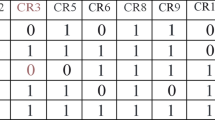
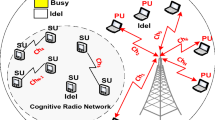
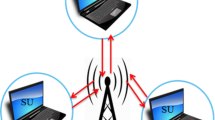
Abstract
Cognitive radio was introduced to fill up the imbalance between spectrum scarcity and spectrum underutilization. So to make such an ideology work, a network which can utilize all the available channel in the best efficient manner, without causing any harmful interface to primary user (PU) and maintaining the Quality of Service (QoS) for cognitive user (CU) is required. In both Mesh as well as ad-hoc networks, effective utilization of the white-spaces by the CUs maintaining the QoS for both primary and CU is a challenging task due to the frequent and instant change in their channel status. In this paper an intelligent-MAC (i-MAC) for cognitive radio (CR) using two transceivers based on hybrid approach of combination of cooperative decision and contention-free approach is proposed. Cooperative decision, to overcome hidden node or the case when there is no common channel between the CU’s and contention-free approach, to solve the issues in contention mechanism, where same channel is selected simultaneously by multiple CU’s. Proposed CR-i-MAC permits an effective dynamic spectrum access to CUs without effecting the QoS for PU’s. The simulative performance analysis of proposed CR-i-MAC is tested in various critical cases like multi-channel single-radio and multi-channel multi-radio over different on demand routing protocols like dynamic source routing, ad-hoc on demand distance vector and weighted cumulative expected transmission time using network simulator (NS-2). The performance of the network is measured on the basis of parameters like throughput, delay and interference. The analysis of the simulation results shows that the proposed CR-i-MAC outperforms various other CR MAC’s in terms of both increased throughput and reduced delays thereby making the system stable and efficient.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitola III, J. & Maguire, G. Q., Jr. (1999). Cognitive radio: Making software radios more personal. IEEE Personal Communications, 6(4), 13–18. doi:10.1109/98.788210.
Haykin, S. (2005). Cognitive radio: Brain-empowered wireless communications. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 23(2), 201–220. doi:10.1109/JSAC.2004.839380.
FCC spectrum policy task force. (2008). Report of spectrum efficiency working group. Second report and order, Federal Communications Commission, ET-Docket 04-186 and 02-380, Adopted November 4, 2008. Released November 14, 2008.
Akyildiz, I. F., Lee, W. Y., Vuran, M. C., & Mohanty, S. (2006). Next generation/dynamic spectrum access/cognitive radio wireless networks: A survey. Computer Networks Elsevier, 50(13), 2127–2159. doi:10.1016/j.comnet.2006.05.001.
Singh, J. S. P., Singh, J., & Kang, A. S. (2013). Cognitive radio: State of research domain in next generation wireless networks—A critical analysis. International Journal of Computer Application, 74(10), 1–9. doi:10.5120/12918-9741.
Akyildiz, I. F., Lee, W. Y., & Chowdhury, K. R. (2009). CRAHNs: Cognitive radio ad hoc networks. Ad Hoc Networks Elsevier, 7(5), 810–836. doi:10.1016/j.adhoc.2009.01.001.
Cormio, C., & Chowdhury, K. R. (2009). A survey on MAC protocols for cognitive radio networks. Ad Hoc Networks Elsevier, 7(7), 1315–1329. doi:10.1016/j.adhoc.2009.01.002.
Akyildiz, I. F. (2005). A survey on wireless mesh networks. IEEE Communication Magazine, 43(9), S23–S30. doi:10.1109/MCOM.2005.1509968.
Zhao, Q., Tong, L., Swami, A., & Chen, Y. (2007). Decentralized cognitive MAC for opportunistic spectrum access in ad hoc networks: A POMDP framework. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 25(3), 589–600. doi:10.1109/JSAC.2007.070409.
Hsu, A. C. C., Wei, D. S. L., & Kuo, C. C. J. (2007). A cognitive MAC protocol using statistical channel allocation for wireless ad-hoc networks. IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (pp. 105–110). doi:10.1109/WCNC.2007.25.
Motamedi, A., & Bahai, A. (2007). MAC Protocol design for spectrum-agile wireless networks: Stochastic control approach. In 2nd IEEE International Symposium on New Frontier in Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks (pp. 448-451). doi:10.1109/DYSPAN.2007.65.
