Abstract
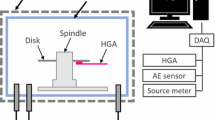
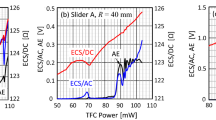
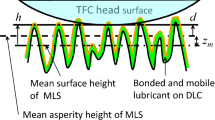
Head wear of thermal flying height control sliders is studied experimentally by (a) comparing the touch-down power before and after a wear test consisting of 300 consecutive touch-down cycles, (b) examining scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images, and (c) investigating atomic force microscopy (AFM) measurements of unworn and worn heads. The effect of bonded lubricant ratio, relative humidity, temperature, and heater power on head wear is investigated. The experiments were carried out on a commercial load/unload tester inside an environmental test chamber. We conclude that (a) head wear increases with increasing bonded lubricant ratio, (b) temperature has a minor effect on head wear for the temperature range of 30–50 °C, (c) head wear increases with decreasing relative humidity, and (d) head wear increases with increasing heater power during the wear test. SEM images show wear of the write shield for changes in touch-down power typically larger than 6 mW. AFM measurements show changes in surface roughness of heads with changes in touch-down power as small as 1.3 mW compared to new, unused head. A wear coefficient on the order of 10−11 to 10−13 was estimated.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wei, B., Zhang, B., Johnson, K.E.: Nitrogen-induced modifications in microstructure and wear durability of ultrathin amorphous-carbon films. J. Appl. Phys. 83(5), 2491–2499 (1998)
Machcha, A.R., McMillan, T.C., Tang, W.T., Talke, F.E.: The tribology of tri-pad sliders with hydrogenated and nitrogenated Disks. IEEE Trans. Magn. 3(5), 3654–3656 (1996)
Scharf, T.W., Ott, R.D., Yang, D., Barnard, J.A.: Structural and tribological characterization of protective amorphous diamond-like carbon and amorphous CN[sub x] overcoats for next generation hard disks. J. Appl. Phys. 85(6), 3142–3154 (1999)
Grill, A.: Tribology of diamondlike carbon and related materials: an updated review. Surf. Coat. Technol. 94–95, 507–513 (1997)
Grischke, M., Bewilogua, K., Trojan, K., Dimigen, H.: Application-oriented modifications of deposition processes for diamond-like-carbon-based coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 74–75, 739–745 (1995)
Lei, R.Z., Gellman, A.J., Jones, P., Lei, R.Z., Gellman, A.J., Jones, P.: Thermal stability of Fomblin Z and Fomblin Zdol thin Films on amorphous hydrogenated carbon. Tribol. Lett. 11(1), 1–5 (2001)
Kasai, P.H., Raman, V.: Lubricant transfer in disk drives. Tribol. Lett. 48(3), 367–374 (2012)
Schultz, B.E.: Thermal Fly-Height Control (TFC) Technology in Hitachi Hard Disk Drives, p. 4. Hitachi Global Storage Technologies, San Jose (2007)
Shimizu, Y., Ono, K., Umehara, N., Xu, J.: Experimental and numerical simulation study on low-surface energy slider with thermal flying-height control function. IEEE Trans. Magn. 45(10), 3620–3623 (2009)
Mate, C.M., Payne, R.N., Baumgart, P., Kuboi, K.: Meniscus adhesion at ultra-low flying slider-disk interfaces. In: World Tribology Congress III, vol 1, (2005)
Li, N., Meng, Y., Bogy, D.B.: Experimental study of the slider-lube/disk contact state and its effect on head-disk interface stability. IEEE Trans. Magn. 48(8), 2385–2391 (2012)
Lee, S., Yeo, C.-D.: Thermo-mechanical contact and micro-wear in head disk interface. In: Proceedings of the ASME/STLE 2011 International Joint Tribology Conference, pp. 9–11. (2014)
Song, W., Ovcharenko, A., Yang, M., Zheng, H., Talke, F.E.: Contact between a thermal flying height control slider and a disk asperity. Microsyst. Technol. 18(9–10), 1549–1557 (2012)
Song, W., Ovcharenko, A., Knigge, B., Yang, M., Talke, F.E.: Effect of contact conditions during thermo-mechanical contact between a thermal flying height control slider and a disk asperity. Tribol. Int. 55, 100–107 (2012)
Zhang, C., Ovcharenko, A., Yang, M., Knudson, N., Talke, F.E.: An investigation of thermal asperity sensors during contact with disk asperities. Microsyst. Technol. 20(8–9), 1529–1534 (2014)
