Abstract
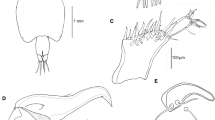
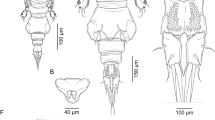
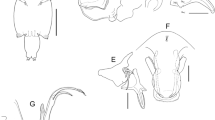
A new species of parasitic copepod, Caligus tunisiensis n. sp. (Caligidae), is described based on two female specimens collected from the gills of the painted comber, Serranus scriba (L.), caught in the Mediterranean Sea, off the Tunisian coasts. The new species belongs to the Caligus productus-species group established by Boxshall & Gurney (1980) as it shares the following set of character states: (i) antenna with well-developed posterior process on proximal segment; (ii) posterior margin of distal exopodal segment of leg 1 lacking typical plumose setae, or retaining single vestigial seta; and (iii) 2-segmented exopod of leg 4 armed with IV spines on compound distal exopodal segment. Detailed morphological comparisons between the new species and the core members of the C. productus-species group revealed that the new species closely resembles with C. productus Dana, 1852 and C. temnodontis Brian, 1924. However, the new species can be distinguished from its congeners in having: (i) a female maxilliped bearing a prominent bi-lobate myxal process, opposing tip of the claw; (ii) leg 4 protopod ornamented with a patch of spinules on the posterolateral surface; and (iii) an abdomen ornamented with two rows of minute spinules at the posterolateral corners.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahri, L. (1995). Analyse génétique et parasitologique des populations du loup commun, Dicentrarchus labrax et du loup ponctué Dicentrarchus punctatus des côtes tunisiennes. MSc thesis, Université de Tunis El Manar, 121 pp.
Ben Hassine, O. K. (1983). Les Copépodes parasites de poisons Mugilidae en Méditerranée occidentale (côtes françaises et tunisiennes). Morphologie, Bio-écologie, cycles évolutifs. PhD thesis, U.S.T.L., Montpellier, 452 pp.
Benmansour, B. (2001). Biodiversité et bioécologie des copépodes parasites des poissons téléostéens. PhD thesis, Université de Tunis El Manar, 454 pp.
Benmansour, B., & Ben Hassine, O. K. (1997). Première mention en Tunisie de certains Caligidae et Lernaeopodidae (Copepoda) parasites de poisons Téléostéens. Acta Ichthyologica et Piscatoria, 20, 157–175.
Benmansour, B., & Ben Hassine, O. K. (1998). Preliminary analysis of parasitic copepod species richness among coastal fishes of Tunisia. Italian Journal of Zoology, 65, 341–344.
Boxshall, G. A. (1990). The skeletomusculature of siphonostomatoid copepods, with an analysis of adaptive radiation in structure of the oral cone. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 328, 167–212.
Boxshall, G. A. (2018). The sea lice (Copepoda: Caligidae) of Moreton Bay (Queensland, Australia) with descriptions of thirteen new species. Zootaxa, 4398, 1–172.
Boxshall, G. A., & El-Rashidy, H. H. (2009). A review of the Caligus productus species group, with the description of a new species, new synonymies and supplementary descriptions. Zootaxa, 2271, 1–26.
Boxshall, G. A., & Gurney, A. R. (1980). Description of two new and one poorly known species of the genus Caligus Müller, 1785 (Copepoda: Siphonostomatoida). Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History), 39, 161–178.
Cabral, P., & Raibaut, A. (1986). Découverte dʼun copépode caligide nouveau, parasite du tégument du loup, Dicentrarchus labrax (L., 1758) (Pisces, Moronidae) en élévage et en milieu naturel. Bulletin de la Société Zoologique de France, 111, 123–130.
Essafi, K., Cabral, P., & Raibaut, A. (1984). Copépodes parasites de poissons des îles Kerkennah (Tunisie méridionale). Les archives de lʼInstitut Pasteur Tunis, 61, 475–523.
Froese, R., & Pauly, D. (2020). FishBase. World Wide Web electronic publication. www.fishbase.org. Accessed on 14 April 2020.
Huys, R., & Boxshall, G. A. (1991). Copepod Evolution. London: The Ray Society.
ICZN (2012). International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature: Amendment of articles 8, 9, 10, 21 and 78 of the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature to expand and refine methods of publication. Bulletin of Zoological Nomenclature, 69, 161–169.
Kamanli, S. A., Kihara, T. C., Ball, A. D., Morritt, D., & Clark, P. F. (2017). A 3D imaging and visualisation workflow, using confocal microscopy and advanced image processing for brachyuran crab larvae. Journal of Microscopy, 266, 307–323.
Limaye, A. (2012). Drishti: a volume exploration and presentation tool. In: Stock, S. R. (Ed.) Proceedings of SPIE Vol. 8506. Developments in X-Ray Tomography VIII, 85060X, 17 October 2012, San Diego, California, USA.
