Abstract
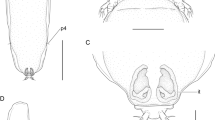
Nematodes collected from the stomach and large intestine of Rhinoclemmys punctularia (Daudin) from the eastern Amazon, Brazil, are assigned to a new genus, Vogtnema n. gen., allocated in the family Atractidae (Cosmocerdoidea). Vogtnema n. gen. differs from all other genera of Atractidae based on the combination of the following morphological characters: four lips V-shaped (two subdorsal and two subventral) without sclerotized structures associated, absence of sclerotized formations and/or pieces surrounding the oral opening, oral aperture surrounded by flange internal membranous structures; in males the larger spicule is alate. The type species Vogtnema asymmetrica n. gen., n. sp. has the five precloacal pairs of papillae situated on the right side of the body that are more prominent than those on the left side. We also provide an identification key to the genera of the family Atractidae.


Similar content being viewed by others
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Anderson, R. C, Chabaud, A. G., & Willmott, S. (2009), Keys to the Nematode Parasites of Vertebrates. Archival Volume. CAB International, Wallingford (UK).
Baker, M. R. (1987). Synopsis of the Nematoda parasitic in amphibians and reptiles. Memorial University of Newfoundland, Occasional Papers in Biology, 11, 1–325.
Baylis, H. A., & Daubney, R. (1922). Report on the parasitic nematodes in the collection of the Zoological Survey of India. Memoirs of the Indian Museum, 7, 342–343.
Berenger, J. G. (1947). Revisión de la familia Atractidae Travassos, 1920 com descripción de dos nuevas especies. Revista Ibérica de Parasitología, 7, 3–90.
Bursey, C. R., & Flanagan, J. P. (2002). Atractis marquezi n. sp. (Nematoda: Atractidae) and a revision of Atractis Dujardin, 1845, sensu Baker, 1987. Journal of Parasitology, 88, 320–324. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1645/0022-3395(2002)088[0320:AMNSNA]2.0.CO;2
Bursey, C. R., Reavill, D., & Greiner, E. (2009). Pneumoatractis podocnemis n. gen., n. sp. (Nematoda: Atractidae) from the Yellow-Spotted Amazon River Turtle, Podocnemis unifilis (Testudines: Pelomedusidae). Comparative Parasitology, 76, 149–153. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1654/4379.1
Chabaud, A. G., Cuisance, D., & Colas, F. (1989). Leiperenia moreli n. sp. (Nematoda: Atractidae), parasite de l’éléphant d’Afrique. Systematic Parasitology, 14, 135–140. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00016907
Costa, S. C. G. (1961). Sobre a sistemática da família Cobboldinidae Skyardin, 1948 (Nematoda). Atas da Sociedade de Biologia do Rio de Janeiro, 5, 30–31.
Dyer, W. G., & Carr, J. L. (1990). Some Ascaridid, Spirurid, and Rhabditid Nematodes of the Neotropical Turtle Genus Rhinoclemmys in Mexico and South America. Journal of Parasitology, 76, 259–262. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.2307/3283028
Ferrara, C. R., Fagundes, C. K., Morcatty, T. Q., & Vogt, R. C. (2017). Quelônios Amazônicos: Guia de Identificação e Distribuição. Manaus: Wildlife Conservation Society.
Fitzsimmons, W. M. (1958). On Probstmayria reptiliae n. sp., from Homopus femoralis and Some Notes on the Genus Probstmayria. Journal of Helminthology, 32, 211–218. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X0001974X
Gedoelst, L. (1919). Un Oxyuride Nouveau parasite d'un reptile. Compte Rendu Hebdomadaires des Séances et Mémoires de la Société de Biologie, 82, 910–913.
Gibbons, L. M., Khalil, L. F., & Marinkelle, C. J. (1995). New nematode genus, Podocnematractis, for Atractis ortleppi Thapar, 1925 (Cosmocercoidea: Atractidae) and the description of another new species, P. colombiaensis from turtles Podocnemis spp. in Colombia. Systematic Parasitology, 30, 47–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00009244
Gibbons, L. M., Knapp, S. E., & Krecek, R. C. (1996). Diceronema versterae gen. n., sp. n. (Atractidae; Cosmocercoidea) from the Black Rhinoceros, Diceros bicornis bicornis, in South Africa. Journal of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 63, 98–104.
Gibbons, L. M., Khalil, L. F., & Marinkelle, C. J. (1997). Paraorientatractis semiannulata n. g., n. sp. (Cosmocercoidea: Atractidae) from the Large Intestine of the Side-Necked Turtle, Podocnemis unifilis Troschel, 1848 (Testudines: Pelomedusidae) in Brazil. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz, 92, 359–364. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0074-02761997000300011
Gibbons, M. L., & Platt, T. R. (2006). Rhinoclemmysnema n. g. and three new species of nematodes of the family Atractidae (Cosmocercoidea), with notes on the helminth fauna of Rhinoclemmys pulcherrrima (Testudines: Bataguridae) in Costa Rica. Journal of Helminthology, 80, 333–340. https://doi.org/10.1017/joh2006360
Gupta, V., & Johri, S. (1987). On a new genus Pseudocyrtosomum (Atractidae: Nematoda) from Kachuga dhongoka Gray from Lucknow. Indian Journal of Helminthology, 39, 83–87.
