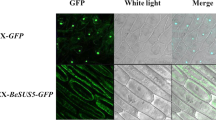
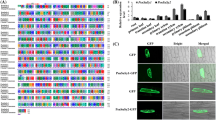
Abstract
Improvement of wood quality is an important focus of forest genetics and breeding research. Sucrose synthase (SS) catalyzes the reaction of sucrose and uridine diphosphate into uridine diphosphate glucose and fructose. It is a key enzyme involved in cell wall formation during secondary growth by providing the UDP-Glucose substrate for cellulose biosynthesis. In this study, we isolated the single-copy gene PtSS3 from the SS gene family of Populus tomentosa and analyzed its structure. To identify its function in secondary growth, we generated 19 transgenic lines of P. tomentosa using PtSS3 overexpression (OE) and artificial microRNA (amiRNA) constructs. We also performed comprehensive analyses of the transgenic P. tomentosa plants, including phenotypic analyses, quantitative real-time PCR, enzyme activity assays and sugar metabolism. We found significantly higher PtSS3 enzyme activity, fructose, and glucose levels and significantly lower sucrose levels in the stems and leaves of OE-PtSS3 plants. The opposite trend was observed in the amiRNA-PtSS3 lines. Gene expression analyses showed that PtSS3 transcript levels in stems and leaves were up-regulated in the OE-PtSS3 lines and down-regulated in the amiRNA-PtSS3 lines, and the OE-PtSS3 plants grew taller than the wild-type and amiRNA-PtSS3 plants. These findings indicate that PtSS3 plays an important role in sucrose metabolism and growth of trees.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah M, Cao Y, Cheng X, Meng D, Chen Y, Shakoor A, Gao J, Cai Y (2018) The Sucrose synthase gene family in chinese pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd): structure, expression, and evolution. Molecules 23:1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051144
An XM, Wang DM, Wang ZL, Li B, Bo WH, Cao GL, Zhang ZY (2011) : expression of PtLFY in P. tomentosa floral buds and PtLFY-IR-mediated gene silencing in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum). Plant Cell Rep 30:89–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-010-0947-0Populus tomentosa
An X, Chen Z, Wang J, Ye M, Ji L, Wang J, Liao W, Ma H (2014) Identification and characterization of the Populus sucrose synthase gene family. Gene 539:58–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2014.01.062
Baier MC, Barsch A, Kuster H, Hohnjec N (2007) Antisense repression of the medicago truncatula nodule-enhanced sucrose synthase leads to a handicapped nitrogen fixation mirrored by specific alterations in the symbiotic transcriptome and metabolome. Plant Physiol 145:1600–1618. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.106955
Baud S, Vaultier MN, Rochat C (2004) Structure and expression profile of the sucrose synthase multigene family in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 55:397–409
Chang S, Puryear J, Cairney J (1993) A simple and efficient method for isolating RNA from pine trees. Plant Mol Biol Rep 11:113–116
Chen Z, Rao P, Yang X, Su X, Zhao T, Gao K, Yang X, An X (2018) A global view of transcriptome dynamics during male floral bud development in Populus tomentosa. Sci Rep 8:722. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-18084-5
Chourey PS, Taliercio EW, Carlson SJ, Ruan Y-L (1998) Genetic evidence that the two isozymes of sucrose synthase present in developing maize endosperm are critical, one for cell wall integrity and the other for starch biosynthesis. Mol Gen Genet 259:88–96
Coleman HD, Ellis DD, Gilbert M, Mansfield SD (2006) Up-regulation of sucrose synthase and UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase impacts plant growth and metabolism. Plant Biotechnol J 4:87–101. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7652.2005.00160.x
Duncan KA, Hardin SC, Huber SC (2006) The three maize sucrose synthase isoforms differ in distribution, localization, and phosphorylation. Plant Cell Physiol 47:959–971. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcj068
Fan J, Wang H, Li X, Sui X, Zhang Z (2018) Down-regulating cucumber sucrose synthase 4 (CsSUS4) suppresses the growth and development of flowers and fruits. Plant Cell Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcy239
Gerber L, Zhang B, Roach M, Rende U, Gorzsas A, Kumar M, Burgert I, Niittyla T, Sundberg B (2014) Deficient sucrose synthase activity in developing wood does not specifically affect cellulose biosynthesis, but causes an overall decrease in cell wall polymers. New Phytol 203:1220–1230. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12888
Goren S, Lugassi N, Stein O, Yeselson Y, Schaffer AA, David-Schwartz R, Granot D (2017) Suppression of sucrose synthase affects auxin signaling and leaf morphology in tomato. PLoS ONE 12:e0182334
Hirose T, Scofield GN, Terao T (2008) An expression analysis profile for the entire sucrose synthase gene family in rice. Plant Sci 174:534–543
Khraiwesh B, Ossowski S, Weigel D, Reski R, Frank W (2008) Specific gene silencing by artificial MicroRNAs in Physcomitrella patens: an alternative to targeted gene knockouts. Plant Physiol 148:684–693. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.128025
Kord B, Samdaliri M, Heritability T (2013) © IDOSI publications, 2011 the impact of site index on wood density and fiber biometry of populus deltoids clones. World Appl Sci J 34:293
Lorenz G, Bo Z, Melissa R, Umut R, András G, Manoj K, Ingo B, Totte N, Bjorn S (2014) Deficient sucrose synthase activity in developing wood does not specifically affect cellulose biosynthesis, but causes an overall decrease in cell wall polymers. New Phytol 203:1220–1230
