Abstract
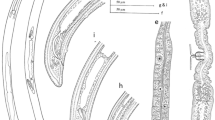
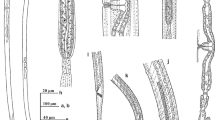
Meteterakis saotomensis n. sp. is described from Schistometopum thomense (Bocage), a gymnophionan endemic to the oceanic island of São Tomé in the Gulf of Guinea. The specimens were assigned to Meteterakis Karve, 1930, based on the possession of a head with three rounded lips, not set-off from the body, the absence of interlabia and cordons, females with a long vagina and males with a preanal sucker, surrounded by a cuticularised rim and caudal alae that are supported by fleshy papillae. The new species is characterised by: body length 4.2–4.5 mm (males) and 5.1–6.4 mm (females); total length of oesophagus, including pharyngeal portion and oesophageal bulb, 820–856 µm (males) and 898–1,070 µm (females); length of pharynx 57–58 µm (males) and 65–68 µm (females); spicules equal, 410–521 µm long, with tessellated ornamentation throughout their length and alae, and with bevelled tip; gubernaculum or ‘gubernacular mass’ absent; tail length 164–176 µm (males) and 214–239 µm (females), with elongated tip; vulva at 2.3–2.8 mm from anterior end, with anterior lip forming small flap. This is the second species of Meteterakis reported from gymnophionan hosts and the first from the Afrotropical region. Selected comparative morphological data for Meteterakis spp. are presented, and data on host range and geographic distribution are updated. The name M. striaturus Oshmarin & Demshin, 1972 is corrected to M. striatura to reflect the female gender of the genus name.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson, M. L. (1986). Meteterakis vaucheri n. sp. (Nematoda; Heterakoidea) from Varanus grayi (Varanidae) in the Philippines. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 64, 814–817.
Aisien, S. O., Ayeni, F., & Ilechie, I. (2004). Helminth fauna of anurans from the Guinea savanna at New Bussa, Nigeria. African Zoology, 39, 133–136.
Aisien, M. S. O., Ogoannah, S. O., & Imasuen, A. A. (2009). Helminth parasites of amphibians from a rainforest reserve in southwestern Nigeria. African Zoology, 44, 1–7.
Baker, M. R. (1980). Bufonerakis andersoni n. gen. (Nematoda: Heterakoidea) from Bufo arenarum of South America. Journal of Helminthology, 54, 49–53.
Baker, M. R. (1984). The systematics and zoogeography of Spinicaudinae and Meteterakinae (Heterakoidea: Nematoda) parasitic in reptiles and amphibians. Systematic Parasitology, 6, 275–287.
Biswas, P. K., & Chakravarty, G. K. (1963). The systematic studies of the zoo-parasitic oxyuroid nematodes. Zeitschrift für Parasitenkunde, 23, 411–428.
Bursey, C. R., Goldberg, S. R., & Kraus, F. (2005). Endoparasites in Sphenomorphus jobiensis (Sauria: Scincidae) from Papua New Guinea with description of three new species. Journal of Parasitology, 91, 1385–1394.
Canaris, A. G., & Gardner, S. L. (2003). Bibliography of helminth species described from African vertebrates 1800-1967. Faculty Publications from the Harold W. Manter Laboratory of Parasitology. Paper 3. (http://digitalcommons.unl.edu/parasitologyfacpubs/3). (20 December 2014).
Chabaud, A. G. (1978). Keys to genera of the Superfamilies Cosmocercoidea, Seuratoidea, Heterakoidea and Subuluroidea. In: Anderson, R. C., Chabaud, A. G. & Willmott, S. (Eds) CIH keys to the nematode parasites of vertebrates, No. 6. Farnham Royal: Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux, pp. 49–61.
Chakravarty, G. K. (1944). On the nematode worms in the collection of the Zoological Laboratory, University of Calcutta. Part I. Families Heterakidae and Kathlanidae. Calcutta University Journal of the Department of Science, New Series, 1, 70–77.
Crusz, H., & Ching, C. C. (1975). Parasites of the relict fauna of Ceylon. VI. More new helminths from amphibians and reptiles, a new host-record and redescription of Acanthocephalus serendibensis Crusz and Mills 1970. Annales de Parasitologie Humaine et Comparée, 50, 531–558.
Crusz, H., & Sanmugasunderam, V. (1973). Parasites of the relict fauna of Ceylon. 3. Nematodes from a rhacophorid frog and reptiles of the hill country. Annales de Parasitologie Humaine et Comparée, 48, 767–795.
Crusz, H., & Santiapillai, A. (1982). Parasites of the relict fauna of Ceylon. VIII. Helminths from Ichthyophis spp. (Amphibia: Gymnophiona). Annales de Parasitologie Humaine et Comparée, 57, 317–327.
Delêtre, M., & Measey, G. J. (2004). Sexual selection vs ecological causation in a sexually dimorphic caecilian, Schistometopum thomense (Amphibia Gymnophiona Caeciliidae). Ethology Ecology & Evolution, 16, 243–253.
Deshmukh, P. G., & Choudhari, A. C. (1980). Meteterakis aurangabadensis n. sp. from toad, Bufo melanostictus. Indian Journal of Parasitology, 4, 37–40.