Cordeiro, C., & Challapali, K. (2007). C-MAC: A cognitive MAC protocol for multi-channel wireless networks. In 2nd IEEE International Symposium on New Frontier in Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks (pp. 147–157). doi:10.1109/DYSPAN.2007.27.
Chen, T., Zhang, H., Maggio, G. M., & Chlamtac, I. (2007). CogMesh: A cluster-based cognitive radio network. in 2nd IEEE International Symposium on New Frontier in Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks (pp. 168-178). doi:10.1109/DYSPAN.2007.29.
Jia, J., Zhang, Q., & Shen, X. (2008). HC-MAC: A hardware-constrained cognitive MAC for efficient spectrum management. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 26(1), 106–117. doi:10.1109/JSAC.2008.080110.
Su, H., & Zhang, X. (2008). Cross-layer based opportunistic MAC protocols for QoS provisionings over cognitive radio wireless networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications., 26(1), 118–129. doi:10.1109/JSAC.2008.080111.
Kondareddy, Y. R., & Agrawal, P. (2008). Synchronized MAC protocol for multi-hop cognitive radio networks. IEEE International Conference on Communications (pp. 3198–3202). doi:10.1109/ICC.2008.602.
Su, H., & Zhang, X. (2008). CREAM-MAC: An efficient cognitive radio-enabled multi-channel MAC protocol for wireless networks. IEEE International Symposium on World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks (pp. 1–8). doi:10.1109/WOWMOM.2008.4594853.
Hamdaoui, B., & Shin, K. G. (2008). OS-MAC: An efficient MAC protocol for spectrum-agile wireless networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 7(8), 915–930. doi:10.1109/TMC.2007.70758.
Flegyhzi, M., Cagalj, M., & Hubaux, J. P. (2009). Efficient MAC in cognitive radio systems: A game-theoretic approach. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 8(4), 1984–1995. doi:10.1109/TWC.2009.080284.
Joshi, G. P., Kim, S. W. & Kim, B. S. (2009). An efficient MAC protocol for improving the network throughput for cognitive radio networks. In 3rd International Conference on Next Generation Mobile Applications, Services and Technologies (pp. 271– 275). doi:10.1109/NGMAST.2009.38.
Ke, Y., & Yoo, SJ., (2009). MCR-MAC: Multi-channel cognitive radio MAC protocol for cooperative incumbent system protection in wireless ad-hoc network. In 1st International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks (pp. 6–11). doi:10.1109/ICUFN.2009.5174275.
Kahraman, B., & Buzluca, F. (2010). Protection and fairness oriented cognitive radio MAC protocol for ad hoc networks (PROFCR). European Wireless Conference (pp. 282–287). doi:10.1109/EW.2010.5483429.
Lim, S., & Lee, T.-J. (2011). Self-scheduling multi-channel cognitive radio MAC protocol based on cooperative communication. IEICE Transaction on Communication, 94(6), 1657–1668. doi:10.1587/transcom.E94.B.1657.
Lau, L. C., Lin, C. C., & Wang, S. Y. (2011). Bi-directional cognitive radio MAC protocol for supporting TCP flows. IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference (pp. 1–5). doi:10.1109/VETECF.2011.6092891.
Hernandez-Guillen, J., Colina, E. R., Jimnez, R. M., Chalke, M. P. (2012). CRUAM-MAC: A novel cognitive radio MAC protocol for dynamic spectrum access. In IEEE Latin-America Conference on Communications (pp. 1–6). doi:10.1109/LATINCOM.2012.6505997.
Dappuri, B., Venkatesh, T. G., & Thomas, V., (2013). MAC protocols for cognitive radio networks with passive and active primary users. In International Conference on Wireless Communications & Signal Processing (WCSP) (pp. 1–7). doi:10.1109/WCSP.2013.6677245.
Timalsina, S. K., Moh, S., Chung, I., & Kang, M. (2013). A concurrent access MAC protocol for cognitive radio ad hoc networks without common control channel. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 69, 1–13. doi:10.1186/1687-6180-2013-69.
Pandit, S., & Singh, G. (2015). Backoff algorithm in cognitive radio MAC protocol for throughput enhancement. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 64(5), 1991–2000. doi:10.1109/TVT.2014.2334605.
