Abstract
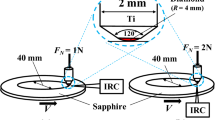
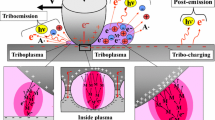
Previously, high-intensity triboplasma was discovered in the rear outside gap of the sliding contact by measuring the triboluminescence. However, we have almost no information on the triboplasma generation inside of the sliding contact. This is because the intensity of the photon emission from the inside of the sliding contact is too weak to be detected compared to that from the high-intensity rear outside plasma. On the other hand, plasma generated at the front outside of the contact was also difficult to observe since the intensity was also so weak. In the present article, the author investigated the triboplasma generation at the inside, front outside and very vicinity of the sliding contact together with the rear outside of the sliding contact by measuring the two-dimensional images and intensities of the UV, visible and IR photons emitted from the sliding contact while sliding a diamond pin with a 4-mm tip radius on a sapphire disk in dry sliding in dry air under a normal force of 2 N and a sliding velocity of 34 cm/s. The results showed that extremely weak triboplasma is generated even in the small asperity gap of the sliding contact, that the sliding contact is surrounded by weak circular plasma and that weak plasma is generated further in the front of the sliding contact. Namely, four kinds of triboplasma were observed inside and outside of the sliding contact including the previously reported rear outside high-intensity plasma, (1) weak front outside plasma, (2) weaker circular outside plasma surrounding the contact, (3) weakest inside plasma and (4) high-intensity plasma, visible at the rear outside of the contact. Based on the experimental results, a new model of triboelectromagnetic phenomena has been proposed.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haper, W.R.: Contact and Frictional Electrification. Oxford University Press, London (1967)
Nakayama, K.: The plasma generated and photons emitted in an oil-lubricated sliding contact. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 40, 1103–1107 (2007)
Nakayama, K.: Triboplasma generation and triboluminescence: influence of stationary sliding partner. Tribol. Lett. 37, 215–218 (2010)
Nakayama, K., Hashimoto, H.: Triboemision, tribochemical reaction, and friction and wear in ceramics under various n-butane gas pressures. Tribol. Int. 29, 385–393 (1996)
Nakayama, K., Mirza, S.M.: Verification of the decomposition of perfluoropolyether fluid due to tribomicroplasma. Tribol. Trans. 49, 17–25 (2006)
Kato, K., Umehara, N., Adachi, K.: Friction, wear and N2-lubrication of carbon nitride coatings: a review. Wear 254, 1062–1069 (2003)
Kano, M., et al.: Ultralow friction of DLC in presence of glycerol mono-oleate (GMO). Trobol. Lett. 18, 245–251 (2005)
Erdemir, A., Fontaine, J., Donnet, C.: An overview of superlubricity in diamond-like carbon films. In: Donnet, D., Erdemir, A. (eds.) Tribology of Diamond Carbon Film, pp. 237–262. Springer, New York (2008)
Ohta, T., et al.: Coolants effects on tool wear in machining single-crystal silicon with diamond tools. Key Eng. Mater. 389–390, 144–150 (2009)
Nakayama, K.: UV, visible and IR photon emission distribution from the inside and outside of the PFPE lubricated sliding contact point and the mechanisms of the photon emission and plasma generation in oil. In: Proceedings of the Tribology Conference on Tokyo, 2007-5, pp. 339–340 (in Japanese)
Matta, C., Erlyilmaz, O.L., De Barros Bouchet, M.I., Erdemir, A., Martion, J.M., Nakayama, K.: On the possible role of triboplasma in friction and wear of diamond-like carbon films in hydrogen-containing environments. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 42, 075307 (2009)
von Engel, A.: Ionized gases, p. 195. AIP Press, New York (1994)
Nakayama, K., Tanaka, M.: Silulation analysis of triboplasma generation using the particle-in-cell/Monte Carlo collision (PIC/MCC) method. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 45, 495203 (2012)
Miyahara, Y., Tokoroyama, T., Umehara, N., Fuwa, Y.: In-situ observation for tribomicroplasma and transfer layer forming of carbon nitride coating. J. Jpn. Soc. Tribol. 56, 378–384 (2011). (in Japanese)
Nakayama, K.: Contact geometry and distribution of plasma generated in the vicinity of sliding contact. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 46, 6007–6601 (2007)
Kristianpoller, N., Rehavy, A.: Luminescence center in Al2O3. J. Lumin. 18(19), 239–243 (1979)
Toyoda, T., Obikawa, T., Shigenari, T.: Photoluminescence spectroscopy of Cr3+ in ceramics Al2O3. Mater. Sci. Eng. B54, 33–37 (1998)
Pan, C., Chen, S., Shen, P.: Photoluminescence and transformation of dense Al2O3: Cr3+ condensates synthesized by laser-ablation route. J. Cryst. Growth 310, 699–705 (2008)
Patra, A., Tallman, R.E., Weinstein, B.A.: Effect of crystal structure and dopant concentration on the luminescence of Cr3+ in Al2O3 nanocrystals. Opt. Mater. 27, 1396–1401 (2005)
Chen, Y., Kolopus, J.L., Sibley, W.A.: Luminescence of the F+ center in MgO. Phys. Rev. 186, 865–870 (1969)
Kapper, L.A., Kroes, R.L., Henseley, E.B.: F+ and F, centers in magnesium oxide. Phys. Rev. 1, 4151–4157 (1970)