Frost, D. R. (Ed.) (2014). Amphibian Species of the World: an online reference. Version 6.0. American Museum of Natural History, New York, USA. (http://research.amnh.org/herpetology/amphibia/index.php). (20 December 2014).
Gambhir, R. K., Tarnita, T., Chinglenkhomba, A., Gyaneswori, I., & Indrani, C. (2006). A new species of the genus Meteterakis Karve, 1930 (Nematoda: Heterakidae) from Bufo melanostictus Schneider. Flora and Fauna, 12, 57–59.
Gupta, V., & Naiyer, N. (1993). On a new nematode Meteterakis guptai sp. nov. from a lizard Calotes versicolor (Daudin) from Lucknow. Indian Journal of Helmithology, 45, 184–187.
Hasegawa, H. (1987). Meteterakis ishikawanae sp. n. (Nematoda: Heterakidae) from the Frog, Rana ishikawae, on Okinawa Island, Japan. Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 54, 237–241.
Hasegawa, H. (1990). Helminths collected from amphibians and reptiles on Amami-Oshima Island, Japan. Memories of the National Science Museum, Tokyo, 23, 83–92.
Hering-Hagenbeck, S. F. B. N., & Boomker, J. (2000). A check-list of the nematode parasites of South African Serpentes (snakes) and Sauria (lizards). Onderstepoort Journal of Veterinary Research, 67, 1–13.
Hsü, H. F. (1933). On some parasitic nematodes collected in China. Parasitology, 24, 512–541.
Inglis, W. G. (1958). A revision of the nematode genus Meteterakis Karve, 1930. Parasitology, 48, 9–31.
Karve, J. N. (1930). Some parasitic nematodes of frogs and toads. Annals of Tropical Medicine and Parasitology, 24, 481–491.
McAllister, C. T., Bursey, C. R., & Freed, P. S. (2010). Helminth parasites (Cestoidea, Nematoda, Pentastomida) of selected herpetofauna from Cameroon, West Africa. Acta Parasitologica, 55, 90–93.
Measey, G. J., & van Dongen, S. (2006). Bergmann’s rule and the terrestrial caecilian Schistometopum thomense (Amphibia: Gymnophiona: Caeciliidae). Evolutionary Ecology Research, 8, 1049–1059.
Myers, B. J., Wolfgang, R. W., & Kuntz, R. E. (1960). Helminth parasites from vertebrates taken in the Sudan (East Africa). Canadian Journal of Zoology, 38, 833–836.
Naidu, T. S. V., & Thakare, V. K. (1981). On two new nematodes from fishes and amphibians of Vidarbha Region, Maharashtra State, India. Rivista di Parassitologia, 42, 415–424.
Oshmarin, P. G., & Demshin, N. I. (1972). The helminths of domestic and some wild animals of the Democratic Republic Vietnam. Trudy Biologo-pochvennogo Instituta Vladivostok, 11, 5–115 (In Russian).
Sandosham, A. A. (1954). Malaysian parasites XV. Seven new worms from miscellaneous hosts. Studies from the Institute for Medical Research, Federation of Malaya, 26, 212–226.
Soota, T. D., & Chaturvedi, Y. (1970). The helminth fauna of Andaman and Nicobar. Part II. Nematoda. Proceedings of the Indian Science Congress Association, 57, 449–450.
Soota, T. D., & Chaturvedi, Y. (1972). The helminth fauna of Andaman and Nicobar. Nematoda. Records of the Zoological Survey of India, 66, 287–301.
Stoelting, R. E., Measey, G. J., & Drewes, R. C. (2014). Population genetics of the São Tomé caecilian (Gymnophiona: Dermophiidae: Schistometopum thomense) reveals strong geographic structuring. PLoS ONE, 9, e104628.
Uetz, P., & Hošek, J. (2014). The Reptile Database. (http://www.reptile-database.org). (20 December 2014).
Wang, P.-Q. (1980). Studies on some new nematodes of the suborder Oxyurata from Fujian, China. Acta Zootaxonomica Sinica, 5, 242–252.
Zhang, S. Q., & Zhang, L. P. (2011). A new species of Meteterakis Karve, 1930 (Nematoda: Heterakoidea) from Indotestudo elongata (Blyth) in China with a key to the species of Meteterakis. Zootaxa, 2869, 63–68.
Acknowledgements
GJM would like to thank the DST-NRF Centres of Excellence for Invasive Biology. Marc Delêtre is recognised for his help with dissecting hosts. Professor Luping Zhang (Hebei Normal University) kindly provided a copy of a paper from a journal we found difficult to obtain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported by a visit grant of the Natural History Museum of Geneva, Switzerland, and a grant of the National Research Foundation, South Africa, to one of the authors (KJ). Any opinion, finding and conclusion or recommendation expressed in this material is that of the authors and the NRF does not accept any liability in this regard. Field-work by GJM was supported through a European Commission Marie Curie Fellowship: HPMF-CT-2001-01407.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable institutional, national and international guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Junker, K., Mariaux, J., Measey, G.J. et al. Meteterakis saotomensis n. sp. (Nematoda: Heterakidae) from Schistometopum thomense (Bocage) (Gymnophiona: Dermophiidae) on São Tomé Island. Syst Parasitol 92, 131–139 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-015-9588-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-015-9588-6