Abstract
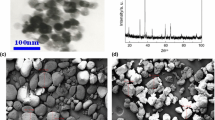
Composite particles of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and titanium dioxide (TiO2) were prepared by a sol-flux method. Characterization of TiO2/CNTs nanocomposite was performed by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscope (TEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The results show that TiO2 nanocrystals (mixed anatase and rutile) are successfully deposited on the surface of CNTs, forming a granular coating with a thickness of about 2 nm. It is possible that the growth of TiO2 on the surface of CNTs is implemented by anchoring TiO2 through hydroxyl and carboxylic functional groups. In the presence of TiO2/CNTs nanocomposite, the peak temperature of the high-temperature decomposition of ammonium perchlorate (AP) decreased by 52.5 °C, better than other samples including the one of simply mixed TiO2 and CNTs. The catalytic influence is evident even with 1% catalyst concentration. The thermal kinetic constant for the catalytic decomposition of AP is computed using model free (isoconversional) Flynn–Wall–Ozawa approach. It shows that although the two exothermic decomposition peaks merged into one, the low-temperature decomposition stage still exists, and accounts for about thirty percent of the whole reaction.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chaturvedi S, Dave PN (2013) A review on the use of nanometals as catalysts for the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. J Saudi Chem Soc 17(2):135–149
Boldyrev V (2006) Thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. Thermochim Acta 443(1):1–36
Kishore K, Sunitha M (1978) Mechanism of catalytic activity of transition metal oxides on solid propellant burning rate. Combust Flame 33:311–314
Chatragadda K, Vargeese AA (2017) Synergistically catalysed pyrolysis of hydroxyl terminated polybutadiene binder in composite propellants and burn rate enhancement by free-standing CuO nanoparticles. Combust Flame 182:28–35
Fujimura K, Miyake A (2010) The effect of specific surface area of TiO2 on the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. J Therm Anal Calorim 99(1):27–31
Vargeese AA, Muralidharan K (2013) Effect of anatase–brookite mixed phase titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the high temperature decomposition kinetics of ammonium perchlorate. Mater Chem Phys 139(2–3):537–542
Reid DL, Russo AE, Carro RV, Stephens MA, LePage AR, Spalding TC, Petersen EL, Seal S (2007) Nanoscale additives tailor energetic materials. Nano Lett 7(7):2157–2161
Iijima S (1991) Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 354(6348):56
Ren Y, Wu X, Li M (2016) Highly stable SiOx/multiwall carbon nanotube/N-doped carbon composite as anodes for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 206:328–336
Liang X-L, Dong X, Lin G-D, Zhang H-B (2009) Carbon nanotube-supported Pd–ZnO catalyst for hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol. Appl Catal B 88(3–4):315–322
Li W, Wang X, Chen Z, Waje M, Yan Y (2006) Pt− Ru supported on double-walled carbon nanotubes as high-performance anode catalysts for direct methanol fuel cells. J Phys Chem B 110(31):15353–15358
Qu J, Cloud JE, Yang Y, Ding J, Yuan N (2014) Synthesis of nanoparticles-deposited double-walled TiO2-B nanotubes with enhanced performance for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(24):22199–22208
Zhou W, Pan K, Qu Y, Sun F, Tian C, Ren Z, Tian G, Fu H (2010) Photodegradation of organic contamination in wastewaters by bonding TiO2/single-walled carbon nanotube composites with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Chemosphere 81(5):555–561
Yingliang HLWHL, Zibei JZS (2010) TiO2/Carbon nanotube composites and their synergistic effects on enhancing the photocatalysis efficiency. Progress Chem 5:012
Yoldas BE (1986) Hydrolysis of titanium alkoxide and effects of hydrolytic polycondensation parameters. J Mater Sci 21(3):1087–1092
Zhou O, Fleming R, Murphy D, Chen C, Haddon R, Ramirez A, Glarum S (1994) Defects in carbon nanostructures. Science 263(5154):1744–1747
Datsyuk V, Kalyva M, Papagelis K, Parthenios J, Tasis D, Siokou A, Kallitsis I, Galiotis C (2008) Chemical oxidation of multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 46(6):833–840
Slink WE, DeGroot PB (1981) Vanadium-titanium oxide catalysts for oxidation of butene to acetic acid. J Catal 68(2):423–432
Song Z, Hrbek J, Osgood R (2005) Formation of TiO2 nanoparticles by reactive-layer-assisted deposition and characterization by XPS and STM. Nano Lett 5(7):1327–1332
Vyazovkin S, Wight CA (1999) Kinetics of thermal decomposition of cubic ammonium perchlorate. Chem Mater 11(11):3386–3393
Acknowledgements
This work has received support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (50842054).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, SH., Liu, JF., Kong, XT. et al. Preparation of TiO2/CNTs nanocomposite and its catalytic performance on the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. Transit Met Chem 45, 545–551 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11243-020-00406-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11243-020-00406-8