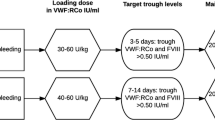
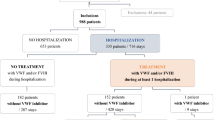
Abstract
Von Willebrand Disease (VWD) is characterized by a qualitative or quantitative defect in von Willebrand factor that results in prolonged bleeding due to the inability to form a stable platelet plug. VWD is the most common inherited bleeding disorder. The mainstay of treatment of VWD includes desmopressin; with plasma-derived von Willebrand Factor concentrates reserved for patients with severe VWD or those with desmopressin intolerability. Although efficacious, plasma-derived factor concentrates can have risks associated with them including minimal risk of pathogenic transmission, potential to contain extraneous plasma proteins and cause severe allergic reactions, and a supply limited by plasma donor availability. Vonicog alfa is a recombinant von Willebrand Factor product. Two phase III trials evaluated the safety and efficacy of vonicog alfa in preventing perioperative bleeding and treating acute bleeding in patients with VWD. Beyond the clinical trials, there has been little real-world experience published regarding experiences with this medication. This article comprehensively reviews the efficacy, safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of vonicog alfa. These points will be discussed using institutional experiential data from the University of Virginia (UVA) Health System in relation to the clinical studies. The goal of this review article is to offer insights to clinical directions, discuss operational challenges, and offer guidance for future studies and formulary decisions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruggeri ZM, Zimmerman TS (1987) Von Willebrand factor and von Willebrand Disease. Blood 70(4):895–904
Rodeghiero F, Castaman G, Dini E (1987) Epidemiological investigation of the prevalence of von Willebrand’s disease. Blood 69(2):454–459
James PD, Goodeve AC (2011) Von Willebrand disease. Genet Med 13(5):365
Singal M, Kouides PA (2016) Recombinant von Willebrand factor: a first-of-its-kind product for von Willebrand disease. Drugs Today (Barc) 52(12):653–664
Mannucci PM, Kepmton C, Millar C, Romond E, Shapiro A, Birschmann I et al (2013) Pharmacokinetics and safety of a novel recombinant human von Willebrand factor manufactured with a plasma-free method: a prospective clinical trial. Blood 122(5):648–657
Peyvandi F, Mamaev A, Wang JD, Stasyshyn O, Timofeeva M, Curry N et al (2019) Phase 3 study of recombinant von Willebrand factor in patients with severe von Willebrand disease who are undergoing elective surgery. J Thromb Haemost 17(1):52–62
Gill JC, Castaman G, Windyga J, Kouides P, Ragni M, Leebeek FW et al (2015) Hemostatic efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics of a recombinant von Willebrand factor in severe von Willebrand disease. Blood 126(17):2038–2046
Weyand AC, Jesudas R, Pipe SW (2018) Advantage of recombinant von Willebrand factor for peri-operative management in paediatric acquired von Willebrand syndrome. Haemophilia 24(3):e120–e121
Rajpurkar M, Frey MJ, Sabo C, Hollon W (2019) Recombinant Von Willebrand factor concentrate in 2A Von Willebrand disease: comparison to plasma-derived Von Willebrand factor concentrate therapy. Blood Coagul Fibrinol 30(4):168–170
Koster T, Blann AD, Briët E, Vandenbroucke JP, Rosendaal FR (1995) Role of clotting factor VIII in effect of von Willebrand factor on occurrence of deep-vein thrombosis. Lancet 345(8943):152–155
Coppola A, Franchini M, Makris M, Santagostino E, Di Minno G, Mannucci PM (2012) Thrombotic adverse events to coagulation factor concentrates for treatment of patients with haemophilia and von Willebrand disease: a systematic review of prospective studies. Haemophilia 18(3):e173–e178
Miesbach W (2019) Phase 3 study of recombinant von Willebrand factor in patients with severe von Willebrand disease who are undergoing elective surgery: comment. J Thromb Haemost 17(8):1403–1405
Baxalta US Inc. Vonvendi (von Willebrand factor [recombinant]) package insert. Lexington, MA; Feb 2019
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tran, T., Arnall, J., Moore, D.C. et al. Vonicog alfa for the management of von Willebrand disease: a comprehensive review and single-center experience. J Thromb Thrombolysis 49, 431–440 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-019-02018-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-019-02018-1