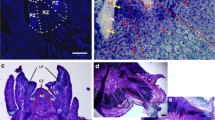
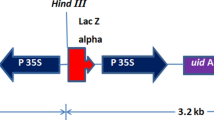
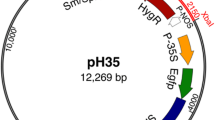
Abstract
Weed management is a critical issue in the production of narrow-leaf lupin (NLL) (Lupinus angustifolius L.). The gene pool has limited herbicide tolerance, early vigour or short season productivity, hampering conventional breeding approaches. Previous transformation of NLL used the bar gene encoding tolerance to the herbicide glufosinate, for selection. However that methodology achieved <1 % success at T1, with one confounding factor being chimerism of the T0 shoots. Therefore glyphosate tolerance was examined as a potential alternative selectable marker with possible commercial application. Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer using four vectors with two promoter and two transit peptide (tp) sequences in factorial combination was followed by three methods of selection post-transformation, following failure to achieve transformation by the published glufosinate selection method. An overall heritable transformation efficiency of 0.14 % was achieved from a total of 36,607 inoculated explants. Transformation with constructs containing the ubiquitin 3 promoter had a higher success rate (0.20 %) than with the CaMV promoter (0.07 %) however no difference between the two tp sequences was observed. The highest rate of transformation (0.45 %) was obtained by glyphosate selection during early phase of growth on regeneration media. This regeneration selection method more frequently produced highly tolerant events, with more heritable expression stability in T2 generation than alternative methods. Single insertion, single copy events were obtained. However these were recovered with significantly lower frequency than previously observed with the glufosinate selection method. Nonetheless such events have potential to contribute weed management options for broad-acre NLL production.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arteca RN (1995) Plant growth substances: principles and applications. Chapman and Hall, New York
Atkins CA, Smith PMC, Gupta S, Jones MGK, Caligari PDS (1998) Genetics, cytology and biotechnology. In: Gladstones JS, Atkins C, Hamblin J (eds) Lupin as crop plants—biology, production and utilization. CAB International, New York, pp 67–92
Atkins C, Emery RJN, Smith PMC (2011) Consequences of transforming narrow leafed lupin (Lupinus angustifolius [L.]) with an ipt gene under control of a flower-specific promoter. Transgen Res 20:1321–1332
Bowram D, Hashem A (2008) The role of weed management in sustaining systems for lupin production. In: Palta JA, Berger JB (eds) Lupins for health and wealth, Proceedings of 12th international lupin conference, 14–18 Sept, Fremantle, WA, pp 11–14
Brown T (1999) Analysis of DNA sequences by blotting and hybridization. Curr Protoc Mol Biol 68:2.9.1–2.9.20
Goggin DE, Lipscombe R, Fedorova E, Millar AH, Mann A, Atkins CA, Smith PMC (2003) Dual intracellular localization and targeting of aminoimidazole ribonucleotide synthetase in cowpea. Plant Physiol 131:1033–1041
Hammer PE (2010) Identification of a new class of EPSP synthase. Patents WO 2006/1105862 A2; US 2006/0253921 A1; AU 2006/235263 A1 and US 7700842
James C (2014) ISAAA Report on Global Status of Biotech/GM Crops. ISAAA Brief 49-2014, International Service for the Acquisition of Agri-biotech Applications (ISAAA), USA. http://www.isaaa.org/resources/publications/briefs/46/executivesummary/default.asp
Lee H, Park S-Y, Zhang ZJ (2013) An overview of genetic transformation of soybean. In: Board JE (ed) A comprehensive survey of international soybean research—genetics, physiology, agronomy and nitrogen relationships. INTECH Open Science, Rijeka, pp 489–506. doi:10.5772/51076
Mobin M, Wu C-H, Tewari RK, Paek K-Y (2015) Studies on the glyphosate-induced amino acid starvation and addition of precursors on caffeic acid accumulation and profiles in adventitious roots of Echinacea purpurea (L.) Moench. Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Cult 120:291–301
Molvig L, Tabe LM, Eggum BO, Moore AE, Craig S, Spencer D, Higgins TJV (1997) Enhanced methionine levels and increased nutritive value of seeds of transgenic lupins (Lupinus angustifolius L.) expressing a sunflower seed albumin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:8393–8398
Pigeaire A, Aberneth D, Smith PMC, Simpson K, Fletcher N, Lu C-Y, Atkins CA, Cornish E (1997) Transformation of a grain legume crop (Lupinus angustifolius L.) via Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated gene transfer to shoot apices. Plant Mol Breed 3:341–349
Reed KC, Mann DA (1985) Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucl Acid Res 13:7207–7221
Schönbrunn E, Eschenburg S, Shuttleworth WA, Schloss JV, Amrhein N, Evans JN, Kabsch W (2001) Interaction of the herbicide glyphosate with its target enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate 3-phosphate synthase in atomic detail. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:1376–1380
Sedcole RT (1977) Number of plants necessary to recover a trait. Crop Sci 17:667–668
Tabe LM, Wardley-Richardson T, Ceriotti A, Aryan A, McNabb W, Moore A, Higgins TJ (1995) A biotechnological approach to improving the nutritive value of alfalfa. J Anim Sci 73:2752–2759
Tabe L, Wirtz M, Molvig L, Droux M, Hell R (2010) Overexpression of serine acetlytransferase produced large increases in O-acetylserine and free cysteine in developing seeds of a grain legume. J Exp Bot 61:721–733
Tiwari S, Tuli R (2012) Optimization of factors for efficient recovery of transgenic peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Cult 109:111–121
Wijayanto T, Barker SJ, Wylie SJ, Gilchrist DG, Cowling WA (2009) Significant reduction of fungal disease symptoms in transgenic lupin (Lupinus angustifolius) expressing the anti-apoptotic baculovirus gene P35. Plant Biotechnol J 7:778–790
Wild A, Wendler C (1991) Effect of glufosinate (phosphinothricin) on amino acid content, photorespiration, and photosynthesis. Pestic Sci 30:422–424
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the Grain Research and Development Corporation (GRDC) through research grant UWA00129. The authors also thank Dr. Linda Tabe (CSIRO) for the vector pTAB 10; Professor Craig Atkins and Dr. Penny Smith for use of the transit peptide sequences; Dr. Jorge Mayer; Professors Craig Atkins and Kadambot Siddique for useful discussion and contributions to this study.
Author contribution
Project design SJB and WE; construct development KM, SA and MFH; transformation, shoot culture YK, NK, PK, LH and COL; molecular testing MFH, SA, KM, COL, DD, LH, and PK; plant growth and herbicide bioassay JJ, YK, LH and PS; communication and team integration TF and LH; data analysis SJB, PS, WE, LH, DD, YK, PK; plant images YK; manuscript preparation SJB, WE, MFH, LH and PS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barker, S.J., Si, P., Hodgson, L. et al. Regeneration selection improves transformation efficiency in narrow-leaf lupin. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 126, 219–228 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-016-0992-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-016-0992-7