Ma H, Dong Y, Chen Z, Liao W, Lei B, Gao K, Li S, An X (2015) Variation in the growth traits and wood properties of hybrid white poplar clones. Forests 6:1107–1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/f6041107
Morell M, Copeland L (1985) Sucrose synthase of soybean nodules. Plant Physiol 78:149–154
Regmi KC, Zhang S, Gaxiola RA (2015) Apoplasmic loading in the rice phloem supported by the presence of sucrose synthase and plasma membrane-localized proton pyrophosphatase. Ann Bot 117:mcv174
Ruan YL (2003) Suppression of sucrose synthase gene expression represses cotton fiber cell initiation, elongation, and seed development. Plant Cell Online 15:952–964. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.010108
Ruan Y-L (2007) Rapid cell expansion and cellulose synthesis regulated by plasmodesmata and sugar: insights from the single-celled cotton fibre. Funct Plant Biol 34:1. https://doi.org/10.1071/fp06234
Salnikov VV, Grimson MJ, Seagull RW, Haigler CH (2003) Localization of sucrose synthase and callose in freeze-substituted secondary-wall-stage cotton fibers. Protoplasma 221:175
Satoshi F, Takahisa H, Koichi M (2010) Sucrose synthase is an integral component of the cellulose synthesis machinery. Plant Cell Physiol 51:294
Schwab R, Ossowski S, Riester M, Warthmann N, Weigel D (2006) Highly specific gene silencing by artificial microRNAs in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18:1121–1133. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.105.039834
Silva JM, Li MZ, Chang K, Ge W, Golding MC, Rickles RJ, Siolas D, Hu G, Paddison PJ, Schlabach MR, Sheth N, Bradshaw J, Burchard J, Kulkarni A, Cavet G, Sachidanandam R, McCombie WR, Cleary MA, Elledge SJ, Hannon GJ (2005) Second-generation shRNA libraries covering the mouse and human genomes. Nat Genet 37:1281–1288. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1650
Smith AM, Kruger NJ, Lunn JE (2012) Source of sugar nucleotides for starch and cellulose synthesis. Proceedings Nat Acad Sci USA 109:776 (author reply E777)
Stein O, Granot D (2019) An overview of sucrose synthases in plants. Front Plant Sci 10:95. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00095
Subbaiah CC, Sachs MM (2001) Altered patterns of sucrose synthase phosphorylation and localization precede callose induction and root tip death in anoxic maize seedlings. Plant Physiol 125:585–594
Taylor NG (2008) Cellulose biosynthesis and deposition in higher plants. New Phytol 178:239–252. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02385.x
Warthmann N, Chen H, Ossowski S, Weigel D, Herve P (2008) Highly specific gene silencing by artificial miRNAs in rice. PLoS ONE 3:e1829. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001829
Wei Z, Qu Z, Zhang L, Zhao S, Bi Z, Ji X, Wang X, Wei H (2015) Overexpression of poplar xylem sucrose synthase in tobacco leads to a thickened cell wall and increased height. PLoS ONE 10:e0120669. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0120669
Xu F, Joshi CP (2010) Overexpression of aspen sucrose synthase gene promotes growth and development of transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Adv Biosci Biotechnol 01:426–438. https://doi.org/10.4236/abb.2010.15056
Xu SM, Brill E, Llewellyn DJ, Furbank RT, Ruan YL (2012) Overexpression of a potato sucrose synthase gene in cotton accelerates leaf expansion, reduces seed abortion, and enhances fiber production. Mol Plant 5:430–441. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssr090
Zhang B, Liu JY (2017) Serine phosphorylation of the cotton cytosolic pyruvate kinase GhPK6 decreases its stability and activity. FEBS Open Bio 7:358–366. https://doi.org/10.1002/2211-5463.12179
Zhang Q, Zhang ZY, Lin SZ, Zheng HQ, Lin YZ, An XM, Li Y, Li HX (2008) Characterization of resistance gene analogs with a nucleotide binding site isolated from a triploid white poplar. Plant Biol 10:310–322. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1438-8677.2008.00029.x
Zhang L, Gao C, Mentink-Vigier F, Tang L, Zhang D, Wang S, Cao S, Xu Z, Liu X, Wang T, Zhou Y, Zhang B (2019) Arabinosyl deacetylase modulates the arabinoxylan acetylation profile and secondary wall formation. Plant Cell. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00894
Zheng H, Lin S, Zhang Q, Lei Y, Zhang Z (2009) Functional analysis of 5' untranslated region of a TIR-NBS-encoding gene from triploid white poplar. Mol Genet Genom MGG 282:381–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-009-0471-5
Zhu X, Wang M, Li X, Jiu S, Wang C, Fang J (2017) Genome-wide analysis of the sucrose synthase gene family in grape (Vitis vinifera): structure, evolution, and expression profiles. Genes 8:111
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Program on Transgenic Research (2018ZX08020002-002-004), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31570661), and the medium-long-term project of young teachers (2015ZCQ-SW-01). We gratefully acknowledge the infrastructure support of the Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Tree Breeding by Molecular Design, the National Engineering Laboratory for Tree Breeding, College of Biological Sciences and Biotechnology, Beijing Forestry University. We also thank the families who participated by giving research assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table S1
Primer sequences used to amplify the PtSS3 gene (DOCX 14 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Gao, K., Lei, B. et al. Altered sucrose metabolism and plant growth in transgenic Populus tomentosa with altered sucrose synthase PtSS3. Transgenic Res 29, 125–134 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-019-00184-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-019-00184-9