Abstract
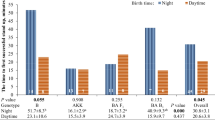
The aim of the present study was to assess if weaning time (morning or evening) and feed provision (immediate or 4 h delayed) can influence growth performance and expression of juvenile lamb behaviour immediately after and at the age of 50–125 days old. Forty lambs were randomly assigned to 4 groups: E1 (evening + immediate), E2 (evening + delayed), M1 (morning + immediate) and M2 (morning + delayed). All lambs were especially active during the first hour after weaning. However, their activity within the first 24 h after weaning was mainly affected by their circadian rhythms, since lambs were more active during the day compared to night. On the other hand, no effect of alfalfa hay provision on lamb activity during these first 24 h was observed. At the age of 50–125 days old, body weight was measured, and an isolation and flight distance test was implemented. There were no significant differences among lambs in body weight, number of jumps and heart rates assessed during isolation test and flight distance. However, the number of vocalizations was lower (65–110th day, P < 0.05) for the E2 compared to E1 lambs. Breed also slightly affected (95th day, P < 0.05) the average heart rate of lambs, with greater values for Karagouniko compared to Chios lambs. It is concluded that no discernible effects of weaning or feeding time were observed on growth performance and the display of stress-induced behavioural components of juvenile lambs till the age of 125 days old.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
AFRC (Agricultural and Food Research Council), 1993. Energy and protein requirements of ruminants: an advisory manual. Technical committee on responses to nutrients. CAB International, Wallingford, UK, pp. 100–106.
Anisman, H., Zaharia, M.D., Meaney, M.J., Merali, Z., 1998. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience, 16, 149–164.
Backes, E.A., Caldwell, J.D., Shanks, B.C., Ness, K.R., Stewart, A.N.V., Kreider, D.L., Looper M.L., 2015. Performance and behaviour by spring-born Katahdin lambs weaned using traditional or fenceline-weaning methods in the morning or evening. Sheep and Goat Research Journal, 30, 13-17.
Bates, J., Wachs, T., VandenBos, G., 1995. Trends in research on temperament. Psychiatric Services 46, 661–663.
Boissey, A., Bouix, J., Orgeur, P., Pascal, P., Bibe, B., LeNeindre, P., 2005. Genetic analysis of emotional reactivity of sheep: Effects of genotype of the lambs and their dams. Genetics Selection Evolution, 37, 381–401.
Boivin, X., Braastad, B.O., 1996. Effects of handling during temporary isolation after early weaning on goat kids’ later response to humans. Applied Animal Behaviour Science, 48, 61-71.
Broom, D.M., 2006. Behaviour and welfare in relation to pathology. Applied Animal Behaviour Science, 97, 73-83.
Burrow, H.M., 1997. Measurements of temperament and their relationships with performance traits of beef cattle. Animal Breeding Abstracts, 65, 477–495.
Cockram, M.S., Ranson, M., Imlah, P.J., Burrells, C., Harkiss, G.D., 1994. The behavioural, endocrine and immune responses of sheep to isolation. Animal Production, 58, 389–399.
Correa, M.P.C., Cardoso, M.T., Castanheira, M., Landim, A.V., Dallago, B.S.L., Louvandini, H., McManus, C., 2012. Heat tolerance in three genetic groups of lambs in central Brazil. Small Ruminant Research, 104, 70-77.
Damián, J.P., Hötzel, M.J., Banchero, G., Ungerfeld, R., 2013. Behavioural response of grazing lambs to changes associated with feeding and separation from their mothers at weaning. Research in Veterinary Science, 95, 913-918.
Dodd, C.L., Pitchford, W.S., Edwards, J.E.H., Hazel, S.J., 2012. Measures of behavioural reactivity and their relationships with production traits in sheep: A review. Applied Animal Behaviour Science, 140, 1-15.
Enriquez, D., Hötzel, M.J., Ungerfeld, R., 2011. Minimising the stress of weaning of beef calves: a review. Acta Veterinaria Scandinavica, 53, 1-8.
