Abstract
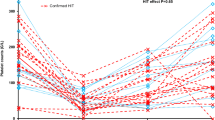
A definitive diagnosis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is difficult to make, especially in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. In this retrospective cohort study, we assessed the platelet count trends and the response to fondaparinux in a population of patients of suspected HIT after pulmonary endarterectomy (PEA). Patients enrolled in this study were over the age of 18 years, and survived longer than 7 days after PEA between January 1, 2011 and December 31, 2015. HIT likelihood was assessed by the 4 T’s score and interpreted by our institutional algorithm. 54 patients were operated, and 49 patients met the inclusion criteria. Six patients met the criteria for suspected HIT and were treated with fondaparinux until the platelet recovered. No significant difference was observed of clinical characteristics between intermediate to high HIT likelihood patients (HIT SUSPECTED) and low HIT likelihood patients (NO HIT SUSPECTED). HIT SUSPECTED patients reached platelet count lowest later (about 5.5 days after PEA), while NO HIT SUSPECTED patients is about 4.0 days after PEA. Percentage of platelet counts decrease (> 50%) was larger than NO HIT SUSPECTED patients (< 50%). There was no difference in mortality or residual pulmonary hypertension between HIT SUSPECTED and NO HIT SUSPECTED patients. Two HIT SUSPECTED patients who used heparin after PEA died, the other four survived by replacing heparin or low molecular weight heparin with fondaparinux. Suspected HIT patients should be surveilled carefully. Platelet counts trends may have some hints in the prevention of HIT. Fondaparinux may be effective for patients with suspected HIT.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Linkins LA, Dans AL, Moores LK, Bona R, Davidson BL, Schulman S, Crowther M (2012) Treatment and prevention of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 141(2 Suppl):e495S–530S. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.11-2303
Arepally GM (2017) Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood 129(21):2864–2872. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-11-709873
Warkentin TE, Davidson BL, Buller HR, Gallus A, Gent M, Lensing AWA, Piovella F, Prins MH, Segers AEM, Kelton JG (2011) Prevalence and risk of preexisting heparin-induced thrombocytopenia antibodies in patients with acute VTE. Chest 140(2):366–373. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.10-1599
Sokolovic M, Pratt AK, Vukicevic V, Sarumi M, Johnson LS, Shah NS (2016) Platelet Count Trends and Prevalence of Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia in a Cohort of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenator Patients. Crit Care Med. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000001869
Selleng S, Selleng K (2016) Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in cardiac surgery and critically ill patients. Thromb Haemost 116(5):843–851. https://doi.org/10.1160/TH16-03-0230
Farm M, Bakchoul T, Frisk T, Althaus K, Odenrick A, Norberg EM, Berndtsson M, Antovic JP (2017) Evaluation of a diagnostic algorithm for Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia. Thromb Res 152:77–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2017.02.015
Eckman PM, John R (2012) Bleeding and thrombosis in patients with continuous-flow ventricular assist devices. Circulation 125(24):3038–3047. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.040246
Galie N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, Gibbs S, Lang I, Torbicki A, Simonneau G, Peacock A, Vonk Noordegraaf A, Beghetti M, Ghofrani A, Gomez Sanchez MA, Hansmann G, Klepetko W, Lancellotti P, Matucci M, McDonagh T, Pierard LA, Trindade PT, Zompatori M, Hoeper M (2015) 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). The European respiratory journal 46(4):903–975. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.01032-2015
Kim NH, Delcroix M, Jenkins DP, Channick R, Dartevelle P, Jansa P, Lang I, Madani MM, Ogino H, Pengo V, Mayer E (2013) Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 62(25 Suppl):D92–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2013.10.024
Colorio CC, Martinuzzo ME, Forastiero RR, Pombo G, Adamczuk Y, Carreras LO (2001) Thrombophilic factors in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Blood Coagulation & Fibrinolysis : An International Journal in Haemostasis and Thrombosis 12(6):427–432
Lankeit M, Krieg V, Hobohm L, Kolmel S, Liebetrau C, Konstantinides S, Hamm CW, Mayer E, Wiedenroth CB, Guth S (2017) Pulmonary endarterectomy in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. J Heart and Lung Transplantation. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2017.06.011
