Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to investigate oxidative stress in etiopathogenesis by analyzing serum total antioxidant capacity (TAC), total oxidant status (TOS), binding capacity of exogenous cobalt to human albumin (IMA), serum advanced oxidation protein products (AOPP), paraoxonase (PON), arylesterase, IgE, and C-reactive protein (CRP) in bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC).
Methods
The study included 16 female patients diagnosed with BPS/IC and 25 healthy female subjects forming the control group. A bladder biopsy was performed on all patients in the BPS/IC group by carrying out cystoscopy with hydrodistention under general anesthesia. The results of serum TAC, TOS, IMA, AOPP, PON, arylesterase, IgE, and CRP of the subjects in both groups were compared.
Results
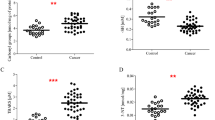
The mean age of the 16 female patients in the BPS/IC group was 43.6 ± 14.5 years, and the mean age of the 25 healthy subjects in the control group was 42.0 ± 10.3 years. According to the criteria of International Society for the Study of Interstitial Cystitis (ESSIC), eight patients were classified as Type 2A, three patients as Type 2B, four patients as Type 2C, and one patient as Type 3C. In the BPS/IC group, while TAC was found significantly lower than in the control group, IMA, IgE, and CRP were found significantly higher (P < 0.05). When binary logistic regression analysis was performed, the created model was determined to have 81.3 % sensitivity and 80 % specifity.
Conclusions
In the etiology of BPS/IC, mechanism of oxidative damage comes into prominence. In the diagnosis of BPS/IC, IgE, CRP, and TAC are not specific markers when used separately; however, a higher specifity and sensitivity could be reached when used jointly in the suspected patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fal M, Johansson SL, Aldenborg F (1987) Chronic interstitial cystitis: a heterogeneous syndrome. J Urol 137(1):35–38
van de Merwe JP, Nordling J, Bouchelouche P, Bouchelouche K, Cervigni M, Daha LK et al (2008) Diagnostic criteria, classification, and nomenclature for painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis: an ESSIC proposal. Eur Urol 53(1):60–67
Okragly AJ, Niles AL, Saban R, Schmidt D, Hoffman RL, Warner TF, Moon TD et al (1999) Elevated tryptase, nerve growth factor, neurotrophin-3 and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor levels in theurine of interstitial cystitis and bladder cancer patients. J Urol 161(2):438–441
Nickel JC, Shoskes DA, Irvine-Bird K (2010) Prevalence and impact of bacteriuria and/or urinary tract infection in interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Urology 76(4):799–803
Talati A, Ponniah K, Strug LJ, Hodge SE, Fyer AJ, Weissman MM (2008) Panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and a possible medical syndrome previously linked to chromosome 13. Biol Psychiatry 63(6):594–601
Malone L, Schuler C, Leggett RE, Levin RM (2014) Effect of estrogen and ovariectomy on response of the female rabbit urinary bladder to two forms of in vitro oxidative stres. Int Urogynecol J 25(6):791–798
Gutteridge JM, Halliwell B (2000) Free radicals and antioxidants in the year 2000: a historical look to the future. Ann N Y Acad Sci 899:136–147
Erel O (2004) A novel automated direct measurement method for total antioxidant capacity using a new generation, more stable ABTS radical cation. Clin Biochem 37(4):277–285
Erel O (2005) A new automated colorimetric method for measuring total oxidant status. Clin Biochem 38(12):1103–1111
Camps J, Marsillach J, Joven J (2009) The paraoxonase: role in human diseases and methodological difficulties in measurement. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 46:83–106
Furlong CE, Suzuki SM, Stevens RC, Marsillach J, Richter RJ, Jarvik GP et al (2010) Human PON1, a biomarker of risk of disease and exposure. Chem Biol Interact 187(1–3):355–361
James RW (2006) A long and winding road: defining the biological role and clinical importance of paraoxonases. Clin Chem Lab Med 44:1052–1059
Novak F, Vavrova L, Kodydkova J, Novak F Sr, Hynkova M, Zak A et al (2010) Decreased paraoxonase activity in critically ill patients with sepsis. Clin Exp Med 10:21–25
Bar-Or D, Lau E, Winkler JV (2000) A novel assay for cobalt-albumin binding and its potential as a marker for myocardial ischemia—a preliminary report. J Emerg Med 19(4):311–315
Berenshtein E, Mayer B, Goldberg C, Kitrossky N, Chevion M (1997) Patterns of mobilization of copper and iron following myocardial ischemia: possible predictive criteria for tissue injury. J Mol Cell Cardiol 29:3025–3034
Witko-Sarsat V, Friedlander M, Nguyen Khoa T, Capeillère-Blandin C, Nguyen AT, Canteloup S et al (1998) Advanced oxidation protein products as novel mediators of inflammation and monocyte activation in chronic renal failure. J Immunol 161(5):2524–2532