Hall, S.J.G., Kirkpatrick, S.M., Broom, D.M., 1998. Behavioural and physiological responses of sheep of different breeds to supplementary feeding, social mixing and taming, in the context of transport. Animal Science, 67, 475-483.
Hargreaves, A.L., Hutson, G.D., 1990. The effect of gentling on heart rate, flight distance and aversion of sheep to a handling procedure. Applied Animal Behaviour Science, 26, 243-252.
Kilgour, R.J., Szantar-Coddington, M.R., 1995. Arena behaviour of ewes selected for superior mothering ability differs from that of unselected ewes. Animal Reproduction Science, 37, 133–141.
Landau, S.Y., Provenza, F.D., 2020. Of browse, goats, and men: contribution to the debate on animal traditions and cultures. Applied Animal Behaviour Science, 105127
Le Neindre, P., Poindron, P., Trillat, G., Orgeur, P., 1993. Influence of breed on reactivity of sheep to humans. Genetics Selection Evolution, 25, 447-458.
Lynch, E., McGee, M., Earley, B., 2019. Weaning management of beef calves with implications for animal health and welfare. Journal of Applied Animal Research, 47, 167-175.
Mohapatra, A., De, K., Saxena, V.K., Mallick, P.K., Devi, I., Singh, R., 2021. Behavioural and physiological adjustments by lambs in response to weaning stress. Journal of Veterinary Behavior, 41, 47-51.
Napolitano, F., De Rosa, G., Sevi, A., 2008. Welfare implications of artificial rearing and early weaning in sheep. Applied Animal Behaviour Science 110, 58-72.
Neill, C.R., Tokach, M.D., Nelssen, J.L., Goodband, R.D., DeRouchey, J.M., Dritz, S.S, Groesbeck, C.N., Brown, K.R., 2007. Effects of afternoon or morning weaning protocol on pig growth performance. Journal of Swine Health and Production, 15, 19–21.
Ness, K., Caldwell, J., Coffey, K., Shanks, B., Hubbell III, D., Stewart, A., Backes, E., Tucker, J., Clifford-Rathert, C., Wurst, A., 2012. Performance by fall-born calves weaned in the morning or evening using either fenceline or traditional weaning methods. Arkansas Animal Science Department Report 12, AAES Research Series 606, 31-33.
Norouzian, M.A., 2015. Effect of weaning method on lamb behaviour and weight gain. Small Ruminant Research, 133, 17-20.
Ogunbameru, B.O., Kornegay, E.T., Wood, C.M., 1992. Effect of evening or morning weaning and immediate or delayed feeding on postweaning performance of pigs. Journal of Animal Science, 70, 337-342.
Orgeur, P., Mavric, N., Yvore, P., Bernard, S., Nowak, R., Schaal, B., Lévy, F., 1998. Artificial weaning in sheep: consequences on behavioural, hormonal and immuno-pathological indicators of welfare. Applied Animal Behaviour Science, 58, 87-103.
Orgeur, P., Bernard, S., Naciri, M., Nowak, R., Schaal, B., Lévy, F., 1999. Psychobiological consequences of two different weaning methods in sheep. Reproduction, Nutrition and Development, 39, 231-244.
Pajor, F., Laczo, E., Poti, P., 2007. Sustainable sheep production: evaluation of effect of temperament on lamb production. Cereal Research Communications, 35, 873–876.
Panopoulou, E., Deligeorgis, S., Papadimitriou, T., Rogdakis, E., 1989. Carcass composition, size of fat cells and NADPH-generating dehydrogenases activity in adipose tissue of the fat tailed Chios and the thin tailed Karagouniko sheep breed. Journal of Animal Breeding and Genetics, 106, 51-58.
Pascual-Alonso, M., Miranda-de la Lama, G.C., Aguayo-Ulloa, L., Ezquerro, L., Villarroel, M., Marín, R.H., Maria, G.A., 2015. Effect of postweaning handling strategies on welfare and productive traits in lambs. Journal of Applied Animal Welfare Science, 18, 42-56.