Singh, G.P., Knigge, B.E., Payne, R., Wang, R.-H., Mate, C.M., Arnett, P.C., Davis, C., Nayak, V., Wu, X., Schouterden, K., Baumgart, P.: A novel wear-in-pad approach to minimizing spacing at the head/disk interface. IEEE Trans. Magn. 40(4), 3148–3152 (2004)
Ma, X., Gui, J., Marchon, B., Jhon, M.S., Bauer, C.L., Rauch, G.C.: Lubricant replenishment on carbon coated discs. IEEE Trans. Magn. 35(5), 2454–2456 (1999)
Min, B.G., Choi, J.W., Brown, H.R., Yoon, D.Y.: Spreading characteristics of thin liquid films of PFPE on solid surfaces. Tribol. Lett. 1, 225–232 (1995)
Nakazawa, S., Kawakubo, Y.: Effects of humidity and temperature on head wear on thin-film disk. In: Proceedings of the INTERMAG 2006 Conference, vol. 1(1995), p. 2001. (2006)
Karis, T.E., Tyndall, G.W., Waltman, R.J.: Lubricant bonding effects on thin film disk tribology. Tribol. Trans. 44(2), 249–255 (2001)
Ma, X., Tang, H., Gui, J.: Temperature effect on spreading of perfluoropolyethers on amorphous carbon films. Tribol. Lett. 10(4), 203–209 (2001)
Yanagisawa, M.: Water adsorption on lubricated surfaces for magnetic storage devices. Tribol. Trans. 44(2), 197–202 (2001)
Shukla, N., Svedberg, E., van de Verdonk, R.J.M., Ma, X., Gui, J., Gellman, A.J.: Water adsorption on lubricated a-CHx in humid environments. Tribol. Lett. 15(1), 9–14 (2003)
Tao, Z., Bhushan, B.: Bonding, degradation, and environmental effects on novel perfluoropolyether lubricants. Wear 259(7–12), 1352–1361 (2005)
Zhao, Z., Bhushan, B.: Humidity effect on friction/stiction and durability of head-disk interface with polar perfluoropolyether lubricant. J. Appl. Phys. 81(8), 5387 (1997)
Wang, Y., Wei, X., Tsui, K., Chow, T.W.S.: Tribological degradation of head-disk interface in hard disk drives under accelerated wear condition. IEEE Trans. Magn. 50(3), 27–33 (2014)
Kobayashi, N., Tani, H., Shimizu, T., Koganezawa, S., Tagawa, N.: Slider wear on disks lubricated by ultra-thin perfluoropolyether lubricants with different molecular weights. Tribol. Lett. 53(1), 43–49 (2013)
Liu, B., Zhang, M., Yu, S., Gonzaga, L., Hor, Y.S., Xu, J.: Femto slider: fabrication and evaluation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 39(2), 909–914 (2003)
Aoki, Y., Takahashi, K., Li, J., Xu, J., Ooeda, Y.: Humidity effect on head-disk clearance. Microsyst. Technol. 17(5–7), 1051–1056 (2011)
Stirniman, M.: Environmental effects on the interaction of perfluoropolyethers with thin-film carbon surfaces. Tribol. Lett. 58(1), 14 (2015)
Karis, T.E., Tawakkul, M.A.: Water adsorption and friction on thin film magnetic recording disks. Tribol. Trans. 46(3), 469–478 (2003)
Archard, J.F., Hirst, W.: The wear of metals under unlubricated conditions. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 236(1206), 397–410 (1956)
Lu, R., Zhang, H., Mitsuya, Y., Fukuzawa, K., Itoh, S.: Influence of surface roughness and coating on the friction properties of nanometer-thick liquid lubricant films. Wear 319(1–2), 56–61 (2014)
Zheng, J., Bogy, D.B.: Investigation of flying-height stability of thermal fly-height control sliders in lubricant or solid contact with roughness. Tribol. Lett. 38(3), 283–289 (2010)
Zheng, J., Bogy, D.B., Zhang, S., Yan, W.: Effects of altitude on thermal flying-height control actuation. Tribol. Lett. 40(3), 295–299 (2010)
Machcha, A.R., Azarian, M.H., Talke, F.E.: An investigation of nano-wear during contact recording. Wear 197, 211–220 (1996)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Susan Lee, J.P. Peng, Jian Xu, and Kaynam Chung from Western Digital for their help and support during the experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matthes, L.M., Brunner, R., Knigge, B. et al. Head Wear of Thermal Flying Height Control Sliders as a Function of Bonded Lubricant Ratio, Temperature, and Relative Humidity. Tribol Lett 60, 39 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-015-0614-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-015-0614-2