Abstract
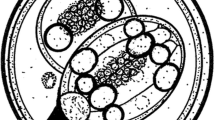
The flat-headed snake, Tantilla gracilis Baird and Girard is a small reptile belonging to the family Colubridae. Feces from a single T. gracilis from McCurtain County, Oklahoma, USA, was collected and examined for coccidia; it was found to be passing a new species of Caryospora. Oöcysts of Caryospora sargentae n. sp. are spheroidal to typically subspheroidal with a moderately-pitted bi-layered wall, measure (L × W) 20.7 × 19.2 µm, and have a length/width (L/W) ratio of 1.1; a micropyle and oöcyst residuum were absent but one to several small, irregular to spheroidal masses of non-refractile debris within the oocyst was present as well as a polar granule attached to the inner oöcyst wall. Sporocysts are ovoidal and measure 15.0 × 11.0 µm, L/W 1.4; a nipple-like Stieda body is present as well as a distinct rounded sub-Stieda body. The sporocyst residuum is composed of a large, dense, irregular mass of various sized granules located between and often obscuring the sporozoites. This is the third coccidian described from the flat-headed snake. In addition, we include some data on the endogenous development of the coccidian.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, D. R., Duszynski, D. W. & Marquardt, W. C. (1968). Three new coccidia (Protozoa: Telosporea) from kingsnakes, Lampropeltis spp., in Illinois, with a description of Eimeria zamenis Phisalix, 1921. Journal of Parasitology, 54, 577–581. https://doi.org/10.2307/3277085
Cobb, V. A. (2004). Diet and prey size of the flathead snake, Tantilla gracilis. Copeia, 2004, 397–402.
Crother, B. I. (ed.). (2017). Scientific and standard English names of amphibians and reptiles of North America north of Mexico, with comments regarding confidence in our understanding. 8th edition. SSAR Herpetological Circular 43, 1–104.
Duszynski, D. W., Couch, L. & Upton, S. J. (2003). The coccidian genus Caryospora. World Wide Web electronic publication. https://www.k-state.edu/parasitology/worldcoccidia/CARYOSPORA.
Duszynski, D. W. & Upton, S. J. (2009). The biology of the coccidia (Apicomplexa) of snakes: A scholarly handbook for identification and treatment. CreateSpace: A DBA of on-demand Publishing LLC. Amazon.com Inc., pp. 422.
Ernst, C. H. & Ernst, E. M. (2003). Snakes of the United States and Canada. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Books, pp. 668.
Force, E. R. (1935). A local study of the opisthoglyph snake Tantilla gracilis Baird and Girard. Papers of the Michigan Academy of Sciences, Arts, and Letters, 20, 645–659.
ICZN (2012). International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature: Amendment of articles 8, 9, 10, 21 and 78 of the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature to expand and refine methods of publication. Bulletin of Zoological Nomenclature, 69, 161–169.
McAllister, C. T., Robison, H.W., Seville, R. S., Roehrs, Z. P. & Trauth, S. E. (2011). Caryospora duszynskii (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) from the speckled kingsnake, Lampropeltis holbrooki (Reptilia: Ophidia), in Arkansas, with a summary of previous reports. Journal of the Arkansas Academy of Science, 65, 176–179.
McAllister, C. T., Roehrs, Z. P. & Seville, R. S. (2012). A new species of Caryospora (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) from the flathead snake, Tantilla gracilis (Ophidia: Colubridae), in southeastern Oklahoma. Journal of Parasitology, 98, 640–642. https://doi.org/10.1645/ge-2975.1
McAllister, C. T., Seville, R. S. & Connior, M. B. (2015). A new host for Caryospora lampropeltis (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) from the eastern hognose snake, Heterodon platirhinos (Ophidia: Colubroidea: Dipsadinae), from Arkansas, U.S.A., with a summary of hosts of this coccidian. Comparative Parasitology, 82, 151–154. https://doi.org/10.1654/4699.1
McAllister, C. T., Upton, S. J., Trauth, S. E. & Dixon, J. R. (1995). Coccidian parasites (Apicomplexa) from snakes in the southcentral and southwestern United States: New host and geographic records. Journal of Parasitology, 81, 63–68. https://doi.org/10.2307/3284007
Modrý, D., Šlapeta, J. & Koudela, B. (2005). Mice serve as paratenic hosts for transmission of Caryospora duszynskii (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) between snakes of the genus Elaphe. Folia Parasitologica, 52, 205–208.
