(5 Pt 1):733–738
Szabó Z, Kakuk G, Fülöp T et al (2002) Effects of haemodialysis on maximum P wave duration and P wave dispersion. Nephrol Dial Transplant 17(9):1634–1638
Canaud B, Bragg-Gresham JL, Marshall MR et al (2006) Mortality risk for patients receiving hemodiafiltration versus hemodialysis: European results from the DOPPS. Kidney Int 69(11):2087–2093
Francisco RC, Aloha M, Ramon PS (2012) Effects of high-efficiency postdilution online hemodiafiltration and high-flux hemodialysis on serum phosphorus and cardiac structure and function in patients with end-stage renal disease. Int Urol Nephrol 45(5):1373–1378
Mostovaya IM, Blankestijn PJ (2013) What have we learned from CONTRAST? Blood Purif 35(Suppl):1
Kerr PB, Argiles A, Flavier JL et al (1992) Comparison of hemodialysis and hemodiafiltration: a long-term longitudinal study. Kidney Int 41(4):1035–1040
Panichi V, Paoletti S, Consani C (2008) Inflammatory pattern in hemodiafiltration. Contrib Nephrol 161:185–190
van Tellingen A, Grooteman MP, Schoorl M et al (2002) Intercurrent clinical events are predictive of plasma C-reactive protein levels in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 62(2):632–638
Blankestijn PJ, Vos PF, Rabelink TJ et al (1995) High-flux dialysis membranes improve lipid profile in chronic hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 5(9):1703–1708
Bonforte G, Grillo P, Zerbi S et al (2002) Improvement of anemia in hemodialysis patients treated by hemodiafiltration with high-volume on-line-prepared substitution fluid. Blood Purif 20(4):357–363
Ohtake T, Oka M, Ishioka K et al (2012) Cardiovascular protective effects of on-line hemodiafiltration: comparison with conventional hemodialysis. Ther Apher Dial 16(2):181–188
Ok E, Asci G, Toz H et al (2013) Mortality and cardiovascular events in online haemodiafiltration (OL-HDF) compared with high-flux dialysis: results from the Turkish OL-HDF Study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 28(1):192–202
Barta K, Czifra Á, Kun C et al (2014) Hemodiafiltration beneficially affects QT interval duration and dispersion compared to hemodialysis. Clin Exp Nephrol 18(6):952–959
Acknowledgments
Our research project was sponsored by the TÁMOP-4.2.2.A-11/1/KONV-2012-0045 and TÁMOP-4.2.6-151-2015-0001 projects. These projects are implemented through the New Hungary Development Plan and co-financed by the European Union and the European Social Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have a relationship with companies that may have a financial or non-financial interest in the information contained in the manuscript. The authors have no other funding, financial relationships, or conflicts of interest to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Páll, A., Czifra, Á., Sebestyén, V. et al. Hemodiafiltration and hemodialysis differently affect P wave duration and dispersion on the surface electrocardiogram. Int Urol Nephrol 48, 271–277 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-015-1144-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-015-1144-4