Abstract
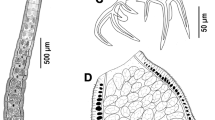
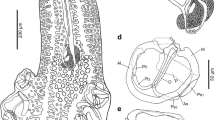
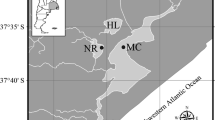
Gorgorhynchus occultus n. sp. is described from Sutorectus tentaculatus (Peters) (Orectolobidae) collected off Bunbury, Western Australia in 1986. The new species differs from all other species of Gorgorhynchus Chandler, 1934 by having a suite of characters including a proboscis hook formula of 18–20 rows of 8–9 hooks, a well-developed neck, irregular circles of small spines in a single anterior field, the male reproductive system limited to the posterior quarter of the trunk and three cement glands. In a survey of 284 sharks collected between 2015 and 2018 from 10 localities in Australian waters, 11 individuals were infected with acanthocephalan cystacanths. One individual of Sphyrna mokarran (Rupell) (Sphyrnidae) was infected with Corynosoma cetaceum Johnston & Best, 1931. Serrasentis sagittifer (Linton, 1889) (Rhadinorhynchidae) was found in five individuals of S. mokarran, four individuals of Syphyrna lewini (Griffith & Smith) and one individual of Carcharhinus coatesi (Whitley) (Carcharhinidae). These infections may be accidental because it has been suggested that acanthocephalans cannot tolerate the high levels of urea used by marine and esturine elasmobranchs for osmoregulation. The two most common host species examined, S. mokarran and S. lewini had the highest intensities and prevalences of infection with S. sagittifer. Although more individuals of S. lewini were examined, S. mokarran had the higher prevalence of infection.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin, O. M. (2013). Classification of the Acanthocephala. Folia Parasitologica, 60, 273–305.
Amin, O. M., & Van Ha, N. (2011). On four species of echinorhynchid acanthocephalans from marine fish in Halong Bay, Vietnam, including the description of three new species and a key to the species of Gorgorhynchus. Parasitology Research, 109, 841–847.
Barton, D. P., & Smales, L. R. (2015). Acanthocephalan cystacanths from flatfish (Order Pleuronectiformes) in tropical Australia. Journal of Parasitology, 101, 429–435.
Barton, D. P., Smales, L. R., & Morgan, J. A. T. (2018). A redescription of Serrasentis sagittifer (Rhadinorhynchidae: Serrasentinae) from Racycentron canadum with comments on its biology and its relationship to other species of Serrasentis. Journal of Parasitology, 104, 117–132.
Bethea, D. M., Carlson, J. K., Hollensead, L. D., Papastamatiou, Y. P., & Graham, B. S. (2011). A comparison of the foraging ecology and bioenergetics of the early life-stages of two sympatric hammerhead sharks. Bulletin of Marine Science, 87, 873–889.
Bilqees, F. M., & Khan, A. (2005). Two new helminth parasites from Pakistan, with redescription of the acanthocephalan Centrorhynchus fasciatum (Westrumb, 1821). Pakistan Journal of Zoology, 37, 257–263.
Cislo, P. R., & Caira, J. N. (1993). The parasite assemblage in the spiral intestine of the shark Mustelus canis. Journal of Parasitology, 79, 886–899.
Garcia-Varela, M., & Nadler, S. A. (2005). Phylogenetic relationships of Palaeacanthocephala (Acanthocephala), inferred from SSU and LSU rDNA gene sequences. Journal of Parasitology, 91, 1401–1409.
Golvan, Y. J. (1969). Systematique des Acanthocephales (Acanthocephala Rudolphi 1801) L’Ordre des Palaeacanthocephala Meyer 1931 La Super-famille des Echinorhynchoidea (Cobbold 1876) Golvan et Houin 1963. Memoires du Museum National d’Histoire Naturelle Serie A Zoologie, 57, 373 pp.
Kovalenko, L. M. (1981). Acanthocephalans of some fish in the tropical zone of the Pacific Ocean. Zoologicheskii Zhurnal, 60, 1140–1144. (In Russian).
Pichelin, S., Smales, L. R., & Cribb, T. H. (2016). A review of the genus Sclerocollum Schmidt & Paperna, 1978 (Acanthocephala: Cavisomidae) from rabbitfishes (Siganidae) in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Systematic Parasitology, 93, 101–114.
Smales, L. R. (2015). Chapter 6. Acanthocephala. In: Schmidt-Rhaesa, A. (Ed.) Handbook of Zoology, Vol 3 Gastrotricha and Gnathifera. Berlin: De Gruyter, pp. 317–336.
Tricas, T. C., Deacon, K., Last, P., McKosker, J. E., Walker, T. I., & Taylor, L. (1997). Sharks and Rays. Surrey Hills New South Wales: Readers Digest, 288 pp.
Verweyen, L., Klimpel, S., & Palm, H. W. (2011). Molecular phylogeney of the Acanthocephala (Class Palaeacanthocephala) with a paraphyletic assemblage of the Orders Polymorphida and Echinorhynchida. PLoS One, 6, e28285.
Weaver, H. J., & Smales, L. R. (2014). Two species of Acanthocephala (Rhadinorhynchidae and Transvenidae) from elasmobranchs from Australia. Comparative Parasitology, 81, 110–113.
Williams, H. H., McVicar, A. H., & Ralph, R. (1970). The alimentary canal of fish as an environment for helminth parasites. In: Taylor, A. E. R & Muller, R. (Eds), Aspects of Fish Parasitology. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications, pp. 43–77.
Acknowledgements
Thanks are due to the various commercial fishers in Queensland and the Northern Territory as well as the NSW Department of Primary Industries for the collection of shark specimens. Additionally, the authors are indebted to Matt Broadhurst and Sean Blake (New South Wales DPI), Cassie Rigby, Brooke D’Alberto and the many student helpers (James Cook University), and Grant Johnson (NT Department of Primary Industries and Resources) for their assistance in the processing of the shark specimens, and to Shane Penny (NT DPIR) for production of the map. Funding for the various projects that supplied the sharks presented in this paper came from the NT DPIR and the National Environmental Science Programme Marine Biodiversity Hub. Librarians from Central Queensland University provided document delivery services.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable institutional national and international guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. NT sharks: Northern Territory Fisheries Special Permit S17/2531; CDU Animal Ethics A13014; Qld sharks: Queensland General Fisheries Permit 187250; JCU Animal Ethics A2310; NSW sharks: approval to deploy the gill-nets was granted under section 158 of the Commonwealth Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999, from the application of sections 18, 18A, 20, 20A, 23 and 24A of Part 3 and Parts 7 to 9 of Chapter 4 of the Act, by the Commonwealth Minister for the Environment and Energy.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article was registered in the Official Register of Zoological Nomenclature (ZooBank) as 897EED7A-334D-4D39-9628-0CA06D3E895A. This article was published as an Online First article on the online publication date shown on this page. The article should be cited by using the doi number. This is the Version of Record.
This article is part of the Topical Collection Acanthocephala.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smales, L.R., Barton, D.P. & Chisholm, L.A. Acanthocephalans from Australian elasmobranchs (Chondrichthyes) with a description of a new species in the genus Gorgorhynchus Chandler, 1934 (Rhadinorhynchidae). Syst Parasitol 96, 565–573 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-019-09871-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-019-09871-x