Powell, R., Conant, R. & Collins, J. T. (2016). Peterson field guide to reptiles and amphibians. 4th ed. New York: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company, pp. 494.
Presnell, J. K. & Schreibman, M. P. (1997). Humason’s Animal Tissue Techniques, 5th ed. Baltimore, Maryland: John Hopkin’s University Press, pp. 600.
Sievert, G. & Sievert, L. (2021). A field guide to Oklahoma’s amphibians and reptiles, 4th ed. Oklahoma City, Oklahoma: Oklahoma Department of Wildlife Conservation, pp. 234.
Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists (SIH). (2004). Guidelines for use of live amphibians and reptiles in field and laboratory research. Second Edition, Revised by the Herpetological Animal Care and Use Committee (HACC) of the American (Committee Chair: Beaupre S. J., Jacobson, E. R., Lillywhite, H.B., & Zamudio, K.). World Wide Web electronic publication. https://www.fullerton.edu/doresearch/resource_library/policies/IACUC_GuidelinesforUseofAmphibsReptiles%202004.pdf.
Telford, Jr., S. R. (1997). Coccidian parasites (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) of the endemic Florida snake Tantilla relicta Telford (Serpentes: Colubridae). Systematic Parasitology 36, 17–25. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1005759906933
Uetz, P., Freed, P., Aguilar, R. & Hošek, J. (eds.) (2021). The Reptile Database. World Wide Web electronic publication. http://www.reptile-database.org
Upton, S. J., Current, W. L. & Barnard, S. M. (1984). A new species of Caryospora (Apicomplexa: Eimeriorina) from Elaphe spp. (Serpentes: Colubridae) of the southeastern and central United States. Transactions of the American Microscopical Society, 103, 240–244. https://doi.org/10.2307/3226185
Upton, S. J., McAllister, C. T. & Trauth, S. E. (1994). Caryospora masticophis n. sp. (Apicomplexa: from Masticophis flagellum and Coluber constrictor (Serpentes) in Arkansas, U.S.A. Transactions of the American Microscopical Society, 113, 395–399. https://doi.org/10.2307/3226633
Upton, S. J., McAllister, C. T., Trauth, S. E. & Bibb, D. K. (1992). Description of two new species of coccidia (Apicomplexa: Eimeriorina) from flatheaded snakes, Tantilla gracilis (Serpentes: Colubridae) and reclassification of misnomer species within the genera Isospora and Sarcocystis from snakes. Transactions of the American Microscopical Society, 111, 50–60. https://doi.org/10.2307/3226726
Wilber, P. G., Duszynski, D. W., Upton, S. J., Seville, R. S. & Corliss, J. O. (1998). A revision of the taxonomy and nomenclature of the Eimeria spp. (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) from rodents in the Tribe Marmotini (Sciuridae). Systematic Parasitology, 39, 113–135. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1005914010087
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs. Scott L. Gardner and Gabor Racz (HWML) for expert curatorial assistance.
Funding
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable institutional, national and international guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. The Oklahoma Department of Wildlife Conservation provided Scientific Collecting Permit no. 1551646 to CTM.
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article was registered in the Official Register of Zoological Nomenclature (ZooBank) as urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:6160AF83-B373-4D19-885A-47BC984178AD.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McAllister, C.T., Hnida, J.A. & Trauth, S.E. A new caryosporan (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) from flat-headed snake, Tantilla gracilis (Reptilia: Ophidia: Colubridae), from McCurtain County, Oklahoma, USA. Syst Parasitol 99, 309–315 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-022-10028-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-022-10028-6