Price, E.O., Harris, J.E., Borgwardt, R.E., Sween, M.L., Connor, J.M., 2003. Fenceline contact of beef calves with their dams at weaning reduces the negative effects of separation on behaviour and growth rate. Journal of Animal Science, 81, 116-121.
Rogdakis, E., 2002. Indigenous Breeds of Sheep. Agrotypos, Athens, Greece.
Sas/Stat, 2011. Statistical Analysis Systems Version 9.3. SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC.
Schichowski, C., Moors, E., Gauly, M., 2008. Effects of weaning lambs in two stages or by abrupt separation on their behaviour and growth rate. Journal of Animal Science, 86, 220-225.
Simitzis, P.E., Charismiadou, M.A., Kotsampasi, B., Papadomichelakis, G., Christopoulou, E.P., Papavlasopoulou, E.K., Deligeorgis, S.G., 2009. Influence of maternal undernutrition on the behaviour of juvenile lambs. Applied Animal Behaviour Science, 116, 191-197.
Simitzis, P., Petrou, M., Demiris, N., Deligeorgis, S., 2012. Effect of pre-weaning temporary isolation within different age periods on the early post-weaning behaviour of juvenile lambs. Applied Animal Behaviour Science, 141, 43-48.
Simitzis, P., Seferlis, I., Goliomytis, M., Bizelis, I., Politis, I., 2021. Handling and milking frequency affect milk yield and behaviour in dairy ewes. Small Ruminant Research, 198, 106351.
Urbano, S.A., de Andrade Ferreira, M., do Nascimento Rangel, A.H., de Lima Júnior, D.M., de Andrade, R.D.P.X., Novaes, L.P., 2017. Lamb feeding strategies during the pre-weaning period in intensive meat production systems. Tropical and Subtropical Agroecosystems, 20, 49-63.
Wang, S., Ma, T., Zhao, G., Zhang, N., Tu, Y., Li, F., Cui, K., Bi, Y., Ding H., Diao, Q., 2019. Effect of Age and Weaning on Growth Performance, Rumen Fermentation, and Serum Parameters in Lambs Fed Starter with Limited Ewe–Lamb Interaction. Animals 9, 825.
Wolf, B.T., McBride, S.D., Lewis, R.M., Davies, M.H., Haresign, W., 2008. Estimates of genetic parameters and repeatability of behavioural traits of sheep in an arena test. Applied Animal Behaviour Science, 112, 68–80.
Wyse, C.A., Zhang, X., McLaughlin, M., Biello, S.M., Hough, D., Bellingham, M., Curtis, A.M., Robinson, J.E., Evans, N.P., 2018. Circadian rhythms of melatonin and behaviour in juvenile sheep in field conditions: Effects of photoperiod, environment and weaning. Physiology and Behavior, 194, 362-370.
Youssef, M.Y.I., Phillips, C.J.C., Metwally, M., 1995. The effect of pre-weaning grazing experience and presence of adult ewes on grazing behaviour of weaned lambs. Applied Animal Behaviour Science, 2, 281.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Panagiotis Simitzis, Maria Charismiadou and Michael Goliomytis; methodology, Panagiotis Simitzis; formal analysis, Michael Goliomytis; investigation, Panagiotis Simitzis, Apostolos Petropoulos and George Troupakis; writing—original draft preparation, Panagiotis Simitzis; writing—review and editing, Michael Goliomytis, Maria Charismiadou and Panagiotis Simitzis; supervision, Panagiotis Simitzis; project administration, Panagiotis Simitzis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Statement of animal rights
The methods used in the present experiment were approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Department of Animal Science and Aquaculture of the Agricultural University of Athens under the guidelines of “Council Directive 86/609/EEC regarding the protection of animals used for experimental and other scientific purposes”.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Goliomytis, M., Charismiadou, M., Petropoulos, A. et al. Effect of weaning and feed provision times on the performance and several behavioural traits of post-weaning lambs. Trop Anim Health Prod 54, 366 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-022-03369-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-022-03369-3