Jenkins D (2015) Pulmonary endarterectomy: the potentially curative treatment for patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. European Respiratory Review 24(136):263–271. https://doi.org/10.1183/16000617.00000815
Arbustini E, Morbini P, D’Armini AM, Repetto A, Minzioni G, Piovella F, Vigano M, Tavazzi L (2002) Plaque composition in plexogenic and thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: the critical role of thrombotic material in pultaceous core formation. Heart 88(2):177–182
Corsico AG, D'Armini AM, Cerveri I, Klersy C, Ansaldo E, Niniano R, Gatto E, Monterosso C, Morsolini M, Nicolardi S, Tramontin C, Pozzi E, Vigano M (2008) Long-term outcome after pulmonary endarterectomy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 178(4):419–424. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200801-101OC
Delcroix M, Lang I, Pepke-Zaba J, Jansa P, D'Armini AM, Snijder R, Bresser P, Torbicki A, Mellemkjaer S, Lewczuk J, Simkova I, Barbera JA, de Perrot M, Hoeper MM, Gaine S, Speich R, Gomez-Sanchez MA, Kovacs G, Jais X, Ambroz D, Treacy C, Morsolini M, Jenkins D, Lindner J, Dartevelle P, Mayer E, Simonneau G (2016) Long-Term Outcome of Patients With Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: Results From an International Prospective Registry. Circulation 133(9):859–871. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.016522
Pepke-Zaba J, Delcroix M, Lang I, Mayer E, Jansa P, Ambroz D, Treacy C, D'Armini AM, Morsolini M, Snijder R, Bresser P, Torbicki A, Kristensen B, Lewczuk J, Simkova I, Barbera JA, de Perrot M, Hoeper MM, Gaine S, Speich R, Gomez-Sanchez MA, Kovacs G, Hamid AM, Jais X, Simonneau G (2011) Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH): results from an international prospective registry. Circulation 124(18):1973–1981. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.015008
Li JF, Lin Y, Yang YH, Gan HL, Liang Y, Liu J, Yang SQ, Zhang WJ, Cui N, Zhao L, Zhai ZG, Wang J, Wang C (2013) Fibrinogen Aalpha Thr312Ala polymorphism specifically contributes to chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension by increasing fibrin resistance. PLoS ONE 8(7):e69635. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0069635
Duggal N, Haft J, Engoren M, Peters W (2016) Pulmonary Endarterectomy Under Hypothermic Circulatory Arrest in a Patient With Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 30(3):741–745. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jvca.2015.08.005
Schenk S, El-Banayosy A, Prohaska W, Arusoglu L, Morshuis M, Koester-Eiserfunke W, Kizner L, Murray E, Eichler P, Koerfer R, Greinacher A (2006) Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in patients receiving mechanical circulatory support. The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery 131(6):1373–1381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2006.01.048
Schroder JN, Daneshmand MA, Villamizar NR, Petersen RP, Blue LJ, Welsby IJ, Lodge AJ, Ortel TL, Rogers JG, Milano CA (2007) Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in left ventricular assist device bridge to transplant patients. The Annals of thoracic surgery 84(3): 841–845; Doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2007.03.049
Warkentin TE, Arnold DM, Kelton JG, Sheppard JI, Smith JW, Nazy I (2018) Platelet-Activating Antibodies Are Detectable at the Earliest Onset of Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia, With Implications for the Operating Characteristics of the Serotonin-Release Assay. Chest 153(6):1396–1404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2018.01.001
Greinacher A, Alban S, Omer-Adam MA, Weitschies W, Warkentin TE (2008) Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: a stoichiometry-based model to explain the differing immunogenicities of unfractionated heparin, low-molecular-weight heparin, and fondaparinux in different clinical settings. Thromb Res 122(2):211–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2007.11.007
Funding
No part of the research presented has been funded by tobacco industry sources or other organization. This work was partially supported by the fund of National Natural Science Foundation of China (31670928). The funder had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Ethical approval
This study was conducted in accordance with the amended Declaration of Helsinki. The Ethics Committee of Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital of Capital Medical University approved the protocol, and written informed consents were obtained from the patients.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, JF., Wu, LJ., Wen, GY. et al. Platelet count trends and response to fondaparinux in a cohort of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia suspected patients after pulmonary endarterectomy. J Thromb Thrombolysis 51, 703–710 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-020-02260-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-020-02260-y