Ohtsuka, S., & Boxshall, G. A. (2019). Two new species of the genus Caligus (Crustacea, Copepoda, Siphonostomatoida) from the Sea of Japan, with a note on the establishment of a new species group. ZooKeys, 893, 91–113.
Özak, A. A., Sakarya, Y., & Boxshall, G. A. (2019). Caligus adanensis n. sp. (Copepoda: Caligidae Burmeister, 1835) parasitic on garfish, Belone belone (Linnaeus, 1760), from the eastern Mediterranean Sea, off the Turkish coast. Marine Biodiversity, 49, 1877–1890.
Papoutsoglou, S. E. (1976). Metazoan parasites of fishes from Saronicos Gulf, Athens, Greece. Thalassographica , 1, 69–102.
Raibaut, A., Ben Hassine, O. K., & Maamouri, K. (1971). Copépodes parasites des poissons de Tunisie (première série). Bulletin de lʼInstitut National Scientifique et Technique dʼOcéanographie et de Pêche, 2, 169–197.
Raibaut, A., & Ben Hassine, O. K. (1977). Les Copépodes parasites des Muges en Mediterranee. Bulletin du Muséum National dʼHistoire Naturelle, 329, 833–848.
Rodrigues, A. M. V., Özak, A. A., Silva, L. M. H., & Boxshall, G. A. (2018). Caligus mulli n. sp. (Copepoda: Caligidae) parasitic on two Mullid fishes from the eastern Mediterranean and adjacent Atlantic waters. Parasitology Research, 117, 3843–3850.
Walter, T. C., & Boxshall, G. A. (2020). World of Copepods Database. http://www.marinespecies.org/copepoda on 2020-04-06. Accessed on 10 April 2020.
Yamak, S., & Ben Hassine, O. K. (2002) Impact of a fish farm on ichthyofauna and ichthyoparasitofauna of a Tunisian lagoon. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on the Environmental Problems of the Mediterranean Region, 12–15 April 2002, Nicosia, Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus.
Youssef, F., Benmansour, B., Ben Hassine, O. K., & Zouari-Tlig, S. (2016). Some parasitic copepods of selected teleost and chondrichthyan fishes from the Tunisian Gulfs. African Journal of Microbiology Research, 10, 1467–1476.
Acknowledgements
We are extremely grateful to Professor Selma Erat (Head of the Advanced Technologies Research & Application Center (MEITAM) of Mersin University, Mersin, Turkey), and all staff of MEITAM for providing access to Zeiss LSM 700 CLSM and their administrative and technical support during our studies. We also would like to thank to Professor Suphan Karaytuğ and Dr Seher Kuru (Department of Biology, Mersin University) for their hospitality and help during our stay in Mersin University, Mersin, Turkey. The authors also wish to thank the local fishermen for their help in obtaining the fish samples.
Funding
This study was funded by the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research, Tunisia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the University of Tunis El Manar in Tunis, Tunisia. All applicable international, national and/or institutional guidelines for the use and care of animals were followed. Fish samples studied in this study were maintained according to the guidelines of the animal facility at Laboratory of Biodiversity, Parasitology and Ecology of Aquatic Ecosystems Faculty of Sciences of Tunis, University of Tunis El Manar. Specimens of the Caligus species used herein, were collected from purchased dead fish samples caught by the local fishermen. Previously fixed specimens of the other species of Caligus stored in the collections of the Aquatic Parasitology Museum of the Faculty of Fisheries in Cukurova University (CUMAP) were used for the habitus drawings. Therefore, this study was granted exemption from requiring ethics approval.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article was registered in the Official Register of Zoological Nomenclature (ZooBank) as urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:52DED220-87AF-4E66-B7D0-125055514C7A. This article was published as an Online First article on the online publication date shown on this page. The article should be cited by using the doi number. This is the Version of Record.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Video S1 Caligus tunisiensis n. sp., holotype female. Patch of spinules on posterolateral corner of abdomen (WMV 14076 kb)
Video S2 Caligus tunisiensis n. sp., holotype female. Teeth on mandible (WMV 2654 kb)
Video S3 Caligus tunisiensis n. sp., holotype female. Patch of spinules on ventral surface of leg 1 coxa (WMV 5151 kb)
Video S4 Caligus tunisiensis n. sp., holotype female. Patch of spinules on leg 4 protopod (WMV 12069 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamdi, I., Benmansour, B., Zouari-Tlig, S. et al. Caligus tunisiensis n. sp. (Copepoda: Caligidae) parasitic on the painted comber Serranus scriba (L.) (Perciformes: Serranidae) from the Mediterranean Sea, off the Tunisian coast. Syst Parasitol 98, 57–71 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-020-09959-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-020-09959-9