Khatiwada, B., & Moh, S. (2015). A novel multi-channel MAC protocol for directional antennas in ad hoc networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 80(3), 1095–1112. doi:10.1007/s11277-014-2074-7.
Thilina, K. M., Hossain, E., & Kim D. I. (2015). DCCC-MAC: A dynamic common control channel-based MAC protocol for cellular cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology (in press). doi:10.1109/TVT.2015.2438058.
Wang, J., & Huang, Y. (2010). A cross-layer design of channel assignment and routing in cognitive radio networks. In 3rd IEEE International Conference on Computer Science and Information Technology 7 (pp. 542–547). doi:10.1109/ICCSIT.2010.5564800.
Willkomm, D., Machiraju, S., Bolot, J., & Wolisz, A. (2009). Primary user behavior in cellular networks and implications for dynamic spectrum access. IEEE Communications Magazine, 47(3), 88–95. doi:10.1109/MCOM.2009.4804392.
Chehata, A., Ajib, W., & Elbiaze, H. (2011). An on-demand routing protocol for multi-hop multi-radio multi-channel cognitive radio networks. Wireless Days IEEE-IFIP (pp. 1–5). doi:10.1109/WD.2011.6098215.
De Couto, D. S. J., Aguayo, D., Bicket, J., & Morris, R. (2003). A high-throughput path metric for multi-hop wireless routing. Wireless Networks Springer, 11(4), 419–434. doi:10.1007/s11276-005-1766-z.
Singh, J. S. P., Singh, J., Kang, A. S., & Rai, M. K., (2013). Cooperative fusion sensing technique for cognitive radio: An efficient detection method for shadowing environment. International Conference on Computing Sciences, WILKIES 100 Elsevier, 2 (pp. 70–79).
Singh, J. S. P., Rai, M. K., Singh, J., & Kang, A.S. (2014). Trade-off between AND and OR detection method for cooperative sensing in cognitive radio. IEEE Advance Computing Conference (IACC) (pp. 395-399). doi:10.1109/IAdCC.2014.6779356.
Singh, J. S. P., Singh, R., Rai, M. K., Singh, J., & Kang, A. S. (2015). Cooperative sensing for cognitive radio: A powerful access method for shadowing environment. Wireless Personal Communications, 80(3), 1363–1379. doi:10.1007/s11277-014-2088-1.
Salim, S., Moh, S., & Chung, I. (2013). Transmission power control aware routing in cognitive radio ad hoc networks. Wireless Personal Communications Springer, 71(4), 2713–2714. doi:10.1007/s11277-012-0966-y.
IEEE standard for Wireless Local Area Network, MAC and PHY Layer Specifications, STD 802.11-2007. www.iith.ac.in/~tbr/teaching/docs/802.11-2007.
Draves, R., Padhye, J., & Zill, B. (2004). Routing in multi-radio, multi-hop wireless mesh networks. In Proceedings of 10th International Conference on Mobile computing and networking, MobiCom’04 (pp. 114–128). doi:10.1145/1023720.1023732.
Cognitive Radio Cognitive Networks [Available Online] http://faculty.uml.edu/Tricia_Chigan/Research/helpv4.htm. Accessed On 12 February 2015.
Network Simulator-2 (ns2). http://www.isi.edu/nsnam/ns/. Accessed 12 Feb 2015.
Acknowledgments
First author is highly thankful to Dr. Davinder Pal Sharma, DSP Research Lab, University of West Indies, Dr. B.P. Patil, Prof. & Head, Army Institute of Technology, Pune and Dr. Sukhjeet Singh for providing useful information as well as critical remarks. The valuable help rendered by A.S. Kang, Assistant Professor, Department of Electronic Technology, Panjab University, Chandigarh, India and Rajwinder Singh, Assistant Professor, BCET Gurdaspur, India are also acknowledged. Gulshan Kumar, Assistant Professor and Sundas Sheikh, Research Fellow are also acknowledged for providing valuable guidance to improve the appearance and quality of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, J.S.P., Rai, M.K. Cognitive radio intelligent-MAC (CR-i-MAC): channel-diverse contention free approach for spectrum management. Telecommun Syst 64, 495–508 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-016-0188-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-016-0188-9