Abstract
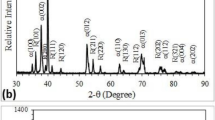
Erosion wear resistance and impact-induced phase transformation of titanium alloys TA2 (pure Ti), TC4 (Ti–6Al–4V) and TC11 (Ti–6.5Al–3.5Mo–1.5Zr–0.3Si) were investigated using a slurry jet tester. The slurry erosion wear resistance of TA2 is comparable to that of 304 stainless steel, especially at the impingement angle 90°. Although TC4 and TC11 have higher hardness, TA2 possesses the best erosion wear resistance except TC11 at 15°. With the increasing erosion time, the eroded surface hardness of TC11 at the impingement angle 90° increases and then decreases, while the volume loss rate drops in the first 15 min, then increases until 30 min, and then slightly decreases again. With XRD characterization and SEM observation, erosion-induced phase transformation from metastable β-phase to α-phase is proved on the surface of titanium alloy TC11. And the thickness of visible phase transformation layer is about 10 μm. Phase transformation influences the erosive wear mechanism of titanium alloys. At the impingement angle of 30°, the material removal of TC4 and TC11 can be described as micro-plowing and lip extruding, while plowing mark is not a typical surface morphology of TA2, indicating a better work-harden ability. So, stabilizing β-phase can be an effective way to improve the erosion wear resistance of titanium alloys.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lisiecki, A., Kurc-Lisiecka, A.: Erosion wear resistance of titanium-matrix composite Ti/Tin produced by diode-laser gas nitriding. Mater. Tehnol. 51(1), 29–34 (2017)
Ding, H.Y., Dai, Z.D., Zhou, F., Zhou, G.H.: Sliding friction and wear behavior of TC11 in aqueous condition. Wear 263, 117–124 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2007.01.106
Khayatan, N., Ghasemi, H.M., Abedini, M.: Synergistic erosion–corrosion behavior of commercially pure titanium at various impingement angles. Wear 380–381, 154–162 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2017.03.016
Dong, H., Bloyce, A., Bell, T.: Slurry abrasion response of surface engineered Ti6Al4VELI. Tribol. Int. 32(9), 517–526 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-679X(99)00082-1
Chen, F.-J., Yao, C., Yang, Z.-G.: Failure analysis on abnormal wall thinning of heat-transfer titanium tubes of condensers in nuclear power plant Part II: Erosion and cavitation corrosion. Eng. Fail. Anal. 37((Supplement C)), 42–52 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2013.11.002
Fu, Y.Q., Du, H.J., Gu, Y.W.: Improvement of erosion resistance of titanium with different surface treatments. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 9(5), 571–579 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1361/105994900770345719
Mann, B.S.: Water droplet and cavitation erosion behavior of laser-treated stainless steel and titanium alloy: their similarities. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 22(12), 3647–3656 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-013-0660-6
Duraiselvam, M., Galun, R., Wesling, V., Mordike, B.L., Reiter, R., Oligmuller, J., Buvanashekaran, G.: Improvement of the cavitation erosion resistance of Ti–6Al–4V through laser alloying titanium aluminide based intermetallic matrix composites. Lasers Eng. 16(5–6), 423–436 (2006)
Dong, H., Xing, L.D.: The research on the mechanism and prevention of solid particle erosion for titanium alloy. In: Ti-2011: Proceedings Of the 12th World Conference on Titanium, vol. Iii, pp. 1877–1880 (2012)
Du, J., Zhang, P., Zhao, J.J., Cai, Z.H.: Erosion-resistant PVD ZrAlCuN coating for titanium alloy. Adv. Compos. Pts 1 And 2 150-151, 51–55 (2011). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.150-151.51
Grogler, T., Zeiler, E., Franz, A., Plewa, O., Rosiwal, S.M., Singer, R.F.: Erosion resistance of CVD diamond-coated titanium alloy for aerospace applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 112(1–3), 129–132 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0257-8972(98)00800-7
Sahoo, R., Mantry, S., Sahoo, T.K., Mishra, S., Jha, B.B.: Effect of microstructural variation on erosion wear behavior of Ti–6Al–4V Alloy. Tribol. Trans. 56(4), 555–560 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1080/10402004.2013.767400
Shao, S., Xi, H.Z., Chang, Y.P.: Study on the Salt Spray Corrosion and Erosion Behavior of TC4 Titanium Alloy. Fundamental Of Chemical Engineering, Pts 1–3(233–235), 2409–2412 (2011). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.233-235.2409
Kumar, N., Shukla, M.: Finite element analysis of multi-particle impact on erosion in abrasive water jet machining of titanium alloy. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 236(18), 4600–4610 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cam.2012.04.022
Bermudez, M.D., Carrion, F.J., Martinez-Nicolas, G., Lopez, R.: Erosion-corrosion of stainless steels, titanium, tantalum and zirconium. Wear 258(1–4), 693–700 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2004.09.023
Mochizuki, H., Yokota, M., Hattori, S.: Effects of materials and solution temperatures on cavitation erosion of pure titanium and titanium alloy in seawater. Wear 262(5–6), 522–528 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2006.06.011
Huang, L., Folkes, J., Kinnell, P., Shipway, P.H.: Mechanisms of damage initiation in a titanium alloy subjected to water droplet impact during ultra-high pressure plain waterjet erosion. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 212(9), 1906–1915 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2012.04.013
Neville, A., McDougall, B.A.B.: Erosion- and cavitation-corrosion of titanium and its alloys. Wear 250, 726–735 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(01)00709-8
Fidan, S., Avcu, E., Karakulak, E., Yamanoglu, R., Zeren, M., Sinmazcelik, T.: Effect of heat treatment on erosive wear behaviour of Ti6Al4V alloy. Mater. Sci. Technol. 29(9), 1088–1094 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1179/1743284713Y.0000000239
Yang, J., Swisher, J.H.: Erosion–corrosion behavior and cathodic protection of alloys in seawater-sand slurries. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2(6), 843–850 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/Bf02645684
Mitelea, I., Bordeasu, I., Utu, I.D., Karancsi, O.: Improvement of the cavitation erosion resistance of titanium alloys deposited by plasma spraying and remelted by laser. Mater. Plast. 53(1), 29–33 (2016)
Cai, F., Gao, F., Pant, S., Huang, X., Yang, Q.: Solid particle erosion behaviors of carbon-fiber epoxy composite and pure titanium. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 25(1), 290–296 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1848-8
Lindgren, M., Perolainen, J.: Slurry pot investigation of the influence of erodant characteristics on the erosion resistance of titanium. Wear 321, 64–69 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2014.10.005
Materia, T. http://www.totalmateria.cn/
Ji, X.L., Han, X., Zhou, M.Y., Liu, J.Q.: Effect of heat treatment on the slurry erosion resistance of high strength steel DP980. Int. J. Mater. Res. 105(5), 487–492 (2014)
Zhao, X., Xue, G., Liu, Y.: Gradient crystalline structure induced by ultrasonic impacting and rolling and its effect on fatigue behavior of TC11 titanium alloy. Results Phys. 7(Supplement C), 1845–1851 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2017.05.026
Davis, B.L.: Semiquantitative XRD analysis with the aid of reference intensity ratio estimates. Powder Diffr. 13(3), 185–187 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0885715600010083
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51475140, 51711530226).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, X., Qing, Q., Ji, C. et al. Slurry Erosion Wear Resistance and Impact-Induced Phase Transformation of Titanium Alloys. Tribol Lett 66, 64 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-018-1015-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-018-1015-0