Abstract
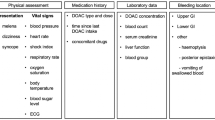
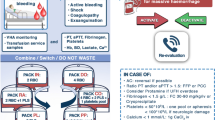
In October 2013, we implemented a hemostatic and antithrombotic (HAT) stewardship program with the primary focus of ensuring appropriate use of intravenous direct thrombin inhibitors (DTI) in patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT). We sought to compare the duration and cost of DTI therapy for the management of HIT before and after implementation of the HAT stewardship program. Following institutional review board approval, we conducted a single center, retrospective chart review of all patients with a suspected diagnosis of HIT as assessed by an anti-heparin-PF4 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay 6 months pre-HAT and post-HAT implementation. Patients were excluded if they were initiated on a DTI at an outside hospital, had a prior episode of HIT, or received mechanical circulatory support. Clinical characteristics, including demographics, comorbidities, medications, laboratory values, clinical and safety outcomes, length of stay, and mortality, were collected. A total of 592 patients were included; 333 patients were evaluated pre-HAT, while 259 patients were evaluated post-HAT. The mean duration of DTI treatment was significantly decreased in the post-HAT cohort (6.64 vs 5.17 days, p = 0.01), primarily driven by decreased duration of use for patients with suspected HIT (4.07 vs 2.86 days, p = 0.01). The HAT Stewardship program demonstrated a total decrease in annual costs associated with the diagnosis and management of HIT of $248,500. Our results indicate that the implementation of the HAT stewardship program had a significant impact on reducing the duration and costs of DTI therapy and the costs of laboratory evaluations in the management of HIT at our institution.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reardon DP, Atay JK, Ashley SW et al (2015) Implementation of a hemostatic and antithrombotic stewardship program. J Thromb Thrombolysis 40(3):379–382
Lo GK, Juhl D, Warkentin TE et al (2006) Evaluation of pretest clinical score (4T’s) for the diagnosis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in two clinical settings. J Thromb Haemost 4:759–765
Pouplard C, Gueret P, Fouassier M et al (2007) Prospective evaluation of the “4Ts” score and particle gel immunoassay specific to heparin/PF4 for the diagnosis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. J Thromb Haemost 5:1373–1379
Strutt JK, Mackey JE, Johnson SM, Sylvia LM (2011) Assessment of the 4Ts pretest clinical scoring system as a predictor of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Pharmacotherapy 31:138–145
Crowther MA, Cook DJ, Albert M et al (2010) The 4Ts scoring system for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in medical-surgical intensive care unit patients. J Crit Care 25:287–293
Sylvester KW, Fanikos J, Anger KE et al (2013) Impact of an immunoglobulin G-specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay on the management of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Pharmacotherapy 33(11):1191–1198
Rao SV, O’Grady K, Pieper KS et al (2006) A comparison of the clinical impact of bleeding measured by two different classifications among patients with acute coronary syndromes. J Am Coll Cardiol 47:809–816
Chesebro JH, Knatterud G, Roberts R et al (1987) Thrombolysis in myocardical infarction (TIMI) trial, phase I: a comparison between intravenous tissue plasminogen activator and intravenous streptokinase. Clinical findings through hospital discharge. Circulation 76:142–154
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Jackie Clark, PharmD, Jennifer Allen, PharmD, and Ellen Colman, PharmD, for their assistance with data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ritchie, B.M., Sylvester, K.W., Reardon, D.P. et al. Treatment of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia before and after the implementation of a hemostatic and antithrombotic stewardship program. J Thromb Thrombolysis 42, 616–622 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-016-1408-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-016-1408-6