Hanno P, Lin A, Nordling J, Nyberg L, van Ophoven A, Ueda T et al (2010) Bladder pain syndrome committee of the international consultation on incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn 29(1):191–198
Eckerson HW, Wyte CM, La Du BN (1983) The human serum paraoxonase/arylesterase polymorphism. Am J Hum Genet 35(6):1126–1138
Haagen L, Brock A (1992) A new automated method for phenotyping arylesterase (E.C.3.1.1.2.) based upon inhibition of enzymatic hydrolysis of 4-nitrophenyl acetate by phenyl acetate. Eur J Clin Chem Clim Biochem 30(7):391–395
Witko-Sarsat V, Friedlander M, Capeillère-Blandin C, Nguyen-Khoa T, Nguyen AT, Zingraff J et al (1996) Advanced oxidation protein products as a novel marker of oxidative stress in uremia. Kidney Int 49(5):1304–1313
Giannantoni A, Costantini E, Di Stasi SM, Tascini MC, Bini V, Porena M (2006) Botulinum A toxin intravesical injections in the treatment of painful bladder syndrome: a pilot study. Eur Urol 49(4):704–709
Palmieri K, Mannikarottu AS, Chichester P, Kogan B, Leggett RE, Whitbeck C et al (2007) The effects of cyclical oestrogen on bladder and urethral structure and function. BJU Int 99(1):171–176
Rehfuss A, Schuler C, Maxemous C, Leggett RE, Levin RM (2010) Cyclical estrogen and free radical damage to the rabbit urinary bladder. Int Urogynecol J 21(4):489–494
Badger WJ, Whitbeck C, Kogan B, Chichester P, Levin RM (2006) The immediate effect of castration on female rabbit bladder blood flow and tissue oxygenation. Urol Int 76:264–268
Bae WJ, Ha US, Kim S, Kim SJ, Hong SH, Lee JY et al (2015) Reduction of oxidative stress may play a role in the anti-inflammatory effect of the novel herbal formulation in a rat model of hydrochloric acid-induced cystitis. Neurourol Urodyn 34(1):86–91
Ehrén I, Hosseini A, Lundberg JO, Wiklund NP (1999) Nitric oxide: a useful gas in the detection of lower urinary tract inflammation. J Urol 162(2):327–329
Birder LA, Wolf-Johnston A, Buffington CA, Roppolo JR, de Groat WC, Kanai AJ (2005) Altered inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and nitric oxide production in the bladder of cats with feline interstitial cystitis. J Urol 173(2):625–629
Kinlay S, Behrendt D, Fang JC, Delagrange D, Morrow J, Witztum JL et al (2004) Long-term effect of combined vitamins E and C on coronary and peripheral endothelial function. J Am Coll Cardiol 43(4):629–634
Kiuchi H, Tsujimura A, Takao T, Yamamoto K, Nakayama J, Miyagawa Y et al (2009) Increased vascular endothelial growth factor expression in patients with bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis: its association with pain severity and glomerulations. BJU Int 104(6):826–831
Lee J, Doggweiler-Wiygul R, Kim S, Hill BD, Yoo TJ (2006) Is interstitial cystitis an allergic disorder? A case of interstitial cystitis treated successfully with anti-IgE. Int J Urol 13(5):631–634
Boucher W, Kempuraj D, Cao J, Papaliodis D, Theoharides TC (2007) Intravesical suplatast tosilate (IPD-1151T) inhibits experimental bladder inflammation. J Urol 177(3):1186–1190
Kaneko G, Nishimoto K, Ito Y, Uchida A (2012) The combination therapy of prednisolone and tacrolimus for severe painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Can Urol Assoc J 6(2):E46–E49
Chiang G, Patra P, Letourneau R, Jeudy S, Boucher W, Green M et al (2000) Pentosanpolysulfate inhibits mast cell histamine secretion and intracellular calcium ion levels: an alternative explanation of its beneficial effect in interstitial cystitis. J Urol 164(6):2119–2125
Giannantoni A, Bini V, Dmochowski R, Hanno P, Nickel JC, Proietti S et al (2012) Contemporary management of the painful bladder: a systematic review. Eur Urol 61(1):29–53
Zeybek A, Sağlam B, Cikler E, Cetinel S, Ercan F, Sener G (2007) Taurine ameliorates stress-induced degeneration of the urinary bladder. Acta Histochem 109(3):208–214
Zhang QH, Zhou ZS, Lu GS, Song B, Guo JX (2013) Melatonin improves bladder symptoms and may ameliorate bladder damage via increasing HO-1 in rats. Inflammation 36(3):651–657
Bazi T, Hajj-Hussein IA, Awwad J, Shams A, Hijaz M, Jurjus A (2013) A modulating effect of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a tea catechin, on the bladder of rats exposed to water avoidance stress. Neurourol Urodyn 32(3):287–292
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank biostatistics master program fellow and psychiatrist Dr. Mustafa Uğurlu for his contributions and support concerning the statistical analysis and interpretation of the data.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ener, K., Keske, M., Aldemir, M. et al. Evaluation of oxidative stress status and antioxidant capacity in patients with painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis: preliminary results of a randomised study. Int Urol Nephrol 47, 1297–1302 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-015-1021-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-015-1021-1