Hasegawa, H., McLennan, M. R., Huffman, M. A., & Matsuura, K. (2021). Notes on morphology and life history of Probstmayria gombensis (Nematoda: Cosmocercoidea: Atractidae), parasitic in eastern chimpanzees, Pan troglodytes schweinfurthii, in Bulindi, Uganda. Journal of Parasitology, 107, 155–162. https://doi.org/10.1645/20-88
ICZN (2012). International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature: Amendment of articles 8, 9, 10, 21 and 78 of the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature to expand and refine methods of publication. Zootaxa, 3450, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.3897/zookeys.219.3994
Khalil, L. F., & Gibbons, L. M. (1988). Two nematodes, Paratractis hystrix (Diesing, 1851) and Buckleyatractis marinkelli n. g., n. sp. (Atractidae: Cosmocercoidea) from Podocnemis spp. in Colombia. Systematic Parasitology, 12, 187–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00007767
Mondal S., & Manna, B. (2013). Rhinoceronema unicornensis gen. n., sp. n. (Cosmocercoidea: Atractidae) from Indian one horned Rhinoceros (Rhinoceros unicornis Linnaeus, 1758) captivated at the Alipore Zoological Garden, Kolkata, India. Journal of Parasitic Diseases, 37, 134–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-012-0147-7
Mondal S., & Manna, B. (2015). Hippopotamenema aliporensis gen. n. sp. n. (Nematoda: Atractidae) from Hippopotamus (Hippopotamus amphibius Linnaeus, 1758) Captivated at the Alipore Zoological Garden, Kolkata, West Bengal, India. Science and Culture, 81, 44–47.
Petter, A. J (1959). Deux nouveaux genres de nématodes atractides, parasites du daman des rochers [Procavia ruficeps (Ehrenberg)]. Bulletin de la Société Zoologique de France, 84, 195–204.
Petter, A. J. (1966). Équilibre des espèces dans les populations de nématodes parasites du colon des tortues terrestres. Mémoires du Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle, Paris, Serie Zoologie, 39, 1–245.
Puylaert, F. A. (1970). Description de Labeonema intermedia gen. n., n. sp., parasite d’un Labeo (Pisces Cyprinidae) (Atractidae-Nematoda-Vermes). Revue de Zoologie et de Botanique Africaines, 82, 370–376.
Ransom, B. H. (1907). Probstmayria vivipara (Probstmayr, 1865) Ransom, 1907, a nematode of horses heretofore unreported from the United States. Transactions of the American Microscopical Society, 27, 33–41. https://doi.org/10.2307/3220886
Silva, M. B., Resende, I. M. C., Paranhos, J. D. N., & Barreto, L. (2011). Reptilia, Testudines, Geoemydidae, Rhinoclemmys punctularia (Daudin, 1801): Distribution extension. Check List, 7, 75–77. https://doi.org/10.15560/7.1.75
Yamaguti, S. (1961). Systema Helminthum. Volume III. The Nematodes of Veterbrates. New York: Interscience Publishers.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Missiene Maria da Silva and Luiz Paulo da Silva Almeida for her support in host necropsies and collection nematodes; to Yuri Willkens for his technical support with SEM analyzes and Dra. Edilene Oliveira da Silva, from Laboratory of Cellular Structural Biology at the Federal University of Pará, Belém, for her technical support with the SEM analyses.
Funding
This study was supported by CAPES/ PPGBAIP/ UFPa, Fundação Amazônia de Amparo a Estudos e Pesquisa (FAPESPA) (01/2021 – PROGRAMA DE APOIO A NUCLEOS EMERGENTES) and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) process number 431809/2018-6 Universal); Research productivity scholarship of CNPq to MELO, F.T.V. (Process number 304955/2018-3) and SANTOS, J.N. (Process number 305552/2019-8). All procedures contributing to this work comply with all applicable institutional, national, and international guidelines for animal care and use Animal Research Ethics Committee, Federal University of Pará, under license N8341260821CEUA/UFPa. The present study was approved by Instituto Chico Mendes de Conservação da Biodiversidade (ICMBio), Brazil, and host specimens were collected under license number SISBIO: 53527-4. This study is part of the Ph.D thesis of Ronald Ferreira de Jesus in Postgraduate Program in the Biology of Infectious and Parasitic Agents (ICB-UFPa).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.F. Jesus wrote the main draft and prepared images. A.N. Santos and B. Nandyara helped with specimen observations and SEM analysis, reviewing, and writing the manuscript. J.N. Santos and F.T.V Melo wrote the manuscript, revised and prepared the line drawings. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
All applicable institutional, national and international guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jesus, R.F., Santos, A.N., Nandyara, B. et al. Vogtnema asymmetrica n. gen., n. sp. (Nematoda: Cosmocercoidea: Atractidae) parasite of Rhinoclemmys punctularia (Daudin) (Testudines: Geoemydidae) from eastern Amazon, Brazil. Syst Parasitol 99, 761–769 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-022-10065-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-022-10065-1