Chen, Y., Kolopus, J.L., Sibley, W.A.: Defect luminescence in irradiated MgO. J. Lumin. 1, 633–640 (1970)
Williams Jr., G.P., Rosenblatt, G.H., Ferry, M.J., Williams, R.T., Chen, Y.: Time resolved luminescence and absorption spectroscopy of defects in MgO and Al2O3. J. Lumin. 40 & 41, 339–340 (1988)
Rosenblatt, G.H., Rowe, M.W., Williams Jr., G.P., Williams, R.T.: Luminescence of F and F+ centers in magnesium oxides. Phys. Rev. 39, 10309–10318 (1989)
Dickinson, J.T., Jensen, L.C., Webb, R.L., Langford, S.C.: Photoluminescence imaging of mechanically produced defects. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 177, 1–8 (1994)
Duley, W.W., Rosatzin, M.: The orange luminescence band in MgO crystals. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 46, 165–170 (1985)
Skuja, L.N., Streletsky, A.N., Pakovich, A.B.: A new intrinsic defect in amorphous SiO2: twofold coordinated silicon. Solid State Commun. 50, 1069–1072 (1984)
Silin, A.R., Skuja, L.N., Trukhin, A.N.: Intrinsic defects generation mechanism in fused silica. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 38 & 39, 195–200 (1980)
Okuzaki, S., Okude, K., Ohishi, T.: Photoluminescence behavior of SiO2 prepared by sol–gel processing. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 265, 61–67 (2000)
Milman, I.I., Moiseykin, E.V., Nikiforov, S.V., Mikhailov, S.G., Solomonov, V.I.: Luminescence properties of α-Al2O3 dosimetric crystals exposed to a high-current electron beam. Radiat. Meas. 38, 443–446 (2004)
Mkov, V.N., Lusichik, A., Lushichik, Ch.B., Kirm, M., Vasilchenko, E., Vieerhauer, S., Harutunvan, V.V., Aleksanvan, E.: Luminescence and radiation defects in electron-irradiated Al2O3 and Al2O3: Cr. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. B266, 2949–2952 (2008)
Llopis, J., Piqueras, J., Bru, L.: Cathodoluminescence from slip planes in deformed MgO. J. Mater. Sci. 13, 1361–1364 (1978)
Datta, S., Boswarva, I.M., Holt, D.B.: Cathodeluminescence in deformed MgO crystals. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 40, 567–571 (1979)
Jones, C.E., Embree, D.: Correlation of the 4.77–4.28-eV luminescence band in silicon dioxide with the oxygen vacancy. J. Appl. Phys. 47, 5365–5371 (2008)
Mitchell, J., Denure, D.G.: A study of SiO layer on Si using cathodoluminescence spectra. Solid State Electron. 16, 825–839 (1973)
Sigel Jr., G.H.: Ultraviolet spetra of silicate glasses: a rview of some experimental evidence. J. Non-cryst. Solids 13, 372–398 (1973)
Sigel Jr., G.H., Friebele, E.J., Ginther, R.J., Griscon, D.L.: Effect of stoichiometry on the radiation response of SiO2. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. NS-21, 56–61 (1974)
Wang, P.W., Haglund Jr., R.F., Kinser, D.L., Mendenhall, M.H., Tolk, N.H., Weeks, R.A.: Luminescence induced by low energy electron desorption in suprasil and spectrosil glasses. J. Non-Cyst. Solids 102, 288–294 (1988)
Itoh, C., Tanimura, K., Itoh, N.: Optical studies of self-trapped excitons in SiO2. J. Phys. C.: Solid State Phys. 21, 4693–4702 (1988)
Guzzi, M., Lucchini, G., Martini, M., Pio, F., Vedda, A., Grilli, E.: Thermally stimulated luminescence above room temperature of amorphous SiO2. Solid State Commun. 75, 75–79 (1990)
Chakrabarti, K., Mathur, V.K.: Optically and thermally stimulated luminescence in MgO. Solid State Commun. 77, 481–483 (1991)
Kawaguchi, Y.: Luminescence spectra at bending fracture of single crystal MgO. Solid State Commun. 117, 17–20 (2001)
Kawaguchi, Y.: Time-resolved fractoluminescence spectra of silica in a vacuum and nitrogen atmosphere. Phys. Rev. 52, 9224–9228 (1995)
Zinc, J.Y., Beese, W., Schneider, J.W.: Triboluminescence of silica core optical fibers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 40, 110–112 (1982)
Kawaguchi, Y.: Fractoluminescence spectra in crystalline quartz. J. Appl. Phys. 37, 1892–1896 (1998)
Chapman, G.N., Walton, A.J.: Triboluminescence of glasses and quartz. J. Appl. Phys. 54, 5961–5965 (1983)
Walters, G.K., Estle, T.L.: Paramagnetic resonance of defects introduced near the surface of solids by mechanical damage. J. Appl. Phys. 32, 1854–1859 (1961)
Kasemo, B., Toernqvist, E., Wallden, L.: Metal–gas interactions studied by surface chemiluminescnce. Mater. Sci. Eng. 42, 23–29 (1980)
Sweeting, L.M.: Triboluminescence with and without air. Chem. Mater. 13, 854–870 (2001)
Nakayama, K., Tanaka, M.: Simulation analysis of triboplasma generation using the particle-in-cell Monte Carlo collision (PIC/MCC) method. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 45, 495203 (2012)
Nakayama, K., Leiva, J.A., Enomoto, Y.: Chemi-emission of electrons from metal surfaces in the cutting process due to metal/gas interactions. Tribol. Int. 28, 507–515 (1995)
Acknowledgments
The author would like to express his thanks for the financial support from the Grant-in-aid for Scientific Research (A)20246035, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakayama, K. Triboplasma Generation and Triboluminescence in the Inside and the Front Outside of the Sliding Contact. Tribol Lett 63, 12 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-016-0700-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-016-0700-0